[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-13689: Negative stain EM map of the extracellular domain of the RET(C634... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
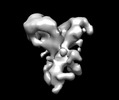
| Title | Negative stain EM map of the extracellular domain of the RET(C634R)/GDF15/GFRAL complex | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Negative stain EM map of the extracellular domain of the RET(C634R)/GDF15/GFRAL complex. The map has been z-flipped to match the structure of the wild-type complex (PDB ID 6Q2J). | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RET / Complex / RTK / Oncogenesis / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
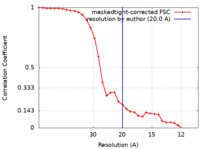
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 20.0 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Liu Y / Muench SP / Goldman A | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 3 items United Kingdom, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2022 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2022Title: Unexpected structures formed by the kinase RET C634R mutant extracellular domain suggest potential oncogenic mechanisms in MEN2A. Authors: Yixin Liu / Orquidea De Castro Ribeiro / Outi Haapanen / Gregory B Craven / Vivek Sharma / Stephen P Muench / Adrian Goldman /   Abstract: The RET receptor tyrosine kinase plays a pivotal role in cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation, and its abnormal activation leads to cancers through receptor fusions or point mutations. ...The RET receptor tyrosine kinase plays a pivotal role in cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation, and its abnormal activation leads to cancers through receptor fusions or point mutations. Mutations that disrupt the disulfide network in the extracellular domain (ECD) of RET drive multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A (MEN2A), a hereditary syndrome associated with the development of thyroid cancers. However, structural details of how specific mutations affect RET are unclear. Here, we present the first structural insights into the ECD of the RET(C634R) mutant, the most common mutation in MEN2A. Using electron microscopy, we demonstrate that the C634R mutation causes ligand-independent dimerization of the RET ECD, revealing an unusual tail-to-tail conformation that is distinct from the ligand-induced signaling dimer of WT RET. Additionally, we show that the RET ECD dimer can form complexes with at least two of the canonical RET ligands and that these complexes form very different structures than WT RET ECD upon ligand binding. In conclusion, this structural analysis of cysteine-mutant RET ECD suggests a potential key mechanism of cancer induction in MEN2A, both in the absence and presence of its native ligands, and may offer new targets for therapeutic intervention. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13689.map.gz emd_13689.map.gz | 2.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13689-v30.xml emd-13689-v30.xml emd-13689.xml emd-13689.xml | 13.8 KB 13.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_13689_fsc.xml emd_13689_fsc.xml | 3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_13689.png emd_13689.png | 35.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_13689_msk_1.map emd_13689_msk_1.map | 2.3 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-13689.cif.gz emd-13689.cif.gz | 4.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13689 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13689 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13689 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13689 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_13689_validation.pdf.gz emd_13689_validation.pdf.gz | 381.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_13689_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_13689_full_validation.pdf.gz | 381.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_13689_validation.xml.gz emd_13689_validation.xml.gz | 6.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_13689_validation.cif.gz emd_13689_validation.cif.gz | 8.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13689 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13689 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13689 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13689 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13689.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 2.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13689.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 2.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Negative stain EM map of the extracellular domain of the RET(C634R)/GDF15/GFRAL complex. The map has been z-flipped to match the structure of the wild-type complex (PDB ID 6Q2J). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 5.25 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_13689_msk_1.map emd_13689_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : RET(C634R)/GDF15/GFRAL
| Entire | Name: RET(C634R)/GDF15/GFRAL |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: RET(C634R)/GDF15/GFRAL
| Supramolecule | Name: RET(C634R)/GDF15/GFRAL / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 Details: The extracellular domain complex was reconstituted using individually purified protein components and purified via gel filtration. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #2: RET(C634R) dimer
| Supramolecule | Name: RET(C634R) dimer / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 Details: RET(C634R)mutant dimer generated by affinity purification and gel filtration |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: GDF15 dimer
| Supramolecule | Name: GDF15 dimer / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 Details: GDF15 dimer was originally expressed as an Fc-tagged fusion and purified via affinity purification. Tag was cleaved after complex assembly. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #4: GFRAL
| Supramolecule | Name: GFRAL / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 Details: The extracellular domain of GFRAL was purified via affinity purification and gel filtration. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.01 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: Buffer was made fresh and filtered through a 0.2 um filter. | ||||||||||||
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: Uranyl Acetate / Details: 2% Uranyl acetate solution | ||||||||||||
| Grid | Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 | ||||||||||||
| Details | This sample was monodisperse. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI 20 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 68 / Average electron dose: 30.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)