[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-23773: Structure of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae ribonucleotide reductase i... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23773 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
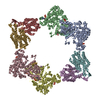
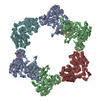
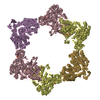
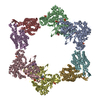
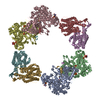
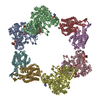
| Title | Structure of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae ribonucleotide reductase in the inactive state | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase / ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase activity, thioredoxin disulfide as acceptor / deoxyribonucleotide biosynthetic process / ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase / ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase activity, thioredoxin disulfide as acceptor / deoxyribonucleotide biosynthetic process /  DNA replication / DNA replication /  ATP binding ATP bindingSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.3 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.3 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Levitz TS / Drennan CL / Brignole EJ | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4 items United States, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2022 Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2022Title: Effects of chameleon dispense-to-plunge speed on particle concentration, complex formation, and final resolution: A case study using the Neisseria gonorrhoeae ribonucleotide reductase inactive complex. Authors: Talya S Levitz / Edward J Brignole / Ivan Fong / Michele C Darrow / Catherine L Drennan /   Abstract: Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) is an essential enzyme that converts ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides and is a promising antibiotic target, but few RNRs have been structurally characterized. We ...Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) is an essential enzyme that converts ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides and is a promising antibiotic target, but few RNRs have been structurally characterized. We present the use of the chameleon, a commercially-available piezoelectric cryogenic electron microscopy plunger, to address complex denaturation in the Neisseria gonorrhoeae class Ia RNR. Here, we characterize the extent of denaturation of the ring-shaped complex following grid preparation using a traditional plunger and using a chameleon with varying dispense-to-plunge times. We also characterize how dispense-to-plunge time influences the amount of protein sample required for grid preparation and preferred orientation of the sample. We demonstrate that the fastest dispense-to-plunge time of 54 ms is sufficient for generation of a data set that produces a high quality structure, and that a traditional plunging technique or slow chameleon dispense-to-plunge times generate data sets limited in resolution by complex denaturation. The 4.3 Å resolution structure of Neisseria gonorrhoeae class Ia RNR in the inactive α4β4 oligomeric state solved using the chameleon with a fast dispense-to-plunge time yields molecular information regarding similarities and differences to the well studied Escherichia coli class Ia RNR α4β4 ring. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23773.map.gz emd_23773.map.gz | 55.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23773-v30.xml emd-23773-v30.xml emd-23773.xml emd-23773.xml | 17.3 KB 17.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_23773_fsc.xml emd_23773_fsc.xml | 8.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_23773.png emd_23773.png | 89.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23773 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23773 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23773 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23773 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7mdiMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23773.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 59.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23773.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 59.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.5998 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ribonucleotide reductase inactive complex
