+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1zgu | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Solution structure of the human Mms2-Ubiquitin complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE/SIGNALING PROTEIN / UEV domain / ubiquitin binding motif / LIGASE-SIGNALING PROTEIN COMPLEX | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / : / Metalloprotease DUBs / : / : / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / Regulation of PTEN localization / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Interleukin-1 signaling / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling ...: / : / Metalloprotease DUBs / : / : / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / Regulation of PTEN localization / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Interleukin-1 signaling / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Translesion synthesis by POLI / : / UCH proteinases / Regulation of PTEN stability and activity / Aggrephagy / Regulation of TP53 Degradation / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / error-free postreplication DNA repair / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / Ubiquitin Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A /  Peroxisomal protein import / UBC13-MMS2 complex / Orc1 removal from chromatin / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / DNA double-strand break processing / positive regulation of protein K63-linked ubiquitination / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / Peroxisomal protein import / UBC13-MMS2 complex / Orc1 removal from chromatin / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / DNA double-strand break processing / positive regulation of protein K63-linked ubiquitination / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation /  postreplication repair / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Ub-specific processing proteases / Dual incision in TC-NER / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / postreplication repair / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Ub-specific processing proteases / Dual incision in TC-NER / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression /  ribosomal large subunit export from nucleus / ribosomal large subunit export from nucleus /  regulation of DNA repair / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / regulation of DNA repair / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway /  Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / Pexophagy / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Regulation of PTEN localization / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / Pexophagy / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Regulation of PTEN localization / Translesion synthesis by POLK /  Regulation of BACH1 activity / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Josephin domain DUBs / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) Regulation of BACH1 activity / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Josephin domain DUBs / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE)Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  SOLUTION NMR / protein-protein docking SOLUTION NMR / protein-protein docking | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lewis, M.J. / Saltibus, L.F. / Hau, D.D. / Xiao, W. / Spyracopoulos, L. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J.Biomol.Nmr / Year: 2006 Journal: J.Biomol.Nmr / Year: 2006Title: Structural Basis for Non-Covalent Interaction Between Ubiquitin and the Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme Variant Human MMS2. Authors: Lewis, M.J. / Saltibus, L.F. / Hau, D.D. / Xiao, W. / Spyracopoulos, L. | ||||||
| History |
| ||||||
| Remark 999 | Sequence Yeast Ubiquitin was used to obtain restraint information, while human Ubiquitin was used ...Sequence Yeast Ubiquitin was used to obtain restraint information, while human Ubiquitin was used to model the interaction. The sequence differences between yeast and human Ubiquitin are absent from the protein-protein binding interface. |
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1zgu.cif.gz 1zgu.cif.gz | 727.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1zgu.ent.gz pdb1zgu.ent.gz | 632.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1zgu.json.gz 1zgu.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zg/1zgu https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zg/1zgu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zg/1zgu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zg/1zgu | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 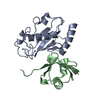
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| |||||||||
| NMR ensembles |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15834.092 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBE2V2, MMS2 / Plasmid: pGEX-6P / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBE2V2, MMS2 / Plasmid: pGEX-6P / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): BL21(DE3)-RIL / References: UniProt: Q15819 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): BL21(DE3)-RIL / References: UniProt: Q15819 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein |  Mass: 8604.845 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: K48R Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Plasmid: pET3a / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Plasmid: pET3a / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): BL21(DE3)-RIL / References: UniProt: P61864, UniProt: P0CG48*PLUS Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): BL21(DE3)-RIL / References: UniProt: P61864, UniProt: P0CG48*PLUS |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  SOLUTION NMR SOLUTION NMR | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMR experiment |
|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Details |
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample conditions |
|
-NMR measurement
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR spectrometer |
|
- Processing
Processing
| NMR software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method: protein-protein docking / Software ordinal: 1 / Details: HADDOCK algorithm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR representative | Selection criteria: lowest energy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR ensemble | Conformer selection criteria: structures with the lowest energy Conformers calculated total number: 50 / Conformers submitted total number: 10 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj


























