[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-33938: Structure of recombinant RyR2 (Ca2+ dataset, class 1, open state) -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of recombinant RyR2 (Ca2+ dataset, class 1, open state) | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Structure of recombinant RyR2 (Ca2 dataset, class 1, open state) | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmanganese ion transmembrane transport / establishment of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum / type B pancreatic cell apoptotic process / Purkinje myocyte to ventricular cardiac muscle cell signaling / suramin binding / regulation of SA node cell action potential / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / left ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / organic cyclic compound binding / regulation of AV node cell action potential ...manganese ion transmembrane transport / establishment of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum / type B pancreatic cell apoptotic process / Purkinje myocyte to ventricular cardiac muscle cell signaling / suramin binding / regulation of SA node cell action potential / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / left ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / organic cyclic compound binding / regulation of AV node cell action potential / calcium-induced calcium release activity / sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ion transport / Stimuli-sensing channels / Ion homeostasis / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / positive regulation of sequestering of calcium ion / cyclic nucleotide binding / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / embryonic heart tube morphogenesis / cardiac muscle hypertrophy / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / calcium ion transport into cytosol / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / neuronal action potential propagation / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / response to caffeine / response to muscle activity / A band / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / calcium ion transmembrane import into cytosol / response to redox state / protein maturation by protein folding / 'de novo' protein folding / negative regulation of heart rate / positive regulation of heart rate / FK506 binding / negative regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / positive regulation of axon regeneration / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane / cellular response to caffeine / channel regulator activity / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / response to magnesium ion / positive regulation of the force of heart contraction / intracellularly gated calcium channel activity / detection of calcium ion / smooth muscle contraction / response to vitamin E / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / calcium channel inhibitor activity / striated muscle contraction / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / T cell proliferation / Ion homeostasis / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / calcium channel complex / cellular response to epinephrine stimulus / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / response to muscle stretch / regulation of heart rate / sarcomere / sarcoplasmic reticulum / establishment of localization in cell / peptidylprolyl isomerase / peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity / calcium-mediated signaling / calcium ion transmembrane transport / response to hydrogen peroxide / calcium channel activity / Stimuli-sensing channels / sarcolemma / Z disc / response to calcium ion / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / calcium ion transport / nuclear envelope / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / protein refolding / scaffold protein binding / transmembrane transporter binding / response to hypoxia / calmodulin binding / signaling receptor binding / calcium ion binding / protein kinase binding / enzyme binding / protein-containing complex / identical protein binding / membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.45 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kobayashi T / Tsutsumi A / Kurebayashi N / Kodama M / Kikkawa M / Murayama T / Ogawa H | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 6 items Japan, 6 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Molecular basis for gating of cardiac ryanodine receptor explains the mechanisms for gain- and loss-of function mutations. Authors: Takuya Kobayashi / Akihisa Tsutsumi / Nagomi Kurebayashi / Kei Saito / Masami Kodama / Takashi Sakurai / Masahide Kikkawa / Takashi Murayama / Haruo Ogawa /  Abstract: Cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2) is a large Ca release channel in the sarcoplasmic reticulum and indispensable for excitation-contraction coupling in the heart. RyR2 is activated by Ca and RyR2 ...Cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2) is a large Ca release channel in the sarcoplasmic reticulum and indispensable for excitation-contraction coupling in the heart. RyR2 is activated by Ca and RyR2 mutations are implicated in severe arrhythmogenic diseases. Yet, the structural basis underlying channel opening and how mutations affect the channel remains unknown. Here, we address the gating mechanism of RyR2 by combining high-resolution structures determined by cryo-electron microscopy with quantitative functional analysis of channels carrying various mutations in specific residues. We demonstrated two fundamental mechanisms for channel gating: interactions close to the channel pore stabilize the channel to prevent hyperactivity and a series of interactions in the surrounding regions is necessary for channel opening upon Ca binding. Mutations at the residues involved in the former and the latter mechanisms cause gain-of-function and loss-of-function, respectively. Our results reveal gating mechanisms of the RyR2 channel and alterations by pathogenic mutations at the atomic level. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_33938.map.gz emd_33938.map.gz | 139.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-33938-v30.xml emd-33938-v30.xml emd-33938.xml emd-33938.xml | 15.8 KB 15.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_33938.png emd_33938.png | 126.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_33938_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33938_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33938_half_map_2.map.gz emd_33938_half_map_2.map.gz | 113.1 MB 113.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33938 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33938 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33938 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33938 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_33938_validation.pdf.gz emd_33938_validation.pdf.gz | 899.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_33938_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_33938_full_validation.pdf.gz | 899.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_33938_validation.xml.gz emd_33938_validation.xml.gz | 14.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_33938_validation.cif.gz emd_33938_validation.cif.gz | 16.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33938 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33938 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33938 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33938 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7vmoMC  7vmlC  7vmmC  7vmnC  7vmpC  7vmrC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_33938.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 149.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_33938.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 149.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Structure of recombinant RyR2 (Ca2 dataset, class 1, open state) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
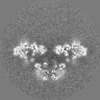
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.239 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
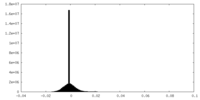
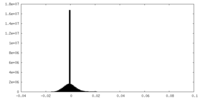
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Structure of recombinant RyR2 (Ca2 dataset, class 1, open state)
| File | emd_33938_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Structure of recombinant RyR2 (Ca2 dataset, class 1, open state) | ||||||||||||
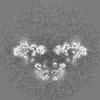
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
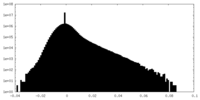
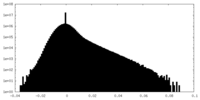
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Structure of recombinant RyR2 (Ca2 dataset, class 1, open state)
| File | emd_33938_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Structure of recombinant RyR2 (Ca2 dataset, class 1, open state) | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Recombinant RyR2 in the presence of Ca2+
| Entire | Name: Recombinant RyR2 in the presence of Ca2+ |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Recombinant RyR2 in the presence of Ca2+
| Supramolecule | Name: Recombinant RyR2 in the presence of Ca2+ / type: complex / Chimera: Yes / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 / Details: in complex with FKBP12.6 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Recombinant cell: HEK293 Homo sapiens (human) / Recombinant cell: HEK293 |
-Supramolecule #2: Ryanodine receptor 2
| Supramolecule | Name: Ryanodine receptor 2 / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
| Supramolecule | Name: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Sugar embedding | Material: buffer |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.45 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 45432 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)