[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-24961: Structure of the periplasmic domain of GldM from Capnocytophaga c... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the periplasmic domain of GldM from Capnocytophaga canimorsus | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | type IX secretion system / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / : / GldM second domain / GldM third domain / Gliding motility-associated protein GldM / Gliding motility-associated protein GldM, C-terminal / Gliding motility-associated protein GldM, N-terminal / GldM C-terminal domain / GldM N-terminal domain Similarity search - Domain/homology | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Capnocytophaga canimorsus Cc5 (bacteria) / Capnocytophaga canimorsus Cc5 (bacteria) /  Capnocytophaga canimorsus (strain 5) (bacteria) Capnocytophaga canimorsus (strain 5) (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
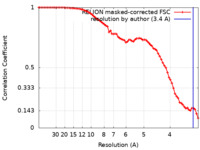
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hennell James R / Deme JC | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2022 Journal: mBio / Year: 2022Title: Structures of the Type IX Secretion/Gliding Motility Motor from across the Phylum . Authors: Rory Hennell James / Justin C Deme / Alicia Hunter / Ben C Berks / Susan M Lea /   Abstract: Gliding motility using cell surface adhesins, and export of proteins by the type IX secretion system (T9SS) are two phylum-specific features of the Bacteroidetes. Both of these processes are ...Gliding motility using cell surface adhesins, and export of proteins by the type IX secretion system (T9SS) are two phylum-specific features of the Bacteroidetes. Both of these processes are energized by the GldLM motor complex, which transduces the proton motive force at the inner membrane into mechanical work at the outer membrane. We previously used cryo-electron microscopy to solve the structure of the GldLM motor core from Flavobacterium johnsoniae at 3.9-Å resolution (R. Hennell James, J. C. Deme, A. Kjaer, F. Alcock, et al., Nat Microbiol 6:221-233, 2021, https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41564-020-00823-6). Here, we present structures of homologous complexes from a range of pathogenic and environmental species at up to 3.0-Å resolution. These structures show that the architecture of the GldLM motor core is conserved across the phylum, although there are species-specific differences at the N terminus of GldL. The resolution improvements reveal a cage-like structure that ties together the membrane-proximal cytoplasmic region of GldL and influences gliding function. These findings add detail to our structural understanding of bacterial ion-driven motors that drive the T9SS and gliding motility. Many bacteria in the phylum use the type IX secretion system to secrete proteins across their outer membrane. Most of these bacteria can also glide across surfaces using adhesin proteins that are propelled across the cell surface. Both secretion and gliding motility are driven by the GldLM protein complex, which forms a nanoscale electrochemical motor. We used cryo-electron microscopy to study the structure of the GldLM protein complex from different species, including the human pathogens Porphyromonas gingivalis and Capnocytophaga canimorsus. The organization of the motor is conserved across species, but we find species-specific structural differences and resolve motor features at higher resolution. This work improves our understanding of the type IX secretion system, which is a virulence determinant in human and animal diseases. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24961.map.gz emd_24961.map.gz | 32 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24961-v30.xml emd-24961-v30.xml emd-24961.xml emd-24961.xml | 20.1 KB 20.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_24961_fsc.xml emd_24961_fsc.xml | 7.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_24961.png emd_24961.png | 46.3 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_24961_msk_1.map emd_24961_msk_1.map | 34.3 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24961.cif.gz emd-24961.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_24961_additional_1.map.gz emd_24961_additional_1.map.gz emd_24961_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24961_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24961_half_map_2.map.gz emd_24961_half_map_2.map.gz | 26.3 MB 26.4 MB 26.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24961 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24961 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24961 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24961 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_24961_validation.pdf.gz emd_24961_validation.pdf.gz | 753.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_24961_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_24961_full_validation.pdf.gz | 753 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_24961_validation.xml.gz emd_24961_validation.xml.gz | 12.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_24961_validation.cif.gz emd_24961_validation.cif.gz | 18 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24961 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24961 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24961 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24961 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 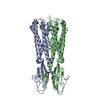 7sb2MC  7satC  7sauC  7saxC  7sazC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24961.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 34.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24961.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 34.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.648 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_24961_msk_1.map emd_24961_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
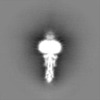
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
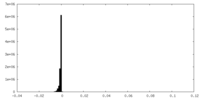
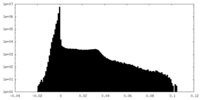
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_24961_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
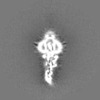
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_24961_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_24961_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Type IX Secretion System/gliding motility GldM periplasmic domain
| Entire | Name: Type IX Secretion System/gliding motility GldM periplasmic domain |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Type IX Secretion System/gliding motility GldM periplasmic domain
| Supramolecule | Name: Type IX Secretion System/gliding motility GldM periplasmic domain type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: The structure of the periplasmic domain of GldM was solved using a sample that also included GldL and was used to solve a structure of GldLM |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Capnocytophaga canimorsus Cc5 (bacteria) Capnocytophaga canimorsus Cc5 (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: GldM
| Macromolecule | Name: GldM / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Capnocytophaga canimorsus (strain 5) (bacteria) Capnocytophaga canimorsus (strain 5) (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.123895 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAGGNSPRQK MINLMYLVFI SMLALNMGKE VLSAFGLMNE KLEASNEKAN NANINAIQAL EQNNAENPDQ FAEAFQKSKK VKELSDSFY NYIEGIKGEV MNQVGEDKKD YQVMDKSDYL DQKFFVGDNY KPEGEEFVRQ INDYKTQLVE LLGGKEGTYG E LVGKIDGN ...String: MAGGNSPRQK MINLMYLVFI SMLALNMGKE VLSAFGLMNE KLEASNEKAN NANINAIQAL EQNNAENPDQ FAEAFQKSKK VKELSDSFY NYIEGIKGEV MNQVGEDKKD YQVMDKSDYL DQKFFVGDNY KPEGEEFVRQ INDYKTQLVE LLGGKEGTYG E LVGKIDGN FNTNDVVDRE GVTRKWLNYN FEGFPYIASV AKLSMMQSDI RATEQEVYAE MLKGQLKSQI SMTNYTTLLE QS KGAYYQG ESFDGAIVLG RKDASTRPNE VELMLDGRKL SASEFQIEDG KVKLKVGAGN AGEHKITGNL YFDQDGKRIA VPV SQVFST IPKPENLYFQ GQFGSWSHPQ FEKGGGSGGG SGGGSWSHPQ FEK UniProtKB: Gliding motility protein GldM |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.0 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| |||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Details: 15 mA | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: Wait time 10 s Blot time 2 s. | |||||||||||||||
| Details | The structure of the periplasmic domain of GldM was solved using a sample that also included GldL and was used to solve a structure of GldLM |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 59.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | A homology model based on the structure of FjoGldM (PDB 6EY4) was used as a starting model and modified to fit the EM density using Coot. Refinement was carried out using Phenix. |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Overall B value: 93.02 |
| Output model |  PDB-7sb2: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z
Z Y
Y X
X