+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ywx | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
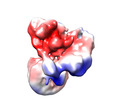
| Title | Structure of the human CCAN CENP-A alpha-satellite complex | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  CELL CYCLE / CELL CYCLE /  Chromosome / Chromosome /  kinetochore / kinetochore /  cell division / cell division /  centromere centromere | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of protein localization to kinetochore / Mis6-Sim4 complex / FANCM-MHF complex / centromere complex assembly / kinetochore organization / metaphase chromosome alignment / spindle attachment to meiosis I kinetochore / Fanconi anaemia nuclear complex / inner kinetochore /  kinetochore binding ...positive regulation of protein localization to kinetochore / Mis6-Sim4 complex / FANCM-MHF complex / centromere complex assembly / kinetochore organization / metaphase chromosome alignment / spindle attachment to meiosis I kinetochore / Fanconi anaemia nuclear complex / inner kinetochore / kinetochore binding ...positive regulation of protein localization to kinetochore / Mis6-Sim4 complex / FANCM-MHF complex / centromere complex assembly / kinetochore organization / metaphase chromosome alignment / spindle attachment to meiosis I kinetochore / Fanconi anaemia nuclear complex / inner kinetochore /  kinetochore binding / centromeric DNA binding / kinetochore binding / centromeric DNA binding /  sex differentiation / CENP-A containing chromatin assembly / resolution of meiotic recombination intermediates / chordate embryonic development / protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region / negative regulation of epithelial cell apoptotic process / attachment of mitotic spindle microtubules to kinetochore / sex differentiation / CENP-A containing chromatin assembly / resolution of meiotic recombination intermediates / chordate embryonic development / protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region / negative regulation of epithelial cell apoptotic process / attachment of mitotic spindle microtubules to kinetochore /  kinetochore assembly / condensed chromosome, centromeric region / replication fork processing / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / mitotic cytokinesis / kinetochore assembly / condensed chromosome, centromeric region / replication fork processing / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / mitotic cytokinesis /  chromosome, centromeric region / centriolar satellite / chromosome organization / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / pericentric heterochromatin / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / interstrand cross-link repair / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Meiotic synapsis / telomere organization / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / chromosome, centromeric region / centriolar satellite / chromosome organization / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / pericentric heterochromatin / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / interstrand cross-link repair / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Meiotic synapsis / telomere organization / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins /  DNA methylation / mitotic spindle organization / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / DNA methylation / mitotic spindle organization / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA /  innate immune response in mucosa / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / Defective pyroptosis / positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / innate immune response in mucosa / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / Defective pyroptosis / positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation /  chromosome segregation / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / HDACs deacetylate histones / Fanconi Anemia Pathway / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / PKR-mediated signaling / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / HDMs demethylate histones / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Metalloprotease DUBs / chromosome segregation / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / HDACs deacetylate histones / Fanconi Anemia Pathway / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / PKR-mediated signaling / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / HDMs demethylate histones / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Metalloprotease DUBs /  kinetochore / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / RMTs methylate histone arginines / kinetochore / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / RMTs methylate histone arginines /  Meiotic recombination / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation /  nuclear matrix / nuclear matrix /  nucleosome assembly / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / HCMV Early Events / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / structural constituent of chromatin / Separation of Sister Chromatids / UCH proteinases / nucleosome assembly / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / HCMV Early Events / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / structural constituent of chromatin / Separation of Sister Chromatids / UCH proteinases /  nucleosome / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / nucleosome / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide /  actin cytoskeleton / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / mitotic cell cycle / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / actin cytoskeleton / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / mitotic cell cycle / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs /  chromosome chromosomeSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 12 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 12 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yatskevich, S. / Muir, K.W. / Bellini, D. / Zhang, Z. / Yang, J. / Tischer, T. / Predin, M. / Dendooven, T. / McLaughlin, S.H. / Barford, D. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  Germany, 3items Germany, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2022 Journal: Science / Year: 2022Title: Structure of the human inner kinetochore bound to a centromeric CENP-A nucleosome. Authors: Stanislau Yatskevich / Kyle W Muir / Dom Bellini / Ziguo Zhang / Jing Yang / Thomas Tischer / Masa Predin / Tom Dendooven / Stephen H McLaughlin / David Barford /  Abstract: Kinetochores assemble onto specialized centromeric CENP-A (centromere protein A) nucleosomes (CENP-A) to mediate attachments between chromosomes and the mitotic spindle. We describe cryo-electron ...Kinetochores assemble onto specialized centromeric CENP-A (centromere protein A) nucleosomes (CENP-A) to mediate attachments between chromosomes and the mitotic spindle. We describe cryo-electron microscopy structures of the human inner kinetochore constitutive centromere associated network (CCAN) complex bound to CENP-A reconstituted onto α-satellite DNA. CCAN forms edge-on contacts with CENP-A, and a linker DNA segment of the α-satellite repeat emerges from the fully wrapped end of the nucleosome to thread through the central CENP-LN channel that tightly grips the DNA. The CENP-TWSX histone-fold module further augments DNA binding and partially wraps the linker DNA in a manner reminiscent of canonical nucleosomes. Our study suggests that the topological entrapment of the linker DNA by CCAN provides a robust mechanism by which kinetochores withstand both pushing and pulling forces exerted by the mitotic spindle. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ywx.cif.gz 7ywx.cif.gz | 915.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ywx.ent.gz pdb7ywx.ent.gz | 722.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ywx.json.gz 7ywx.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yw/7ywx https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yw/7ywx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yw/7ywx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yw/7ywx | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  14351MC  7pb4C  7pb8C 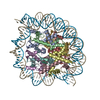 7piiC  7pknC 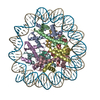 7r5rC  7r5sC  7r5vC 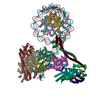 7yyhC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 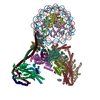
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Centromere protein ... , 16 types, 17 molecules HIKLMNOQUPRTWSXab
| #1: Protein |  / CENP-H / Interphase centromere complex protein 35 / CENP-H / Interphase centromere complex protein 35Mass: 28520.941 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPH, ICEN35 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPH, ICEN35 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9H3R5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9H3R5 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein |  / CENP-I / FSH primary response protein 1 / Follicle-stimulating hormone primary response protein / ...CENP-I / FSH primary response protein 1 / Follicle-stimulating hormone primary response protein / Interphase centromere complex protein 19 / Leucine-rich primary response protein 1 / CENP-I / FSH primary response protein 1 / Follicle-stimulating hormone primary response protein / ...CENP-I / FSH primary response protein 1 / Follicle-stimulating hormone primary response protein / Interphase centromere complex protein 19 / Leucine-rich primary response protein 1Mass: 86820.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPI, FSHPRH1, ICEN19, LRPR1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPI, FSHPRH1, ICEN19, LRPR1 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q92674 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q92674 |
| #3: Protein |  / CENP-K / Interphase centromere complex protein 37 / Protein AF-5alpha / p33 / CENP-K / Interphase centromere complex protein 37 / Protein AF-5alpha / p33Mass: 31696.070 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPK, ICEN37, FKSG14 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPK, ICEN37, FKSG14 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BS16 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BS16 |
| #4: Protein |  / CENP-L / Interphase centromere complex protein 33 / CENP-L / Interphase centromere complex protein 33Mass: 39039.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPL, C1orf155, ICEN33 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPL, C1orf155, ICEN33 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8N0S6 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8N0S6 |
| #5: Protein |  CENPM / CENP-M / Interphase centromere complex protein 39 / Proliferation-associated nuclear element protein 1 CENPM / CENP-M / Interphase centromere complex protein 39 / Proliferation-associated nuclear element protein 1Mass: 19761.945 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPM, C22orf18, ICEN39, PANE1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPM, C22orf18, ICEN39, PANE1 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NSP4 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NSP4 |
| #6: Protein |  / CENP-N / Interphase centromere complex protein 32 / CENP-N / Interphase centromere complex protein 32Mass: 39609.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPN, C16orf60, ICEN32, BM-309 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPN, C16orf60, ICEN32, BM-309 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96H22 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96H22 |
| #7: Protein |  CENPO / CENP-O / Interphase centromere complex protein 36 CENPO / CENP-O / Interphase centromere complex protein 36Mass: 33830.637 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPO, ICEN36, MCM21R / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPO, ICEN36, MCM21R / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BU64 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BU64 |
| #8: Protein |  / CENP-Q / CENP-QMass: 30648.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPQ, C6orf139 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPQ, C6orf139 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q7L2Z9 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q7L2Z9 |