| Entire | Name: Ribonucleotide reductase inactive complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Ribonucleotide reductase inactive complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Ribonucleotide reductase inactive complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant strain: T7 express Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant strain: T7 express |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 528 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase subunit alpha
| Macromolecule | Name: Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase subunit alpha / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number:  ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700825 / FA 1090 Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700825 / FA 1090 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 87.081344 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MGHHHHHHEN LYFQMNTPTD LKVTKRDGRL EAIDLDKIHR VVTWAAEGLE NVSVSQVELK SHIQFYNGIR TDDIHETIIK AAADLISED TPDYQYLAAR LAIFHLRKIA YGEYEPPHLY NHVKKLTDAG KYDRHILEDY SREEFDELNA YIDHERDMSF S YAAVKQLE ...String: MGHHHHHHEN LYFQMNTPTD LKVTKRDGRL EAIDLDKIHR VVTWAAEGLE NVSVSQVELK SHIQFYNGIR TDDIHETIIK AAADLISED TPDYQYLAAR LAIFHLRKIA YGEYEPPHLY NHVKKLTDAG KYDRHILEDY SREEFDELNA YIDHERDMSF S YAAVKQLE GKYLVQNRVT RQIYETPQFL YVLVAMCLFS KYPKEARLDY VKRFYDAVST FKVSLPTPIM SGVRTPTRQF SS CVLIECD DSLDSINATT SAIVKYVSQR AGIGINAGRI RGLDSEIRGG EARHTGCIPF FKMFQAAVKS CSQGGVRGGA ATL FYPLWH IEAESLLVLK NNRGVEDNRI RQLDYGVQIN RLLYTRLIKG GNITLFSPNE VSGLYEAFFA DQDEFERLYT KYEQ DPNIR KRIIPAADLF STLMQERAGT GRIYIQNVDH CNTHSPFDPR VAPVHQSNLC MEIALPTKPL DNINDPDGEI ALCTL SAFN LGALNSLDEL EGLADLTVRA LDALLDYQGY PVEAARTSTM DRRSLGIGVI NYAYYLAKNG VRYSDGSALG LTHRTF EAI QYYLLKASAN LAKEYGACTL FNQTVYSQGK LPIDTYKKDL DAVCGEPLHY DWESLRADIV KYGLRNSTLT ALMPSET SS QIANATNGIE PPRGLVTVKA SKDGILKQVV PEFETLKNAY ETLWQLPGNE GYLKLVGVMQ KFVDQAISAN TAYDPGKF E GNKVSMKQML KDLLTAYKYG VKTLYYHNTR DGADDTQTDI QDDGCAGGAC KI |
-Macromolecule #2: Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase subunit beta
| Macromolecule | Name: Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase subunit beta / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number:  ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700825 / FA 1090 Neisseria gonorrhoeae (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700825 / FA 1090 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.107785 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MGHHHHHHEN LYFQMSYSTF PKTKNDALKE PMFFGQPVNV ARYDQQKYEV FEKLIEKQLS FFWRPEEIDV SRDRIDYANL PEHEKHIFI SNLKYQTLLD SIQGRSPNVA LLPLVSIPEL ETWVETWSFS ETIHSRSYTH IIRNIVNDPS VVFDDIVENE Y ITARAEDI ...String: MGHHHHHHEN LYFQMSYSTF PKTKNDALKE PMFFGQPVNV ARYDQQKYEV FEKLIEKQLS FFWRPEEIDV SRDRIDYANL PEHEKHIFI SNLKYQTLLD SIQGRSPNVA LLPLVSIPEL ETWVETWSFS ETIHSRSYTH IIRNIVNDPS VVFDDIVENE Y ITARAEDI ACYYDDLIEY TQYYNLLGEG VHNVGGKPVT VSLRGLKKKL YLCLMCVNVL EAIRFYVSFA CSFAFAEREL ME GNAKIIK DIARDEALHL TGTQHMLNLM RSGVDDPEMA EIAAELQDEC FQLFKKAAEQ EKEWAAYLFK DGSMIGLNKE ILS QYVEYI TNLRMQAVGL PAGFEGANQN PIPWINAWLS SDNVQVAPQE VEISSYLIGQ IDSEVNTDDL GDFEL |
-Macromolecule #3: CYTIDINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: CYTIDINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: CDP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 403.176 Da |
| Chemical component information | 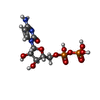 ChemComp-CDP: |
-Macromolecule #4: 2'-DEOXYADENOSINE 5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: 2'-DEOXYADENOSINE 5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: DTP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 491.182 Da |
| Chemical component information | 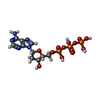 ChemComp-DTP: |
-Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #6: MU-OXO-DIIRON
| Macromolecule | Name: MU-OXO-DIIRON / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: FEO |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 127.689 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-FEO: |
-Macromolecule #7: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 24 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 6 mg/mL | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 Component:
| ||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE Details: Plunged using the chameleon (SPT labtech) Glow discharged at 12 mA for 250 s. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.1 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 92000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.1 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 92000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 620 / Average exposure time: 7.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 53.15 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller