+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
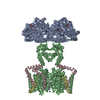
| Title | RyR1-FKBP12 in the open conformation | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | 3D reconstruction of RyR1 in the open conformation | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ryanodine receptor / FKBP12 / channel gating | |||||||||
| Function / homology | ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / RIH domain Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 10.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Samso M / Feng W / Pessah IN / Allen PD | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Biol / Year: 2009 Journal: PLoS Biol / Year: 2009Title: Coordinated movement of cytoplasmic and transmembrane domains of RyR1 upon gating. Authors: Montserrat Samsó / Wei Feng / Isaac N Pessah / P D Allen /  Abstract: Ryanodine receptor type 1 (RyR1) produces spatially and temporally defined Ca2+ signals in several cell types. How signals received in the cytoplasmic domain are transmitted to the ion gate and how ...Ryanodine receptor type 1 (RyR1) produces spatially and temporally defined Ca2+ signals in several cell types. How signals received in the cytoplasmic domain are transmitted to the ion gate and how the channel gates are unknown. We used EGTA or neuroactive PCB 95 to stabilize the full closed or open states of RyR1. Single-channel measurements in the presence of FKBP12 indicate that PCB 95 inverts the thermodynamic stability of RyR1 and locks it in a long-lived open state whose unitary current is indistinguishable from the native open state. We analyzed two datasets of 15,625 and 18,527 frozen-hydrated RyR1-FKBP12 particles in the closed and open conformations, respectively, by cryo-electron microscopy. Their corresponding three-dimensional structures at 10.2 A resolution refine the structure surrounding the ion pathway previously identified in the closed conformation: two right-handed bundles emerging from the putative ion gate (the cytoplasmic "inner branches" and the transmembrane "inner helices"). Furthermore, six of the identifiable transmembrane segments of RyR1 have similar organization to those of the mammalian Kv1.2 potassium channel. Upon gating, the distal cytoplasmic domains move towards the transmembrane domain while the central cytoplasmic domains move away from it, and also away from the 4-fold axis. Along the ion pathway, precise relocation of the inner helices and inner branches results in an approximately 4 A diameter increase of the ion gate. Whereas the inner helices of the K+ channels and of the RyR1 channel cross-correlate best with their corresponding open/closed states, the cytoplasmic inner branches, which are not observed in the K+ channels, appear to have at least as important a role as the inner helices for RyR1 gating. We propose a theoretical model whereby the inner helices, the inner branches, and the h1 densities together create an efficient novel gating mechanism for channel opening by relaxing two right-handed bundle structures along a common 4-fold axis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|---|
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1607.map.gz emd_1607.map.gz | 17 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1607-v30.xml emd-1607-v30.xml emd-1607.xml emd-1607.xml | 9.8 KB 9.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  1607.png 1607.png | 517.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1607 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1607 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1607 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1607 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_1607_validation.pdf.gz emd_1607_validation.pdf.gz | 231.1 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_1607_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_1607_full_validation.pdf.gz | 230.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_1607_validation.xml.gz emd_1607_validation.xml.gz | 5.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1607 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1607 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1607 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1607 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1607.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 21.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1607.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 21.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 3D reconstruction of RyR1 in the open conformation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.8 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ryanodine receptor 1 (RyR1) with FKBP12 bound
| Entire | Name: ryanodine receptor 1 (RyR1) with FKBP12 bound |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: ryanodine receptor 1 (RyR1) with FKBP12 bound
| Supramolecule | Name: ryanodine receptor 1 (RyR1) with FKBP12 bound / type: sample / ID: 1000 Oligomeric state: RyR1 forms a homotetramer and one FKBP12 binds to each RyR1 subunit Number unique components: 2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.26 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: ryanodine receptor isoform 1
| Macromolecule | Name: ryanodine receptor isoform 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: RyR1 / Number of copies: 4 / Oligomeric state: tetramer / Recombinant expression: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.26 MDa |
| Sequence | GO: ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / InterPro: RIH domain |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2.00 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Details: 20 mM Na-MOPS pH 7.4, 0.9 M NaCl, 0.5% (w/v) CHAPS, 2 mM DTT, 0.05 mM calcium, 0.01 mM PCB95 |
| Grid | Details: 300 mesh holey copper grids |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 80 % / Chamber temperature: 77 K / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER Details: Vitrification instrument: two-side blotting plunger Method: Blot for 4 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Average: 87 K |
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: objective lens astigmatism was corrected at 150,000 times magnification |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: ZEISS SCAI / Digitization - Sampling interval: 7.0 µm / Number real images: 233 / Average electron dose: 9 e/Å2 / Details: after scanning pixels were averaged 2x2 / Bits/pixel: 8 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 2.3 µm / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Side entry liquid nitrogen cooled / Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: Each particle |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C4 (4 fold cyclic) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 10.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: FREALIGN SPIDER / Number images used: 8133 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL |
-Atomic model buiding 2
| Initial model | PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









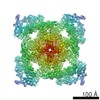

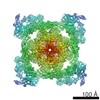

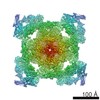
 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)