[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-26802: The CryoEM structure of the [NiFe]-hydrogenase Huc from Mycobacte... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
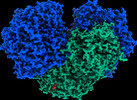
| Title | The CryoEM structure of the [NiFe]-hydrogenase Huc from Mycobacterium smegmatis - Full complex focused refinement of stalk | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information hydrogenase (acceptor) / hydrogenase (acceptor) /  ferredoxin hydrogenase complex / ferredoxin hydrogenase complex /  hydrogenase (acceptor) activity / hydrogenase (acceptor) activity /  ferredoxin hydrogenase activity / 3 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / nickel cation binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / ferredoxin hydrogenase activity / 3 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / nickel cation binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding /  metal ion binding metal ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 8.0 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 8.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Grinter R / Venugopal H / Kropp A / Greening C | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 2 items Australia, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis for bacterial energy extraction from atmospheric hydrogen. Authors: Rhys Grinter / Ashleigh Kropp / Hari Venugopal / Moritz Senger / Jack Badley / Princess R Cabotaje / Ruyu Jia / Zehui Duan / Ping Huang / Sven T Stripp / Christopher K Barlow / Matthew ...Authors: Rhys Grinter / Ashleigh Kropp / Hari Venugopal / Moritz Senger / Jack Badley / Princess R Cabotaje / Ruyu Jia / Zehui Duan / Ping Huang / Sven T Stripp / Christopher K Barlow / Matthew Belousoff / Hannah S Shafaat / Gregory M Cook / Ralf B Schittenhelm / Kylie A Vincent / Syma Khalid / Gustav Berggren / Chris Greening /       Abstract: Diverse aerobic bacteria use atmospheric H as an energy source for growth and survival. This globally significant process regulates the composition of the atmosphere, enhances soil biodiversity and ...Diverse aerobic bacteria use atmospheric H as an energy source for growth and survival. This globally significant process regulates the composition of the atmosphere, enhances soil biodiversity and drives primary production in extreme environments. Atmospheric H oxidation is attributed to uncharacterized members of the [NiFe] hydrogenase superfamily. However, it remains unresolved how these enzymes overcome the extraordinary catalytic challenge of oxidizing picomolar levels of H amid ambient levels of the catalytic poison O and how the derived electrons are transferred to the respiratory chain. Here we determined the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the Mycobacterium smegmatis hydrogenase Huc and investigated its mechanism. Huc is a highly efficient oxygen-insensitive enzyme that couples oxidation of atmospheric H to the hydrogenation of the respiratory electron carrier menaquinone. Huc uses narrow hydrophobic gas channels to selectively bind atmospheric H at the expense of O, and 3 [3Fe-4S] clusters modulate the properties of the enzyme so that atmospheric H oxidation is energetically feasible. The Huc catalytic subunits form an octameric 833 kDa complex around a membrane-associated stalk, which transports and reduces menaquinone 94 Å from the membrane. These findings provide a mechanistic basis for the biogeochemically and ecologically important process of atmospheric H oxidation, uncover a mode of energy coupling dependent on long-range quinone transport, and pave the way for the development of catalysts that oxidize H in ambient air. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_26802.map.gz emd_26802.map.gz | 351.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-26802-v30.xml emd-26802-v30.xml emd-26802.xml emd-26802.xml | 22.4 KB 22.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_26802.png emd_26802.png | 61.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_26802_msk_1.map emd_26802_msk_1.map | 729 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Others |  emd_26802_half_map_1.map.gz emd_26802_half_map_1.map.gz emd_26802_half_map_2.map.gz emd_26802_half_map_2.map.gz | 677.4 MB 677.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26802 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26802 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26802 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26802 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 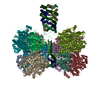 7uusMC  7utdC 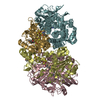 7uurC  8dqvC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_26802.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 729 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_26802.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 729 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.5 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_26802_msk_1.map emd_26802_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_26802_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_26802_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of the type 2 [NiFe]-hydrogenase Huc from Mycobacterium s...
| Entire | Name: Complex of the type 2 [NiFe]-hydrogenase Huc from Mycobacterium smegmatis |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of the type 2 [NiFe]-hydrogenase Huc from Mycobacterium s...
