+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the Fmoc-Tau-PAM4 Type 3 amyloid fibril | |||||||||
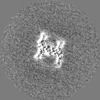
 Map data Map data | Final postprocessed, sharpened, helical symmetrised map of the Fmoc-TauPAM4 fibril morphology IIa | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | amyloid / tau / helical / cross-beta / fibril / neurodegeneration / Fmoc / PROTEIN FIBRIL | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationplus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule / histone-dependent DNA binding / negative regulation of establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / neurofibrillary tangle / microtubule lateral binding / axonal transport / main axon / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / tubulin complex ...plus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule / histone-dependent DNA binding / negative regulation of establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / neurofibrillary tangle / microtubule lateral binding / axonal transport / main axon / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / tubulin complex / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / negative regulation of tubulin deacetylation / generation of neurons / regulation of chromosome organization / rRNA metabolic process / axonal transport of mitochondrion / regulation of mitochondrial fission / axon development / intracellular distribution of mitochondria / central nervous system neuron development / regulation of microtubule polymerization / microtubule polymerization / minor groove of adenine-thymine-rich DNA binding / lipoprotein particle binding / dynactin binding / negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / glial cell projection / apolipoprotein binding / axolemma / protein polymerization / negative regulation of mitochondrial fission / Caspase-mediated cleavage of cytoskeletal proteins / regulation of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization / positive regulation of axon extension / neurofibrillary tangle assembly / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / regulation of cellular response to heat / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / synapse assembly / positive regulation of protein localization / axon cytoplasm / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / supramolecular fiber organization / somatodendritic compartment / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / stress granule assembly / positive regulation of microtubule polymerization / phosphatidylinositol binding / nuclear periphery / positive regulation of superoxide anion generation / protein phosphatase 2A binding / regulation of autophagy / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / astrocyte activation / Hsp90 protein binding / microglial cell activation / synapse organization / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / response to lead ion / PKR-mediated signaling / protein homooligomerization / regulation of synaptic plasticity / SH3 domain binding / memory / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / neuron projection development / microtubule cytoskeleton / cell-cell signaling / single-stranded DNA binding / actin binding / protein-folding chaperone binding / cell body / cellular response to heat / growth cone / double-stranded DNA binding / microtubule binding / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / microtubule / sequence-specific DNA binding / dendritic spine / amyloid fibril formation / learning or memory / neuron projection / nuclear speck / membrane raft / axon / negative regulation of gene expression / neuronal cell body / dendrite / DNA damage response / protein kinase binding / enzyme binding / mitochondrion / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular region / identical protein binding / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wilkinson M / Louros N / Tsaka G / Ramakers M / Morelli C / Garcia T / Gallardo RU / D'Haeyer S / Goossens V / Audenaert D ...Wilkinson M / Louros N / Tsaka G / Ramakers M / Morelli C / Garcia T / Gallardo RU / D'Haeyer S / Goossens V / Audenaert D / Thal DR / Ranson NA / Radford SE / Rousseau F / Schymkowitz J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Belgium, 1 items Belgium, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Local structural preferences in shaping tau amyloid polymorphism. Authors: Nikolaos Louros / Martin Wilkinson / Grigoria Tsaka / Meine Ramakers / Chiara Morelli / Teresa Garcia / Rodrigo Gallardo / Sam D'Haeyer / Vera Goossens / Dominique Audenaert / Dietmar Rudolf ...Authors: Nikolaos Louros / Martin Wilkinson / Grigoria Tsaka / Meine Ramakers / Chiara Morelli / Teresa Garcia / Rodrigo Gallardo / Sam D'Haeyer / Vera Goossens / Dominique Audenaert / Dietmar Rudolf Thal / Ian R Mackenzie / Rosa Rademakers / Neil A Ranson / Sheena E Radford / Frederic Rousseau / Joost Schymkowitz /    Abstract: Tauopathies encompass a group of neurodegenerative disorders characterised by diverse tau amyloid fibril structures. The persistence of polymorphism across tauopathies suggests that distinct ...Tauopathies encompass a group of neurodegenerative disorders characterised by diverse tau amyloid fibril structures. The persistence of polymorphism across tauopathies suggests that distinct pathological conditions dictate the adopted polymorph for each disease. However, the extent to which intrinsic structural tendencies of tau amyloid cores contribute to fibril polymorphism remains uncertain. Using a combination of experimental approaches, we here identify a new amyloidogenic motif, PAM4 (Polymorphic Amyloid Motif of Repeat 4), as a significant contributor to tau polymorphism. Calculation of per-residue contributions to the stability of the fibril cores of different pathologic tau structures suggests that PAM4 plays a central role in preserving structural integrity across amyloid polymorphs. Consistent with this, cryo-EM structural analysis of fibrils formed from a synthetic PAM4 peptide shows that the sequence adopts alternative structures that closely correspond to distinct disease-associated tau strains. Furthermore, in-cell experiments revealed that PAM4 deletion hampers the cellular seeding efficiency of tau aggregates extracted from Alzheimer's disease, corticobasal degeneration, and progressive supranuclear palsy patients, underscoring PAM4's pivotal role in these tauopathies. Together, our results highlight the importance of the intrinsic structural propensity of amyloid core segments to determine the structure of tau in cells, and in propagating amyloid structures in disease. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_16883.map.gz emd_16883.map.gz | 20.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-16883-v30.xml emd-16883-v30.xml emd-16883.xml emd-16883.xml | 18.6 KB 18.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_16883_fsc.xml emd_16883_fsc.xml | 10.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_16883.png emd_16883.png | 78 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-16883.cif.gz emd-16883.cif.gz | 6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_16883_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16883_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16883_half_map_2.map.gz emd_16883_half_map_2.map.gz | 80.7 MB 80.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16883 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16883 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16883 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16883 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_16883_validation.pdf.gz emd_16883_validation.pdf.gz | 818.1 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_16883_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_16883_full_validation.pdf.gz | 817.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_16883_validation.xml.gz emd_16883_validation.xml.gz | 18 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_16883_validation.cif.gz emd_16883_validation.cif.gz | 23.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16883 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16883 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16883 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16883 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8ohpMC  8oh2C  8ohiC  8oi0C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_16883.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_16883.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Final postprocessed, sharpened, helical symmetrised map of the Fmoc-TauPAM4 fibril morphology IIa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.94 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
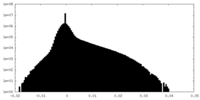
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: halfmap2
| File | emd_16883_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | halfmap2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: halfmap1
| File | emd_16883_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | halfmap1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Amyloid fibril form 2a of Tau-PAM4 peptide adducted with the Fmoc...
| Entire | Name: Amyloid fibril form 2a of Tau-PAM4 peptide adducted with the Fmoc protection group |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Amyloid fibril form 2a of Tau-PAM4 peptide adducted with the Fmoc...
| Supramolecule | Name: Amyloid fibril form 2a of Tau-PAM4 peptide adducted with the Fmoc protection group type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all / Details: Synthesised peptide assembled into amyloid fibril |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Microtubule-associated protein tau
| Macromolecule | Name: Microtubule-associated protein tau / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: 13-residue peptide of the PAM4 motif of Tau, corresponding to residues 350-362 of the Tau repeat domain. The peptide is C-terminally amidated and should have been N-terminally acetylated but ...Details: 13-residue peptide of the PAM4 motif of Tau, corresponding to residues 350-362 of the Tau repeat domain. The peptide is C-terminally amidated and should have been N-terminally acetylated but 10% of the peptide (by mass spec) was still adducted to the Fmoc protection group from peptide synthesis. This contaminant species dominated fibril assembly Number of copies: 24 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.652269 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (VP1)VQSKIGSLD NITH(NH2) UniProtKB: Microtubule-associated protein tau |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.6 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7 Details: Peptide resuspended in MilliQ water for aggregation reaction |
| Grid | Model: EMS Lacey Carbon / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: LACEY / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 279 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: TFS Selectris / Energy filter - Slit width: 10 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 4096 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4096 pixel / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 1957 / Average exposure time: 5.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 32.0 e/Å2 Details: Movies were collected as 1204 EER frames compressed and re-grouped into 35 TIF fractions |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | Initial model built manually in coot, no starting template |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Overall B value: 48 / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient |
| Output model |  PDB-8ohp: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)