+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9p0n | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
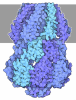
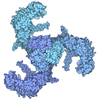
| Title | MscS in Glyco-DIBMA Native Nanodiscs (C7 symmetry) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Small-conductance mechanosensitive channel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / mechanosensitive channel / native nanodisc / polymer / Glyco-DIBMA / cryo-EM / lipid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.99 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Moller, E. / Britt, M. / Zhou, F. / Yang, H. / Anishkin, A. / Ernst, R. / Juan, V.M. / Sukharev, S. / Matthies, D. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025Title: The lipid-mediated mechanism of mechanosensitive channel MscS inactivation. Authors: Elissa Moller / Madolyn Britt / Fei Zhou / Hyojik Yang / Andriy Anishkin / Robert Ernst / Juan M Vanegas / Sergei Sukharev / Doreen Matthies Abstract: Interpretations of experimental conformations of mechanosensitive channels gated by 'force from lipids' become more reliable when native lipids are preserved in the structures. MscS is an adaptive ...Interpretations of experimental conformations of mechanosensitive channels gated by 'force from lipids' become more reliable when native lipids are preserved in the structures. MscS is an adaptive osmolyte release valve that regulates turgor in osmotically stressed cells. MscS promptly opens under abrupt super-threshold tensions in the membrane, but at lower and more gradually applied tensions, it silently inactivates from the closed state. A central question has been whether to assign the commonly observed non-conductive conformation with splayed peripheral helices to a closed or inactivated state. We present a 3-Å MscS cryo-EM structure obtained in Glyco-DIBMA polymers, which avoid complete lipid removal. Within the complex, we observe densities for endogenous phospholipids intercalating between the peripheral and pore-lining helices. The lipidomic analysis shows a 2-3 fold enrichment of phosphatidylglycerol in Glyco-DIBMA-extracted MscS samples. The computed pressure of these lipids on the protein surface enforces the characteristic kinks in the pore-lining helices, sterically stabilizing the separation of the peripheral helices. Mutations of residues coordinating lipids in the crevices eliminate inactivation, allowing us to classify this group of structures as the inactivated state. Our study reveals a novel inactivation mechanism in which intercalated lipids physically decouple the tension-sensing helices from the gate. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9p0n.cif.gz 9p0n.cif.gz | 374.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9p0n.ent.gz pdb9p0n.ent.gz | 314.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9p0n.json.gz 9p0n.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p0/9p0n https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p0/9p0n ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p0/9p0n ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p0/9p0n | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  71088MC  71089 M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 31751.768 Da / Num. of mol.: 7 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Chemical | ChemComp-D21 / ( #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: MscS in Glyco-DIBMA Native Nanodiscs (C7 symmetry) / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.217 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1700 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: ZEMLIN TABLEAU |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 79 K / Temperature (min): 79 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.4 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 20649 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Width: 5760 / Height: 4092 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 3380588 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C7 (7 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.99 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 368753 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 127.8 / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 7OO6 Accession code: 7OO6 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 2.99 Å Stereochemistry target values: REAL-SPACE (WEIGHTED MAP SUM AT ATOM CENTERS) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj