[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9viz: Cryo-EM structure of palytoxin-bound Na+,K+-ATPase in the transie... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9viz | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
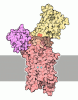
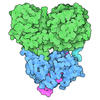
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of palytoxin-bound Na+,K+-ATPase in the transient state of dephosphorylation (E2~P) | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ion pump / P-type ATPase | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of monoatomic ion transport / P-type sodium:potassium-exchanging transporter activity / sodium:potassium-exchanging ATPase complex / sodium ion export across plasma membrane / intracellular sodium ion homeostasis / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / intracellular potassium ion homeostasis / ATPase activator activity / sodium channel regulator activity / monoatomic ion transport ...regulation of monoatomic ion transport / P-type sodium:potassium-exchanging transporter activity / sodium:potassium-exchanging ATPase complex / sodium ion export across plasma membrane / intracellular sodium ion homeostasis / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / intracellular potassium ion homeostasis / ATPase activator activity / sodium channel regulator activity / monoatomic ion transport / proton transmembrane transport / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Squalus acanthias (spiny dogfish) Squalus acanthias (spiny dogfish) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kanai, R. / Vilsen, B. / Cornelius, F. / Toyoshima, C. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 2items Japan, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025Title: How palytoxin transforms the Na,K pump into a cation channel. Authors: Ryuta Kanai / Naoki Tsunekawa / Flemming Cornelius / Bente Vilsen / Chikashi Toyoshima /   Abstract: Palytoxin (PTX), a potent marine toxin, has long been known to transform Na,K-ATPase (NKA), an indispensable ion pump, into a nonselective cation channel. It has been postulated that PTX takes ...Palytoxin (PTX), a potent marine toxin, has long been known to transform Na,K-ATPase (NKA), an indispensable ion pump, into a nonselective cation channel. It has been postulated that PTX takes control of the two gates on either side of a channel-like pore. These gates normally open and close alternately, synchronized with chemical events, never opening simultaneously. A critical question is whether palytoxin takes over the control of the two gates or creates a new pathway. Here, we present structures of NKA with bound palytoxin in three different states. PTX binds to NKA in E2P, occupying the physiological Na exit pathway, similar to istaroxime, a new-generation cardiotonic steroid. Adding Na and ATP/ADP to the NKA·PTX complex induces an open channel traversing the entire membrane alongside the physiological ion pathway. As AlF, a stable transition state analog of phosphate replaces phosphate in the NKA·PTX complex preformed in E2P, the complex appears to undergo the normal reaction cycle from E2P to E1·Na. PTX occupies the space between the transmembrane helices M4 and M6, thereby preventing the closure of the extracellular half of the ion pathway. These structures demonstrate that the architecture of NKA is fundamentally different from "a pore with two gates." Each half of the ion pathway comprises three segments, including a movable component that plays a pivotal role in translocating the bound cations by connecting the constant part to an appropriate inlet. The ion pathway of NKA transforms dynamically, ensuring that the two halves never exist simultaneously. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9viz.cif.gz 9viz.cif.gz | 724.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9viz.ent.gz pdb9viz.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9viz.json.gz 9viz.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vi/9viz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vi/9viz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vi/9viz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vi/9viz | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  65099MC  9viyC  9vj0C  9vj1C  9vj2C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments: Ens-ID: ens_1
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj