+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | X-ray and Cryo-EM structures reveal mutual conformational changes of Kinesin and GTP-state microtubules upon binding. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | EMBO J, Vol. 34, Issue 9, Page 1270-1286, Year 2015 |
| Publish date | May 5, 2015 |
 Authors Authors | Manatsu Morikawa / Hiroaki Yajima / Ryo Nitta / Shigeyuki Inoue / Toshihiko Ogura / Chikara Sato / Nobutaka Hirokawa /   |
| PubMed Abstract | The molecular motor kinesin moves along microtubules using energy from ATP hydrolysis in an initial step coupled with ADP release. In neurons, kinesin-1/KIF5C preferentially binds to the GTP-state ...The molecular motor kinesin moves along microtubules using energy from ATP hydrolysis in an initial step coupled with ADP release. In neurons, kinesin-1/KIF5C preferentially binds to the GTP-state microtubules over GDP-state microtubules to selectively enter an axon among many processes; however, because the atomic structure of nucleotide-free KIF5C is unavailable, its molecular mechanism remains unresolved. Here, the crystal structure of nucleotide-free KIF5C and the cryo-electron microscopic structure of nucleotide-free KIF5C complexed with the GTP-state microtubule are presented. The structures illustrate mutual conformational changes induced by interaction between the GTP-state microtubule and KIF5C. KIF5C acquires the 'rigor conformation', where mobile switches I and II are stabilized through L11 and the initial portion of the neck-linker, facilitating effective ADP release and the weak-to-strong transition of KIF5C microtubule affinity. Conformational changes to tubulin strengthen the longitudinal contacts of the GTP-state microtubule in a similar manner to GDP-taxol microtubules. These results and functional analyses provide the molecular mechanism of the preferential binding of KIF5C to GTP-state microtubules. |
 External links External links |  EMBO J / EMBO J /  PubMed:25777528 / PubMed:25777528 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.7 - 8.1 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-5916: Cryo-Electron Microscopy of Nucleotide-free Kinesin motor domain complexed with GMPCPP-microtubule  PDB-3wrd:  PDB-3x2t: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-GTP: 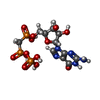 ChemComp-G2P:  ChemComp-SO4:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-ADP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  STRUCTURAL PROTEIN/MOTOR PROTEIN / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN/MOTOR PROTEIN /  Kinesin / Kinesin /  Motor domain / Rigor-conformation / Nucleotide-free kinesin / Motor domain / Rigor-conformation / Nucleotide-free kinesin /  Microtubule / GMPCPP-microtubule / Microtubule / GMPCPP-microtubule /  tubulin / tubulin /  Axonal transport / Axonal transport /  STRUCTURAL PROTEIN-MOTOR PROTEIN complex / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN-MOTOR PROTEIN complex /  MOTOR PROTEIN / nucleotide-free / MOTOR PROTEIN / nucleotide-free /  ATPase / ATPase /  nucleotide binding / nucleotide binding /  transport protein transport protein |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers






