[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6pxe: Crystal structure of the complex between periplasmic domains of a... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6pxe | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of the complex between periplasmic domains of antiholin RI and holin T from T4 phage, in P21 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRAL PROTEIN / VIRAL PROTEIN /  phage / lysis inhibition phage / lysis inhibition | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhost cell periplasmic space / pore-forming activity / molecular function inhibitor activity / viral release from host cell by cytolysis / killing of cells of another organism / host cell plasma membrane /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  membrane membraneSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) Escherichia phage vB_EcoM_NBG2 (virus) Escherichia phage vB_EcoM_NBG2 (virus) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.3 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Krieger, I.V. / Sacchettini, J.C. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2020Title: The Structural Basis of T4 Phage Lysis Control: DNA as the Signal for Lysis Inhibition. Authors: Inna V Krieger / Vladimir Kuznetsov / Jeng-Yih Chang / Junjie Zhang / Samir H Moussa / Ryland F Young / James C Sacchettini /  Abstract: Optimal phage propagation depends on the regulation of the lysis of the infected host cell. In T4 phage infection, lysis occurs when the holin protein (T) forms lesions in the host membrane. However, ...Optimal phage propagation depends on the regulation of the lysis of the infected host cell. In T4 phage infection, lysis occurs when the holin protein (T) forms lesions in the host membrane. However, the lethal function of T can be blocked by an antiholin (RI) during lysis inhibition (LIN). LIN sets if the infected cell undergoes superinfection, then the lysis is delayed until host/phage ratio becomes more favorable for the release of progeny. It has been thought that a signal derived from the superinfection is required to activate RI. Here we report structures that suggest a radically different model in which RI binds to T irrespective of superinfection, causing it to accumulate in a membrane as heterotetrameric 2RI-2T complex. Moreover, we show the complex binds non-specifically to DNA, suggesting that the gDNA from the superinfecting phage serves as the LIN signal and that stabilization of the complex by DNA binding is what defines LIN. Finally, we show that soluble domain of free RI crystallizes in a domain-swapped homotetramer, which likely works as a sink for RI molecules released from the RI-T complex to ensure efficient lysis. These results constitute the first structural basis and a new model not only for the historic LIN phenomenon but also for the temporal regulation of phage lysis in general. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6pxe.cif.gz 6pxe.cif.gz | 188 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6pxe.ent.gz pdb6pxe.ent.gz | 148.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6pxe.json.gz 6pxe.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/px/6pxe https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/px/6pxe ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/px/6pxe ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/px/6pxe | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6pshC  6pskSC  6px4C S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 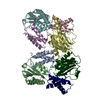
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 8801.884 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Gene: rI, 58.6, rIA, tk.-2 / Production host: Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Gene: rI, 58.6, rIA, tk.-2 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P13304 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P13304#2: Protein |  Mass: 19211.615 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Escherichia phage vB_EcoM_NBG2 (virus) / Gene: vBEcoMNBG2_239 / Production host: Escherichia phage vB_EcoM_NBG2 (virus) / Gene: vBEcoMNBG2_239 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: A0A2U8QQK7, UniProt: P06808*PLUS Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: A0A2U8QQK7, UniProt: P06808*PLUS#3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |  Water Water |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.3 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 46.63 % |
|---|---|
Crystal grow | Temperature: 289 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / pH: 3.5 / Details: 25% PEG 3,350 with 0.1M citric acid pH 3.5 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 120 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 23-ID-D / Wavelength: 0.987 Å / Beamline: 23-ID-D / Wavelength: 0.987 Å |
| Detector | Type: MAR scanner 300 mm plate / Detector: IMAGE PLATE / Date: Nov 12, 2014 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength : 0.987 Å / Relative weight: 1 : 0.987 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.3→45.8 Å / Num. obs: 44230 / % possible obs: 97.4 % / Redundancy: 5.07 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 35.29 Å2 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.1506 / Net I/σ(I): 7.57 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.3→2.34 Å / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.7874 / Num. unique obs: 2168 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure : :  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 6PSK Resolution: 2.3→39.803 Å / SU ML: 0.39 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.36 / Phase error: 33.14
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 84.32 Å2 / Biso mean: 37.7695 Å2 / Biso min: 14.41 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 2.3→39.803 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj
