[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9mw8: Cryo-EM structure of ancestral Dicer helicase bound to 27-bp dsRN... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9mw8 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of ancestral Dicer helicase bound to 27-bp dsRNA in post-hydrolysis closed state | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ANTIVIRAL PROTEIN/RNA / RNA helicase / dsRBM / ANTIVIRAL PROTEIN-RNA complex | ||||||
| Function / homology | ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / RNA / RNA (> 10) Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species | synthetic construct (others) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Aderounmu, A.M. / Consalvo, C.D. / Shen, P.S. / Bass, B.L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025Title: Biochemical and structural basis of Dicer helicase function unveiled by resurrecting ancient proteins. Authors: Adedeji M Aderounmu / Josephine Maus-Conn / Claudia D Consalvo / Peter S Shen / Brenda L Bass /  Abstract: A fully functional Dicer helicase, present in the modern arthropod, uses energy from ATP hydrolysis to power translocation on bound dsRNA, enabling the processive dsRNA cleavage required for ...A fully functional Dicer helicase, present in the modern arthropod, uses energy from ATP hydrolysis to power translocation on bound dsRNA, enabling the processive dsRNA cleavage required for efficient antiviral defense. However, modern Dicer orthologs exhibit divergent helicase functions that affect their ability to contribute to antiviral defense. Moreover, mechanisms that couple ATP hydrolysis to Dicer helicase movement on dsRNA remain enigmatic. We used biochemical and structural analyses of ancestrally reconstructed Dicer helicases to map evolution of dsRNA binding affinity, ATP hydrolysis and translocation. Loss of affinity for dsRNA occurred early in Dicer evolution, coinciding with a decline in translocation activity, despite preservation of ATP hydrolysis activity. Ancestral nematode Dicer also exhibited significant decline in ATP hydrolysis and translocation, but studies of antiviral activities in the modern nematode indicate Dicer retained a role in antiviral defense by recruiting a second helicase. Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) analyses of an ancient metazoan Dicer allowed capture of multiple helicase states revealing the mechanism that connects each step of ATP hydrolysis to unidirectional movement along dsRNA. Our study rationalizes the diversity in modern Dicer helicases by connecting ancestral functions to observations in extant enzymes. #1: Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025 Title: Biochemical and structural basis of Dicer helicase function unveiled by resurrecting ancient proteins. Authors: Adedeji M Aderounmu / Josephine Maus-Conn / Claudia D Consalvo / Peter S Shen / Brenda L Bass /  Abstract: A fully functional Dicer helicase, present in the modern arthropod, uses energy generated during ATP hydrolysis to power translocation on bound dsRNA, enabling the processive dsRNA cleavage required ...A fully functional Dicer helicase, present in the modern arthropod, uses energy generated during ATP hydrolysis to power translocation on bound dsRNA, enabling the processive dsRNA cleavage required for efficient antiviral defense. However, modern Dicer orthologs exhibit divergent helicase functions that affect their ability to contribute to antiviral defense, and moreover, mechanisms that couple ATP hydrolysis to Dicer helicase movement on dsRNA remain enigmatic. Here, we used biochemical and structural analyses of ancestrally reconstructed Dicer helicases to map evolution of dsRNA binding affinity, ATP hydrolysis and translocation. We found that loss of affinity for dsRNA occurred early in Dicer evolution, coinciding with a decline in translocation activity, despite preservation of ATP hydrolysis activity, exemplified by the ancient deuterostome Dicer. Ancestral nematode Dicer also exhibited significant decline in ATP hydrolysis and translocation, but studies of antiviral activities in the modern nematode indicate Dicer retained a role in antiviral defense by recruiting a second helicase. Cryo-EM analyses of an ancient metazoan Dicer allowed capture of multiple helicase states revealing the mechanism that connects each step of ATP hydrolysis to unidirectional movement along dsRNA. Overall, our study rationalizes the diversity in modern Dicer helicases by connecting ancestral functions to observations in extant enzymes. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9mw8.cif.gz 9mw8.cif.gz | 155.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9mw8.ent.gz pdb9mw8.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9mw8.json.gz 9mw8.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mw/9mw8 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mw/9mw8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mw/9mw8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mw/9mw8 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  48697MC 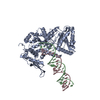 9mw6C  9mw7C  9mx3C  9mx5C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 75480.609 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: RNA chain | Mass: 8572.096 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host: synthetic construct (others) |
| #3: RNA chain | Mass: 8658.198 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host: synthetic construct (others) |
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Ancestral metazoan Dicer helicase in complex 27-bp blunt dsRNA and ATP Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.093 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 315941 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Source name: AlphaFold / Type: in silico model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj

