| #9: Protein |  / CENP-U / Centromere protein of 50 kDa / CENP-50 / Interphase centromere complex protein 24 / KSHV ...CENP-U / Centromere protein of 50 kDa / CENP-50 / Interphase centromere complex protein 24 / KSHV latent nuclear antigen-interacting protein 1 / MLF1-interacting protein / Polo-box-interacting protein 1 / CENP-U / Centromere protein of 50 kDa / CENP-50 / Interphase centromere complex protein 24 / KSHV ...CENP-U / Centromere protein of 50 kDa / CENP-50 / Interphase centromere complex protein 24 / KSHV latent nuclear antigen-interacting protein 1 / MLF1-interacting protein / Polo-box-interacting protein 1Mass: 47609.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPU, ICEN24, KLIP1, MLF1IP, PBIP1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPU, ICEN24, KLIP1, MLF1IP, PBIP1 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q71F23 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q71F23 |
| #10: Protein |  / CENP-P / CENP-PMass: 33210.949 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPP / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q6IPU0 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q6IPU0 |
| #11: Protein |  / CENP-R / Beta-3-endonexin / Integrin beta-3-binding protein / Nuclear receptor-interacting factor 3 / CENP-R / Beta-3-endonexin / Integrin beta-3-binding protein / Nuclear receptor-interacting factor 3Mass: 20228.297 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ITGB3BP, CENPR, NRIF3 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ITGB3BP, CENPR, NRIF3 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13352 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13352 |
| #12: Protein |  / CENP-T / Interphase centromere complex protein 22 / CENP-T / Interphase centromere complex protein 22Mass: 60502.613 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPT, C16orf56, ICEN22 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPT, C16orf56, ICEN22 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96BT3 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96BT3 |
| #13: Protein |  / CENP-W / Cancer-up-regulated gene 2 protein / CENP-W / Cancer-up-regulated gene 2 proteinMass: 10087.236 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPW, C6orf173, CUG2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPW, C6orf173, CUG2 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q5EE01 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q5EE01 |
| #14: Protein |  / CENP-S / Apoptosis-inducing TAF9-like domain-containing protein 1 / FANCM-associated histone fold ...CENP-S / Apoptosis-inducing TAF9-like domain-containing protein 1 / FANCM-associated histone fold protein 1 / FANCM-interacting histone fold protein 1 / Fanconi anemia-associated polypeptide of 16 kDa / CENP-S / Apoptosis-inducing TAF9-like domain-containing protein 1 / FANCM-associated histone fold ...CENP-S / Apoptosis-inducing TAF9-like domain-containing protein 1 / FANCM-associated histone fold protein 1 / FANCM-interacting histone fold protein 1 / Fanconi anemia-associated polypeptide of 16 kDaMass: 15917.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPS, APITD1, FAAP16, MHF1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPS, APITD1, FAAP16, MHF1 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8N2Z9 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8N2Z9 |
| #15: Protein |  / CENP-X / FANCM-associated histone fold protein 2 / FANCM-interacting histone fold protein 2 / ...CENP-X / FANCM-associated histone fold protein 2 / FANCM-interacting histone fold protein 2 / Fanconi anemia-associated polypeptide of 10 kDa / Retinoic acid-inducible gene D9 protein homolog / Stimulated by retinoic acid gene 13 protein homolog / CENP-X / FANCM-associated histone fold protein 2 / FANCM-interacting histone fold protein 2 / ...CENP-X / FANCM-associated histone fold protein 2 / FANCM-interacting histone fold protein 2 / Fanconi anemia-associated polypeptide of 10 kDa / Retinoic acid-inducible gene D9 protein homolog / Stimulated by retinoic acid gene 13 protein homologMass: 8972.415 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPX, FAAP10, MHF2, STRA13 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPX, FAAP10, MHF2, STRA13 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: A8MT69 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: A8MT69 |
| #22: Protein |  / CENP-C / Centromere autoantigen C / Centromere protein C 1 / CENP-C 1 / Interphase centromere ...CENP-C / Centromere autoantigen C / Centromere protein C 1 / CENP-C 1 / Interphase centromere complex protein 7 / CENP-C / Centromere autoantigen C / Centromere protein C 1 / CENP-C 1 / Interphase centromere ...CENP-C / Centromere autoantigen C / Centromere protein C 1 / CENP-C 1 / Interphase centromere complex protein 7Mass: 61856.004 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPC, CENPC1, ICEN7 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPC, CENPC1, ICEN7 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q03188 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q03188 |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules iJ
| #16: DNA chain | Mass: 52725.812 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #17: DNA chain | Mass: 52822.809 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Protein , 4 types, 8 molecules AEBFCGDV
| #18: Protein | Mass: 16023.630 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPA / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P49450 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P49450#19: Protein |  Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, ...Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, H4FE, HIST1H4K, H4/D, H4FD, HIST1H4L, H4/K, H4FK, HIST2H4A, H4/N, H4F2, H4FN, HIST2H4, HIST2H4B, H4/O, H4FO, HIST4H4 Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P62805 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P62805#20: Protein | Mass: 14135.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2AC6, H2AFL, HIST1H2AC / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2AC6, H2AFL, HIST1H2AC / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q93077 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q93077#21: Protein | Mass: 13937.213 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H2BC, H2BFL, HIST1H2BE, H2BFH, HIST1H2BF, H2BFG, HIST1H2BG, H2BFA, HIST1H2BI, H2BFK Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P62807 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P62807 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: CCAN-CENP-A inner centromere complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 12 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 20549 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj















