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of the type 2 [NiFe]-hydrogenase Huc from Mycobacterium smegmatis type: complex / ID: 1 / Chimera: Yes / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 833 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Hydrogenase-2, large subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: Hydrogenase-2, large subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number:  hydrogenase (acceptor) hydrogenase (acceptor) |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 57.447297 KDa |
| Sequence | String: TELDLFVSPL GRVEGDLDVR VTINDGVVTS AWTEAAMFRG FEIILRGKDP QAGLIVCPRI CGICGGSHLY KSAYALDTAW RTHMPPNAT LIRNICQACE TLQSIPRYFY ALFAIDLTNK NYAKSKLYDE AVRRFAPYVG TSYQPGVVLS AKPVEVYAIF G GQWP(DHI)SSF ...String: TELDLFVSPL GRVEGDLDVR VTINDGVVTS AWTEAAMFRG FEIILRGKDP QAGLIVCPRI CGICGGSHLY KSAYALDTAW RTHMPPNAT LIRNICQACE TLQSIPRYFY ALFAIDLTNK NYAKSKLYDE AVRRFAPYVG TSYQPGVVLS AKPVEVYAIF G GQWP(DHI)SSF MVPGGVMSAP TLSDVTRAIA ILEHWNDNWL EKQWLGCSVD RWLENKTWND VLAWVDENES QYNSDCGF F IRYCLDVGLD KYGQGVGNYL ATGTYFEPSL YENPTIEGRN AALIGRSGVF ADGRYFEFDQ ANVTEDVTHS FYEGNRPLH PFEGETIPVN PEDGRRQGKY SWAKSPRYAV PGLGNVPLET GPLARRMAAS APDAETHQDD DPLFADIYNA IGPSVMVRQL ARMHEGPKY YKWVRQWLDD LELKESFYTK PVEYAEGKGF GSTEAARGAL SDWIVIEDSK IKNYQVVTPT AWNIGPRDAS E VLGPIEQA LVGSPIVDAE DPVELGHVAR SFDSCLVCTV H |
-Macromolecule #2: Hydrogenase-2, small subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: Hydrogenase-2, small subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number:  hydrogenase (acceptor) hydrogenase (acceptor) |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) / Strain: MC2 155 Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) / Strain: MC2 155 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.65977 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSAWSHPQFE KGGGSGGGSG GSAWSHPQFE KSGGGGGENL YFQGSGGASV LWFQGGACSG NTMSFLNADE PNVVDLIVDF GLDLLWHPS LGLELGNNAQ KVFWDCAKGE RPLDIFVFEG TVIEAPNGTG QMDMFAGRPM KDWVTDLAGA AQIVVAIGDC A CFGGIPAM ...String: MSAWSHPQFE KGGGSGGGSG GSAWSHPQFE KSGGGGGENL YFQGSGGASV LWFQGGACSG NTMSFLNADE PNVVDLIVDF GLDLLWHPS LGLELGNNAQ KVFWDCAKGE RPLDIFVFEG TVIEAPNGTG QMDMFAGRPM KDWVTDLAGA AQIVVAIGDC A CFGGIPAM EPNPSGSTGL QFHKREKGGF LGPDFRSKMG LPVINVPGCP AHPDWITQIL VALATGRAGD ITLDDLHRPE TF FKTFTQT GCTRVQFFEY KQSTLSFGEG TRTGCLFYEF GCRGPMTHSP CNRILWNRQS SKTRAGMPCL GCTEPEFPHF DLA PGTVFK TQKVSGMIPK EVPEGTDHLT YMGLAAAARI AAPQWSKEDM FVV |
-Macromolecule #3: [NiFe]-Hydrogenase Huc Membrane Associated Subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: [NiFe]-Hydrogenase Huc Membrane Associated Subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) / Strain: MC2 155 Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) / Strain: MC2 155 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 19.275828 KDa |
| Sequence | String: ASNGHSAGQN AIDELPDISP VDGIRRRLDD PQVAEALNSL LDHADLLAVL VKGLDGFVRR GDDIANNLTS AIGELKALNA ADTPIPALA ALKDVDLAGL ANSLATLSGG LVKATPALNA VLDSLTDQRG AEVLSALGDA LVAARTSAPP APRGVRGMWK T LRAAAKDP DVGRGVSYLI EVARVFGSKV |
-Macromolecule #4: NICKEL (III) ION
| Macromolecule | Name: NICKEL (III) ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: 3NI |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 58.693 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-3NI: |
-Macromolecule #5: CARBONMONOXIDE-(DICYANO) IRON
| Macromolecule | Name: CARBONMONOXIDE-(DICYANO) IRON / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: FCO |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 135.89 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-FCO: |
-Macromolecule #6: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #7: MENAQUINONE-9
| Macromolecule | Name: MENAQUINONE-9 / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: MQ9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 785.233 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-MQ9: |
-Macromolecule #8: FE3-S4 CLUSTER
| Macromolecule | Name: FE3-S4 CLUSTER / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 24 / Formula: F3S |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 295.795 Da |
| Chemical component information | 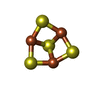 ChemComp-F3S: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 5.0 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.9 Component:
Details: pH 7.9 | |||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil / Material: GOLD / Support film - Material: GOLD / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: HELIUM |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 9868 / Average exposure time: 4.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.4 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Particle selection | Number selected: 2646471 |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: RELION |
| Final 3D classification | Number classes: 1 / Avg.num./class: 153359 / Software - Name: cryoSPARC |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: cryoSPARC |
| Final reconstruction | Number classes used: 1 / Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 8.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC / Number images used: 60448 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: BACKBONE TRACE |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7uus: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z
Z Y
Y X
X