+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8fwe | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
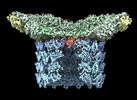
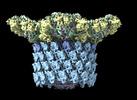
| Title | Neck structure of Agrobacterium phage Milano, C3 symmetry | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRUS / Myophage / redox trigger VIRUS / Myophage / redox trigger | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.46 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.46 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Sonani, R.R. / Wang, F. / Esteves, N.C. / Kelly, R.J. / Sebastian, A. / Kreutzberger, M.A.B. / Leiman, P.G. / Scharf, B.E. / Egelman, E.H. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2023Title: Neck and capsid architecture of the robust Agrobacterium phage Milano. Authors: Ravi R Sonani / Nathaniel C Esteves / Abigail A Horton / Rebecca J Kelly / Amanda L Sebastian / Fengbin Wang / Mark A B Kreutzberger / Petr G Leiman / Birgit E Scharf / Edward H Egelman /  Abstract: Large gaps exist in our understanding of how bacteriophages, the most abundant biological entities on Earth, assemble and function. The structure of the "neck" region, where the DNA-filled capsid is ...Large gaps exist in our understanding of how bacteriophages, the most abundant biological entities on Earth, assemble and function. The structure of the "neck" region, where the DNA-filled capsid is connected to the host-recognizing tail remains poorly understood. We describe cryo-EM structures of the neck, the neck-capsid and neck-tail junctions, and capsid of the Agrobacterium phage Milano. The Milano neck 1 protein connects the 12-fold symmetrical neck to a 5-fold vertex of the icosahedral capsid. Comparison of Milano neck 1 homologs leads to four proposed classes, likely evolved from the simplest one in siphophages to more complex ones in myo- and podophages. Milano neck is surrounded by the atypical collar, which covalently crosslinks the tail sheath to neck 1. The Milano capsid is decorated with three types of proteins, a minor capsid protein (mCP) and two linking proteins crosslinking the mCP to the major capsid protein. The extensive network of disulfide bonds within and between neck, collar, capsid and tail provides an exceptional structural stability to Milano. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8fwe.cif.gz 8fwe.cif.gz | 3.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8fwe.ent.gz pdb8fwe.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8fwe.json.gz 8fwe.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fw/8fwe https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fw/8fwe ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fw/8fwe ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fw/8fwe | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  29503MC  8fwbC  8fwcC  8fwgC  8fwmC  8fxpC  8fxrC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 6 types, 102 molecules JKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklm...
| #1: Protein | Mass: 24490.402 Da / Num. of mol.: 60 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MGH3 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MGH3#2: Protein | Mass: 45840.844 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFW7 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFW7#3: Protein | Mass: 16052.353 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFQ3 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MFQ3#4: Protein | Mass: 20268.541 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MF73 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MF73#5: Protein | Mass: 14673.427 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MHE7 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MHE7#6: Protein | Mass: 22255.439 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MHL8 Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) / References: UniProt: A0A482MHL8 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Agrobacterium phage Milano / Type: VIRUS / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) Agrobacterium phage Milano (virus) |
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: YES / Isolate: SPECIES / Type: VIRION |
| Natural host | Organism: Agrobacterium fabrum str. C58 |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.46 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 10216 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj