[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-34812: Cryo-EM structure of the bi-functional malonyl-CoA reductase from... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 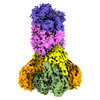 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the bi-functional malonyl-CoA reductase from Roseiflexus castenholzii | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | The 3-hydroxypropionate cycle / Bifunctional enzyme / Short chain dehydrogenase / OXIDOREDUCTASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology | oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor / short chain dehydrogenase / PKS_KR / Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase SDR / NAD(P)-binding domain superfamily / nucleotide binding / Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase SDR Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Roseiflexus castenholzii DSM 13941 (bacteria) Roseiflexus castenholzii DSM 13941 (bacteria) | |||||||||
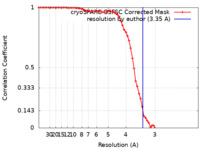
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / negative staining / Resolution: 3.35 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang X / Xu X / Xin J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2023 Journal: mBio / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis of a bi-functional malonyl-CoA reductase (MCR) from the photosynthetic green non-sulfur bacterium . Authors: Xin Zhang / Jiyu Xin / Zhiguo Wang / Wenping Wu / Yutong Liu / Zhenzhen Min / Yueyong Xin / Bing Liu / Jun He / Xingwei Zhang / Xiaoling Xu /  Abstract: Malonyl-CoA reductase (MCR) is a NADPH-dependent bi-functional enzyme that performs alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase (CoA-acylating) activities in the N- and C-terminal fragments, ...Malonyl-CoA reductase (MCR) is a NADPH-dependent bi-functional enzyme that performs alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase (CoA-acylating) activities in the N- and C-terminal fragments, respectively. It catalyzes the two-step reduction of malonyl-CoA to 3-hydroxypropionate (3-HP), a key reaction in the autotrophic CO fixation cycles of green non-sulfur bacteria and the archaea . However, the structural basis underlying substrate selection, coordination, and the subsequent catalytic reactions of full-length MCR is largely unknown. For the first time, we here determined the structure of full-length MCR from the photosynthetic green non-sulfur bacterium (MCR) at 3.35 Å resolution. Furthermore, we determined the crystal structures of the N- and C-terminal fragments bound with reaction intermediates NADP and malonate semialdehyde (MSA) at 2.0 Å and 2.3 Å, respectively, and elucidated the catalytic mechanisms using a combination of molecular dynamics simulations and enzymatic analyses. Full-length MCR was a homodimer of two cross-interlocked subunits, each containing four tandemly arranged short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR) domains. Only the catalytic domains SDR1 and SDR3 incorporated additional secondary structures that changed with NADP-MSA binding. The substrate, malonyl-CoA, was immobilized in the substrate-binding pocket of SDR3 through coordination with Arg1164 and Arg799 of SDR4 and the extra domain, respectively. Malonyl-CoA was successively reduced through protonation by the Tyr743-Arg746 pair in SDR3 and the catalytic triad (Thr165-Tyr178-Lys182) in SDR1 after nucleophilic attack from NADPH hydrides. IMPORTANCE The bi-functional MCR catalyzes NADPH-dependent reduction of malonyl-CoA to 3-HP, an important metabolic intermediate and platform chemical, from biomass. The individual MCR-N and MCR-C fragments, which contain the alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase (CoA-acylating) activities, respectively, have previously been structurally investigated and reconstructed into a malonyl-CoA pathway for the biosynthetic production of 3-HP. However, no structural information for full-length MCR has been available to illustrate the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme, which greatly limits our capacity to increase the 3-HP yield of recombinant strains. Here, we report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of full-length MCR for the first time and elucidate the mechanisms underlying substrate selection, coordination, and catalysis in the bi-functional MCR. These findings provide a structural and mechanistic basis for enzyme engineering and biosynthetic applications of the 3-HP carbon fixation pathways. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
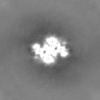
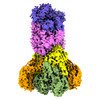
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_34812.map.gz emd_34812.map.gz | 28.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-34812-v30.xml emd-34812-v30.xml emd-34812.xml emd-34812.xml | 15 KB 15 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_34812_fsc.xml emd_34812_fsc.xml | 6.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
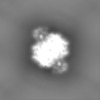
| Images |  emd_34812.png emd_34812.png | 126.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_34812_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34812_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34812_half_map_2.map.gz emd_34812_half_map_2.map.gz | 28 MB 28.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34812 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34812 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34812 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34812 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_34812_validation.pdf.gz emd_34812_validation.pdf.gz | 730.2 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_34812_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_34812_full_validation.pdf.gz | 729.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_34812_validation.xml.gz emd_34812_validation.xml.gz | 13.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_34812_validation.cif.gz emd_34812_validation.cif.gz | 17.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34812 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34812 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34812 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34812 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8hi4MC  8hi5C  8hi6C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_34812.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_34812.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.07 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_34812_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
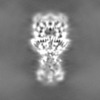
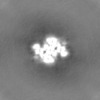
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
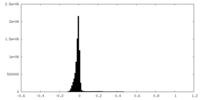
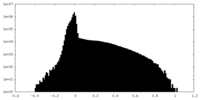
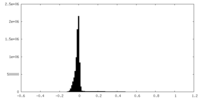
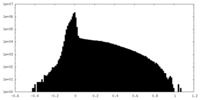
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_34812_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
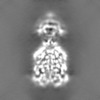
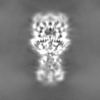
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Malonyl-coenzyme A reductase/Malonate semialdehyde reductase/Shor...
| Entire | Name: Malonyl-coenzyme A reductase/Malonate semialdehyde reductase/Short-chain dehydrogenase |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Malonyl-coenzyme A reductase/Malonate semialdehyde reductase/Shor...
| Supramolecule | Name: Malonyl-coenzyme A reductase/Malonate semialdehyde reductase/Short-chain dehydrogenase type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: The full-length MCR is a homodimer both in solution and cryo-EM structure. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Roseiflexus castenholzii DSM 13941 (bacteria) Roseiflexus castenholzii DSM 13941 (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase SDR
| Macromolecule | Name: Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase SDR / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: F269L is a natural mutation occurred during recombinant expression of the protein Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Roseiflexus castenholzii DSM 13941 (bacteria) Roseiflexus castenholzii DSM 13941 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 134.268375 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSTVRRLEGK VALITGGAGN IGEVITRRFL AEGATVVITG RNAEKLAVYR RRLIDEERVA PERVVALRMD GSDIAQVRAG VAQIVHGGT DVPIPLHRID ILVNNAGSAG PRRRLVDIPL EPSEVQPPDS ETLAQAVGNL VGITWNLTRA AAPHMPSGSS V INISTIFS ...String: MSTVRRLEGK VALITGGAGN IGEVITRRFL AEGATVVITG RNAEKLAVYR RRLIDEERVA PERVVALRMD GSDIAQVRAG VAQIVHGGT DVPIPLHRID ILVNNAGSAG PRRRLVDIPL EPSEVQPPDS ETLAQAVGNL VGITWNLTRA AAPHMPSGSS V INISTIFS RTDYYGRIAY VAPKAALNAL SDGLARELGV RGIRVNTIYP GPIESERIYT MFQAMDALKG QPEGDTASGF LR MMRLSRI DQNGEVVKRF PSPVDVANTA VLLASDESAA FTGHAFEVTH GMEVPTESRT TFVSRPGLRS VDATGKVILI CAG DQVDDA VALADTLRSC RATVVIGFRD PRALEKASVL LREPRHALAA DMYGRPTMTA EARLVRLDPL DPRAAAQTLE QIHA ELGAI HHAVVLPGQS RHAPSASLIE VDDQVVERFL HQELVGTIAL ARELARFWEE YPSGSSMHRV LFVSNPDDQQ GNQYS HILR AAVEQLVRVW RHESEYDSVN PAHQQEGQSS AAVWANQLIR YVNNEMANLD FTCAWVAKLL GSDRRIAEIN LYLPEE IVG TIGVHNPGFG WAESLFGLHM GKVALITGGS AGIGGQIGRL LALSGAHVML AARNADQLEQ MRASIVREVR DASYPDA ES RVAIFPGSDV SDIDGLERLV NHTVRVFGKV DYLINNAGIA GAEEMVIDMP VDAWRHTLRA NLISNYALLR RLAPQMKA A GGAYVLNVSS YFGGEKYVAI PYPNRSDYAV SKAGQRAMVE SLARFLGPEI QINAIAPGPV EGERLKGAGS RPGLFMRRA RLILENKRLN EVFAALLAAR HEGATIADLL PDLFANDIQS IANSAAMPAP LRRLATMLRE TSDAGGSAQS YLMNATIARK LLNRLENGG YITLHDRRAL TVEPPEPFFT EAQIEREAIK VRDGILGMLH LQRMPTEFDV ALATVFYLAD RNVTGETFHP S GGLRFERT VTEGELFGKP GQQRLERLKG SVVYLIGEHL RQHLVLLART FLDEIHVARV VLLTETTQAA TDLAAELSDY EA AGRFVVI PTCGDIEGGI DRAMAEYGRP GPVISTPFRP LPDRALSARN GDWSSVLTTA EFEELVEQQI THHFRVARKA GLI EGANVT LVTPPTSARS TSEEFALANF VKTTLHALTA TAGAESERTV PHVPVNQVDL TRRARSEEPR TPSEEEEELQ RFVN AVLLT SAPLPTPLES RYRARIYRGN AITV UniProtKB: Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase SDR |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining, cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.30 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: Uranyl Acetate |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.3 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 Z
Z Y
Y X
X