+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structural basis for bacterial energy extraction from atmospheric hydrogen. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nature, Vol. 615, Issue 7952, Page 541-547, Year 2023 |
| 掲載日 | 2023年3月8日 |
 著者 著者 | Rhys Grinter / Ashleigh Kropp / Hari Venugopal / Moritz Senger / Jack Badley / Princess R Cabotaje / Ruyu Jia / Zehui Duan / Ping Huang / Sven T Stripp / Christopher K Barlow / Matthew Belousoff / Hannah S Shafaat / Gregory M Cook / Ralf B Schittenhelm / Kylie A Vincent / Syma Khalid / Gustav Berggren / Chris Greening /       |
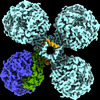
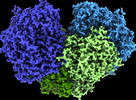
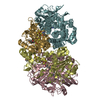
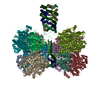
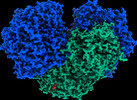
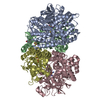
| PubMed 要旨 | Diverse aerobic bacteria use atmospheric H as an energy source for growth and survival. This globally significant process regulates the composition of the atmosphere, enhances soil biodiversity and ...Diverse aerobic bacteria use atmospheric H as an energy source for growth and survival. This globally significant process regulates the composition of the atmosphere, enhances soil biodiversity and drives primary production in extreme environments. Atmospheric H oxidation is attributed to uncharacterized members of the [NiFe] hydrogenase superfamily. However, it remains unresolved how these enzymes overcome the extraordinary catalytic challenge of oxidizing picomolar levels of H amid ambient levels of the catalytic poison O and how the derived electrons are transferred to the respiratory chain. Here we determined the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the Mycobacterium smegmatis hydrogenase Huc and investigated its mechanism. Huc is a highly efficient oxygen-insensitive enzyme that couples oxidation of atmospheric H to the hydrogenation of the respiratory electron carrier menaquinone. Huc uses narrow hydrophobic gas channels to selectively bind atmospheric H at the expense of O, and 3 [3Fe-4S] clusters modulate the properties of the enzyme so that atmospheric H oxidation is energetically feasible. The Huc catalytic subunits form an octameric 833 kDa complex around a membrane-associated stalk, which transports and reduces menaquinone 94 Å from the membrane. These findings provide a mechanistic basis for the biogeochemically and ecologically important process of atmospheric H oxidation, uncover a mode of energy coupling dependent on long-range quinone transport, and pave the way for the development of catalysts that oxidize H in ambient air. |
 リンク リンク |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:36890228 / PubMed:36890228 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 1.52 - 8.0 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-26767, PDB-7utd: EMDB-26801, PDB-7uur: EMDB-26802, PDB-7uus: EMDB-27661, PDB-8dqv: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-3NI:  ChemComp-FCO:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-MQ9: 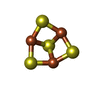 ChemComp-F3S:  ChemComp-OH:  ChemComp-VK3:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-O: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード |  OXIDOREDUCTASE (酸化還元酵素) / [NiFe] Hydrogenase / Membrane associated / OXIDOREDUCTASE (酸化還元酵素) / [NiFe] Hydrogenase / Membrane associated /  Complex / Quinone Transport / Complex / Quinone Transport /  ELECTRON TRANSPORT (電子伝達系) / OXIDOREDUCTASE (EC 1.12.99.6) / [NiFe]-Hydrogenase / Membrane-associated ELECTRON TRANSPORT (電子伝達系) / OXIDOREDUCTASE (EC 1.12.99.6) / [NiFe]-Hydrogenase / Membrane-associated |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について