[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
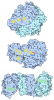
Yorodumi- PDB-8dqv: The 1.52 angstrom CryoEM structure of the [NiFe]-hydrogenase Huc ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8dqv | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The 1.52 angstrom CryoEM structure of the [NiFe]-hydrogenase Huc from Mycobacterium smegmatis - catalytic dimer (Huc2S2L) | |||||||||
 Components Components | (Hydrogenase-2, ... ) x 2 ) x 2 | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  ELECTRON TRANSPORT / [NiFe] Hydrogenase / Membrane-associated / ELECTRON TRANSPORT / [NiFe] Hydrogenase / Membrane-associated /  Complex / Quinone Transport Complex / Quinone Transport | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information hydrogenase (acceptor) / hydrogenase (acceptor) /  ferredoxin hydrogenase complex / ferredoxin hydrogenase complex /  hydrogenase (acceptor) activity / hydrogenase (acceptor) activity /  ferredoxin hydrogenase activity / 3 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / nickel cation binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / ferredoxin hydrogenase activity / 3 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / nickel cation binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding /  metal ion binding metal ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 1.52 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 1.52 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Grinter, R. / Venugopal, H. / Kropp, A. / Greening, C. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 2items Australia, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis for bacterial energy extraction from atmospheric hydrogen. Authors: Rhys Grinter / Ashleigh Kropp / Hari Venugopal / Moritz Senger / Jack Badley / Princess R Cabotaje / Ruyu Jia / Zehui Duan / Ping Huang / Sven T Stripp / Christopher K Barlow / Matthew ...Authors: Rhys Grinter / Ashleigh Kropp / Hari Venugopal / Moritz Senger / Jack Badley / Princess R Cabotaje / Ruyu Jia / Zehui Duan / Ping Huang / Sven T Stripp / Christopher K Barlow / Matthew Belousoff / Hannah S Shafaat / Gregory M Cook / Ralf B Schittenhelm / Kylie A Vincent / Syma Khalid / Gustav Berggren / Chris Greening /       Abstract: Diverse aerobic bacteria use atmospheric H as an energy source for growth and survival. This globally significant process regulates the composition of the atmosphere, enhances soil biodiversity and ...Diverse aerobic bacteria use atmospheric H as an energy source for growth and survival. This globally significant process regulates the composition of the atmosphere, enhances soil biodiversity and drives primary production in extreme environments. Atmospheric H oxidation is attributed to uncharacterized members of the [NiFe] hydrogenase superfamily. However, it remains unresolved how these enzymes overcome the extraordinary catalytic challenge of oxidizing picomolar levels of H amid ambient levels of the catalytic poison O and how the derived electrons are transferred to the respiratory chain. Here we determined the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the Mycobacterium smegmatis hydrogenase Huc and investigated its mechanism. Huc is a highly efficient oxygen-insensitive enzyme that couples oxidation of atmospheric H to the hydrogenation of the respiratory electron carrier menaquinone. Huc uses narrow hydrophobic gas channels to selectively bind atmospheric H at the expense of O, and 3 [3Fe-4S] clusters modulate the properties of the enzyme so that atmospheric H oxidation is energetically feasible. The Huc catalytic subunits form an octameric 833 kDa complex around a membrane-associated stalk, which transports and reduces menaquinone 94 Å from the membrane. These findings provide a mechanistic basis for the biogeochemically and ecologically important process of atmospheric H oxidation, uncover a mode of energy coupling dependent on long-range quinone transport, and pave the way for the development of catalysts that oxidize H in ambient air. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8dqv.cif.gz 8dqv.cif.gz | 548 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8dqv.ent.gz pdb8dqv.ent.gz | 456.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8dqv.json.gz 8dqv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dq/8dqv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dq/8dqv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dq/8dqv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dq/8dqv | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 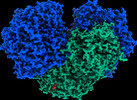 27661MC  7utdC 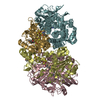 7uurC  7uusC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Hydrogenase-2, ... , 2 types, 4 molecules ACBD
| #1: Protein |  Mass: 57217.078 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / References: UniProt: A0QUM7, Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / References: UniProt: A0QUM7,  hydrogenase (acceptor) hydrogenase (acceptor)#2: Protein |  / NADH ubiquinone oxidoreductase 20 kDa subunit / NADH ubiquinone oxidoreductase 20 kDa subunitMass: 35071.988 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / References: UniProt: I7G634, Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / References: UniProt: I7G634,  hydrogenase (acceptor) hydrogenase (acceptor) |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 7 types, 612 molecules 











| #3: Chemical |  Oxygen Oxygen#4: Chemical | #5: Chemical | #6: Chemical |  Nickel Nickel#7: Chemical |  Menadione Menadione#8: Chemical | ChemComp-F3S /  Iron–sulfur cluster Iron–sulfur cluster#9: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |  Water Water |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex of the type 2 [NiFe]-hydrogenase Huc from Mycobacterium smegmatis Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: NATURAL | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.833 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: MC2 155 Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: MC2 155 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 / Details: pH 7.9 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid type: Quantifoil | |||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm : 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: HELIUM / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 4 sec. / Electron dose: 60.4 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 9868 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 3800000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 1.52 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 153359 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: BACKBONE TRACE / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj