+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8wa3 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of peptide free and Gs-coupled GIPR | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor /  cryo-electron microscopy / cryo-electron microscopy /  G protein-coupled receptor / ligand recognition G protein-coupled receptor / ligand recognition | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationgastric inhibitory peptide receptor activity / glucagon family peptide binding / gastric inhibitory peptide signaling pathway / desensitization of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / sensory perception of chemical stimulus / endocrine pancreas development / mu-type opioid receptor binding / response to fatty acid /  corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 binding / G-protein activation ...gastric inhibitory peptide receptor activity / glucagon family peptide binding / gastric inhibitory peptide signaling pathway / desensitization of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / sensory perception of chemical stimulus / endocrine pancreas development / mu-type opioid receptor binding / response to fatty acid / corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 binding / G-protein activation ...gastric inhibitory peptide receptor activity / glucagon family peptide binding / gastric inhibitory peptide signaling pathway / desensitization of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / sensory perception of chemical stimulus / endocrine pancreas development / mu-type opioid receptor binding / response to fatty acid /  corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 binding / G-protein activation / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / : / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / Ca2+ pathway / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / G protein-coupled peptide receptor activity / G alpha (z) signalling events / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / G alpha (q) signalling events / G alpha (i) signalling events / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / G-protein activation / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / Prostacyclin signalling through prostacyclin receptor / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 1 / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 binding / G-protein activation / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / : / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / Ca2+ pathway / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / G protein-coupled peptide receptor activity / G alpha (z) signalling events / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / G alpha (q) signalling events / G alpha (i) signalling events / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / G-protein activation / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / Prostacyclin signalling through prostacyclin receptor / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 1 / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / Glucagon-type ligand receptors /  alkylglycerophosphoethanolamine phosphodiesterase activity / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / G alpha (12/13) signalling events / G beta:gamma signalling through BTK / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / Ca2+ pathway / G alpha (z) signalling events / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / G alpha (s) signalling events / alkylglycerophosphoethanolamine phosphodiesterase activity / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / G alpha (12/13) signalling events / G beta:gamma signalling through BTK / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / Ca2+ pathway / G alpha (z) signalling events / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / G alpha (s) signalling events /  beta-2 adrenergic receptor binding / G alpha (q) signalling events / photoreceptor outer segment membrane / G alpha (i) signalling events / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / beta-2 adrenergic receptor binding / G alpha (q) signalling events / photoreceptor outer segment membrane / G alpha (i) signalling events / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion /  spectrin binding / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / spectrin binding / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins /  peptide hormone binding / regulation of insulin secretion / photoreceptor outer segment / peptide hormone binding / regulation of insulin secretion / photoreceptor outer segment /  D1 dopamine receptor binding / response to axon injury / positive regulation of cAMP-mediated signaling / response to glucose / adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process / D1 dopamine receptor binding / response to axon injury / positive regulation of cAMP-mediated signaling / response to glucose / adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process /  ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding /  insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / photoreceptor inner segment / adenylate cyclase activator activity / response to nutrient / generation of precursor metabolites and energy / G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of insulin secretion / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / positive regulation of GTPase activity / cellular response to catecholamine stimulus / response to calcium ion / adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / sensory perception of taste / G-protein beta-subunit binding / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / photoreceptor inner segment / adenylate cyclase activator activity / response to nutrient / generation of precursor metabolites and energy / G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of insulin secretion / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / positive regulation of GTPase activity / cellular response to catecholamine stimulus / response to calcium ion / adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / sensory perception of taste / G-protein beta-subunit binding /  heterotrimeric G-protein complex / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / signaling receptor complex adaptor activity / retina development in camera-type eye / heterotrimeric G-protein complex / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / signaling receptor complex adaptor activity / retina development in camera-type eye /  GTPase binding / GTPase binding /  cell body / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / cellular response to hypoxia / G alpha (s) signalling events / cell population proliferation / cell surface receptor signaling pathway cell body / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / cellular response to hypoxia / G alpha (s) signalling events / cell population proliferation / cell surface receptor signaling pathwaySimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)  Bos taurus (cattle) Bos taurus (cattle)  Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Leptolinea tardivitalis (bacteria) Leptolinea tardivitalis (bacteria)synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.86 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.86 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cong, Z.T. / Zhao, F.H. / Li, Y. / Luo, G. / Zhou, Q.T. / Yang, D.H. / Wang, M.W. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 4items China, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Discov / Year: 2024 Journal: Cell Discov / Year: 2024Title: Molecular features of the ligand-free GLP-1R, GCGR and GIPR in complex with G proteins. Authors: Zhaotong Cong / Fenghui Zhao / Yang Li / Gan Luo / Yiting Mai / Xianyue Chen / Yanyan Chen / Shi Lin / Xiaoqing Cai / Qingtong Zhou / Dehua Yang / Ming-Wei Wang /   Abstract: Class B1 G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are important regulators of many physiological functions such as glucose homeostasis, which is mainly mediated by three peptide hormones, i.e., glucagon- ...Class B1 G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are important regulators of many physiological functions such as glucose homeostasis, which is mainly mediated by three peptide hormones, i.e., glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), glucagon (GCG), and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). They trigger a cascade of signaling events leading to the formation of an active agonist-receptor-G protein complex. However, intracellular signal transducers can also activate the receptor independent of extracellular stimuli, suggesting an intrinsic role of G proteins in this process. Here, we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of the human GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R), GCG receptor (GCGR), and GIP receptor (GIPR) in complex with G proteins without the presence of cognate ligands. These ligand-free complexes share a similar intracellular architecture to those bound by endogenous peptides, in which, the G protein alone directly opens the intracellular binding cavity and rewires the extracellular orthosteric pocket to stabilize the receptor in a state unseen before. While the peptide-binding site is partially occupied by the inward folded transmembrane helix 6 (TM6)-extracellular loop 3 (ECL3) juncture of GIPR or a segment of GCGR ECL2, the extracellular portion of GLP-1R adopts a conformation close to the active state. Our findings offer valuable insights into the distinct activation mechanisms of these three important receptors. It is possible that in the absence of a ligand, the intracellular half of transmembrane domain is mobilized with the help of G protein, which in turn rearranges the extracellular half to form a transitional conformation, facilitating the entry of the peptide N-terminus. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8wa3.cif.gz 8wa3.cif.gz | 204.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8wa3.ent.gz pdb8wa3.ent.gz | 153.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8wa3.json.gz 8wa3.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wa/8wa3 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wa/8wa3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wa/8wa3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wa/8wa3 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  37390MC 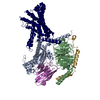 8wg7C  8wg8C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 64950.695 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: T345F Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GIPR / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GIPR / Production host:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P48546 Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P48546 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 45743.441 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Mutation: S54N, G226A, E268A, N271K, K274D, R280K, T284D, I285T, A366S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Bos taurus (cattle) / Gene: GNAS, GNAS1 / Production host: Bos taurus (cattle) / Gene: GNAS, GNAS1 / Production host:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P04896 Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P04896 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 40226.992 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat), (gene. exp.) Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat), (gene. exp.)  Leptolinea tardivitalis (bacteria) Leptolinea tardivitalis (bacteria)Gene: Gnb1, ADM99_06940 / Production host:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P54311, UniProt: A0A0P6XLS5 Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P54311, UniProt: A0A0P6XLS5 |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 7861.143 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Bos taurus (cattle) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host: Bos taurus (cattle) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P63212 Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: P63212 |
| #5: Antibody |  Single-domain antibody Single-domain antibodyMass: 15343.019 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Cryo-EM structure of the human glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor in complex with GIP and G protein Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YESDetails: Cryo-EM structure of peptide free and Gs-coupled GIPR |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : OTHER / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER : OTHER / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 80 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.86 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Num. of particles: 807839 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj














