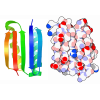
Entry Database : PDB / ID : 9y0rTitle Importin alpha 2 in complex with ATF2 basic region Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-2 Importin subunit alpha-1 Keywords / / / / / Function / homology Function Domain/homology Component
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / Biological species Mus musculus (house mouse)Homo sapiens (human)Method / / / Resolution : 2.2 Å Authors Ghafoori, S.M. / Forwood, J.K. Funding support Organization Grant number Country National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC, Australia)
Journal : To Be Published Title : Importin alpha 2 in complex with ATF2 basic regionAuthors : Ghafoori, S.M. / Forwood, J.K. History Deposition Aug 29, 2025 Deposition site / Processing site Revision 1.0 Sep 17, 2025 Provider / Type
 Open data
Open data Basic information
Basic information Components
Components Keywords
Keywords Function and homology information
Function and homology information
 Homo sapiens (human)
Homo sapiens (human) X-RAY DIFFRACTION /
X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON /
SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.2 Å
MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.2 Å  Authors
Authors Australia, 1items
Australia, 1items  Citation
Citation Journal: To Be Published
Journal: To Be Published Structure visualization
Structure visualization Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol Downloads & links
Downloads & links Download
Download 9y0r.cif.gz
9y0r.cif.gz PDBx/mmCIF format
PDBx/mmCIF format pdb9y0r.ent.gz
pdb9y0r.ent.gz PDB format
PDB format 9y0r.json.gz
9y0r.json.gz PDBx/mmJSON format
PDBx/mmJSON format Other downloads
Other downloads 9y0r_validation.pdf.gz
9y0r_validation.pdf.gz wwPDB validaton report
wwPDB validaton report 9y0r_full_validation.pdf.gz
9y0r_full_validation.pdf.gz 9y0r_validation.xml.gz
9y0r_validation.xml.gz 9y0r_validation.cif.gz
9y0r_validation.cif.gz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y0/9y0r
https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y0/9y0r ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y0/9y0r
ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y0/9y0r F&H Search
F&H Search Links
Links Assembly
Assembly
 Components
Components

 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P15336
Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P15336 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1
X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1  Sample preparation
Sample preparation SYNCHROTRON / Site:
SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Australian Synchrotron
Australian Synchrotron  / Beamline: MX2 / Wavelength: 0.9537 Å
/ Beamline: MX2 / Wavelength: 0.9537 Å Processing
Processing MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.2→29.62 Å / SU ML: 0.2364 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 21.6707
MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.2→29.62 Å / SU ML: 0.2364 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 21.6707  Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj