+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8q4l | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | GBP1 bound by 14-3-3sigma | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  IMMUNE SYSTEM / IMMUNE SYSTEM /  Protein complex / Protein complex /  Phosphorylation Phosphorylation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationGDP phosphatase activity / non-canonical inflammasome complex assembly / protein localization to vacuole / negative regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / symbiont cell surface /  cytolysis in another organism / positive regulation of pyroptosis / vesicle membrane / negative regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production ...GDP phosphatase activity / non-canonical inflammasome complex assembly / protein localization to vacuole / negative regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / symbiont cell surface / cytolysis in another organism / positive regulation of pyroptosis / vesicle membrane / negative regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production ...GDP phosphatase activity / non-canonical inflammasome complex assembly / protein localization to vacuole / negative regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / symbiont cell surface /  cytolysis in another organism / positive regulation of pyroptosis / vesicle membrane / negative regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production / negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / cytolysis in another organism / positive regulation of pyroptosis / vesicle membrane / negative regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production / negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway /  spectrin binding / spectrin binding /  cytokine binding / regulation of epidermal cell division / cytokine binding / regulation of epidermal cell division /  protein kinase C inhibitor activity / positive regulation of epidermal cell differentiation / keratinocyte development / protein kinase C inhibitor activity / positive regulation of epidermal cell differentiation / keratinocyte development /  keratinization / defense response to protozoan / keratinization / defense response to protozoan /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; In phosphorus-containing anhydrides / Regulation of localization of FOXO transcription factors / keratinocyte proliferation / phosphoserine residue binding / Activation of BAD and translocation to mitochondria / negative regulation of keratinocyte proliferation / establishment of skin barrier / cellular response to interleukin-1 / SARS-CoV-2 targets host intracellular signalling and regulatory pathways / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / Chk1/Chk2(Cds1) mediated inactivation of Cyclin B:Cdk1 complex / protein kinase A signaling / negative regulation of stem cell proliferation / SARS-CoV-1 targets host intracellular signalling and regulatory pathways / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / RHO GTPases activate PKNs / protein export from nucleus / negative regulation of innate immune response / protein sequestering activity / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G2 Cell Cycle Arrest / G protein activity / release of cytochrome c from mitochondria / positive regulation of protein export from nucleus / stem cell proliferation / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / TP53 Regulates Metabolic Genes / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; In phosphorus-containing anhydrides / Regulation of localization of FOXO transcription factors / keratinocyte proliferation / phosphoserine residue binding / Activation of BAD and translocation to mitochondria / negative regulation of keratinocyte proliferation / establishment of skin barrier / cellular response to interleukin-1 / SARS-CoV-2 targets host intracellular signalling and regulatory pathways / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / Chk1/Chk2(Cds1) mediated inactivation of Cyclin B:Cdk1 complex / protein kinase A signaling / negative regulation of stem cell proliferation / SARS-CoV-1 targets host intracellular signalling and regulatory pathways / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / RHO GTPases activate PKNs / protein export from nucleus / negative regulation of innate immune response / protein sequestering activity / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G2 Cell Cycle Arrest / G protein activity / release of cytochrome c from mitochondria / positive regulation of protein export from nucleus / stem cell proliferation / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / TP53 Regulates Metabolic Genes /  lipopolysaccharide binding / lipopolysaccharide binding /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement /  Hsp90 protein binding / negative regulation of protein kinase activity / negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / cellular response to type II interferon / GDP binding / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / Interferon gamma signaling / Hsp90 protein binding / negative regulation of protein kinase activity / negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / cellular response to type II interferon / GDP binding / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / Interferon gamma signaling /  actin cytoskeleton / cellular response to tumor necrosis factor / actin cytoskeleton / cellular response to tumor necrosis factor /  actin binding / cytoplasmic vesicle / positive regulation of cell growth / defense response to virus / actin binding / cytoplasmic vesicle / positive regulation of cell growth / defense response to virus /  regulation of cell cycle / defense response to bacterium / regulation of cell cycle / defense response to bacterium /  cadherin binding / cadherin binding /  Golgi membrane / Golgi membrane /  innate immune response / innate immune response /  GTPase activity / GTP binding / GTPase activity / GTP binding /  protein kinase binding / protein kinase binding /  Golgi apparatus / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / Golgi apparatus / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II /  enzyme binding / enzyme binding /  signal transduction / protein homodimerization activity / signal transduction / protein homodimerization activity /  extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / identical protein binding / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / identical protein binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 5.12 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 5.12 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Pfleiderer, M.M. / Liu, X. / Fisch, D. / Anastasakou, E. / Frickel, E.M. / Galej, W.P. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, Germany,  France, European Union, France, European Union,  United Kingdom, 9items United Kingdom, 9items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2023 Journal: Science / Year: 2023Title: PIM1 controls GBP1 activity to limit self-damage and to guard against pathogen infection. Authors: Daniel Fisch / Moritz M Pfleiderer / Eleni Anastasakou / Gillian M Mackie / Fabian Wendt / Xiangyang Liu / Barbara Clough / Samuel Lara-Reyna / Vesela Encheva / Ambrosius P Snijders / ...Authors: Daniel Fisch / Moritz M Pfleiderer / Eleni Anastasakou / Gillian M Mackie / Fabian Wendt / Xiangyang Liu / Barbara Clough / Samuel Lara-Reyna / Vesela Encheva / Ambrosius P Snijders / Hironori Bando / Masahiro Yamamoto / Andrew D Beggs / Jason Mercer / Avinash R Shenoy / Bernd Wollscheid / Kendle M Maslowski / Wojtek P Galej / Eva-Maria Frickel /      Abstract: Disruption of cellular activities by pathogen virulence factors can trigger innate immune responses. Interferon-γ (IFN-γ)-inducible antimicrobial factors, such as the guanylate binding proteins ...Disruption of cellular activities by pathogen virulence factors can trigger innate immune responses. Interferon-γ (IFN-γ)-inducible antimicrobial factors, such as the guanylate binding proteins (GBPs), promote cell-intrinsic defense by attacking intracellular pathogens and by inducing programmed cell death. Working in human macrophages, we discovered that GBP1 expression in the absence of IFN-γ killed the cells and induced Golgi fragmentation. IFN-γ exposure improved macrophage survival through the activity of the kinase PIM1. PIM1 phosphorylated GBP1, leading to its sequestration by 14-3-3σ, which thereby prevented GBP1 membrane association. During infection, the virulence protein TgIST interfered with IFN-γ signaling and depleted PIM1, thereby increasing GBP1 activity. Although infected cells can restrain pathogens in a GBP1-dependent manner, this mechanism can protect uninfected bystander cells. Thus, PIM1 can provide a bait for pathogen virulence factors, guarding the integrity of IFN-γ signaling. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8q4l.cif.gz 8q4l.cif.gz | 151.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8q4l.ent.gz pdb8q4l.ent.gz | 98.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8q4l.json.gz 8q4l.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q4/8q4l https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q4/8q4l ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q4/8q4l ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q4/8q4l | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 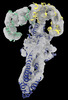 18149MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 66275.539 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GBP1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GBP1 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P32455 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P32455 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 26139.461 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SFN / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SFN / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P31947 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P31947 |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: GBP1 bound by 14-3-3sigma / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.12 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.8 / Details: 150 mM KCl, 20 mM HEPES-KOH pH 7.8 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.25 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: Glow discharged for 20 seconds at 25 mA and 0.3 bar using a Pelco EasyGlow device. | |||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 8 sec. / Electron dose: 65.5 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 14974 |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 420768 | |||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 5.12 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 18717 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj










