[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
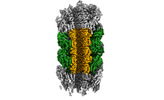
Yorodumi- PDB-8fqc: Structure of baseplate with receptor binding complex of Agrobacte... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8fqc | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of baseplate with receptor binding complex of Agrobacterium phage Milano | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRUS / Myophage / redox trigger / VIRUS / Myophage / redox trigger /  disulfides disulfides | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Sonani, R.R. / Leiman, P.G. / Wang, F. / Kreutzberger, M.A.B. / Sebastian, A. / Esteves, N.C. / Kelly, R.J. / Scharf, B. / Egelman, E.H. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: An extensive disulfide bond network prevents tail contraction in Agrobacterium tumefaciens phage Milano. Authors: Ravi R Sonani / Lee K Palmer / Nathaniel C Esteves / Abigail A Horton / Amanda L Sebastian / Rebecca J Kelly / Fengbin Wang / Mark A B Kreutzberger / William K Russell / Petr G Leiman / ...Authors: Ravi R Sonani / Lee K Palmer / Nathaniel C Esteves / Abigail A Horton / Amanda L Sebastian / Rebecca J Kelly / Fengbin Wang / Mark A B Kreutzberger / William K Russell / Petr G Leiman / Birgit E Scharf / Edward H Egelman /  Abstract: A contractile sheath and rigid tube assembly is a widespread apparatus used by bacteriophages, tailocins, and the bacterial type VI secretion system to penetrate cell membranes. In this mechanism, ...A contractile sheath and rigid tube assembly is a widespread apparatus used by bacteriophages, tailocins, and the bacterial type VI secretion system to penetrate cell membranes. In this mechanism, contraction of an external sheath powers the motion of an inner tube through the membrane. The structure, energetics, and mechanism of the machinery imply rigidity and straightness. The contractile tail of Agrobacterium tumefaciens bacteriophage Milano is flexible and bent to varying degrees, which sets it apart from other contractile tail-like systems. Here, we report structures of the Milano tail including the sheath-tube complex, baseplate, and putative receptor-binding proteins. The flexible-to-rigid transformation of the Milano tail upon contraction can be explained by unique electrostatic properties of the tail tube and sheath. All components of the Milano tail, including sheath subunits, are crosslinked by disulfides, some of which must be reduced for contraction to occur. The putative receptor-binding complex of Milano contains a tailspike, a tail fiber, and at least two small proteins that form a garland around the distal ends of the tailspikes and tail fibers. Despite being flagellotropic, Milano lacks thread-like tail filaments that can wrap around the flagellum, and is thus likely to employ a different binding mechanism. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8fqc.cif.gz 8fqc.cif.gz | 1.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8fqc.ent.gz pdb8fqc.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8fqc.json.gz 8fqc.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fq/8fqc https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fq/8fqc ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fq/8fqc ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fq/8fqc | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 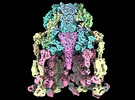 29383MC  8fopC  8fouC  8foyC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: (Schoenflies symbol : C3 (3 fold cyclic : C3 (3 fold cyclic )) )) |
- Components
Components
-Protein , 7 types, 30 molecules C1E1a1f1g1I1K1k1m1P1Q1R1r1s1t1S1T1V1W1X1Y1v1w1x1y1u1z1U1e1A
| #1: Protein | Mass: 49701.758 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFS1 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFS1 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 14673.427 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MHE7 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MHE7#5: Protein | Mass: 53896.094 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFS8 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFS8#7: Protein | Mass: 61649.805 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MGV0 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MGV0#8: Protein | Mass: 31667.646 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MHF3 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MHF3#9: Protein | Mass: 43287.000 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFQ9 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFQ9#10: Protein | | Mass: 20720.535 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFZ0 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFZ0 |
-Baseplate Wedge ... , 3 types, 8 molecules F1G1h1i1H1j1J1l1
| #3: Protein | Mass: 43322.723 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFU4 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFU4#4: Protein | Mass: 19318.713 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus)#6: Protein | Mass: 31414.879 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFT7 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFT7 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 1 molecules 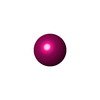
| #11: Chemical | ChemComp-FE /  Iron Iron |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Agrobacterium phage Milano / Type: VIRUS / Entity ID: #1-#10 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) |
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: NO / Isolate: SPECIES / Type: VIRION |
| Natural host | Organism: Agrobacterium fabrum str. C58 |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 14856 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj
