[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
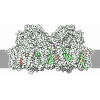
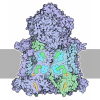
Yorodumi- PDB-9gc2: Cryo-EM structure of Arabidopsis thaliana PSI-LHCI- a603-NH mutant -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9gc2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Arabidopsis thaliana PSI-LHCI- a603-NH mutant | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PHOTOSYNTHESIS / PSI-LHCI / Arabidopsis thaliana / light harvesting / far-red absorption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphotosynthetic NADP+ reduction / photosystem I stabilization / chloroplast photosystem I / response to low light intensity stimulus / chloroplast stromal thylakoid / plastoglobule / chloroplast membrane / response to high light intensity / chloroplast thylakoid / photosynthesis, light harvesting in photosystem I ...photosynthetic NADP+ reduction / photosystem I stabilization / chloroplast photosystem I / response to low light intensity stimulus / chloroplast stromal thylakoid / plastoglobule / chloroplast membrane / response to high light intensity / chloroplast thylakoid / photosynthesis, light harvesting in photosystem I / thylakoid / chloroplast thylakoid lumen / chloroplast envelope / photosystem I reaction center / photosystem I / photosynthetic electron transport in photosystem I / photosystem I / plastid / chlorophyll binding / chloroplast thylakoid membrane / photosynthesis / response to cold / chloroplast / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / calmodulin binding / electron transfer activity / oxidoreductase activity / protein stabilization / protein domain specific binding / mRNA binding / magnesium ion binding / mitochondrion / extracellular region / metal ion binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.29 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Capaldi, S. / Chaves-Sanjuan, A. / Bonnet, D.M.V. / Bassi, R. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: New Phytol / Year: 2025 Journal: New Phytol / Year: 2025Title: Structural determinants for red-shifted absorption in higher-plants Photosystem I. Authors: Stefano Capaldi / Zeno Guardini / Daniele Montepietra / Vittorio Flavio Pagliuca / Antonello Amelii / Elena Betti / Chris John / Laura Pedraza-González / Lorenzo Cupellini / Benedetta ...Authors: Stefano Capaldi / Zeno Guardini / Daniele Montepietra / Vittorio Flavio Pagliuca / Antonello Amelii / Elena Betti / Chris John / Laura Pedraza-González / Lorenzo Cupellini / Benedetta Mennucci / Diane Marie Valerie Bonnet / Antonio Chaves-Sanjuan / Luca Dall'Osto / Roberto Bassi /  Abstract: Higher plants Photosystem I absorbs far-red light, enriched under vegetation canopies, through long-wavelength Chls to enhance photon capture. Far-red absorption originates from Chl pairs within the ...Higher plants Photosystem I absorbs far-red light, enriched under vegetation canopies, through long-wavelength Chls to enhance photon capture. Far-red absorption originates from Chl pairs within the Lhca3 and Lhca4 subunits of the LHCI antenna, known as the 'red cluster', including Chls a603 and a609. We used reverse genetics to produce an Arabidopsis mutant devoid of red-shifted absorption, and we obtained high-resolution cryogenic electron microscopy structures of PSI-LHCI complexes from both wild-type and mutant plants. Computed excitonic coupling values suggested contributions from additional nearby pigment molecules, namely Chl a615 and violaxanthin in the L2 site, to far-red absorption. We investigated the structural determinants of far-red absorption by producing further Arabidopsis transgenic lines and analyzed the spectroscopic effects of mutations targeting these chromophores. The two structures solved were used for quantum mechanics calculations, revealing that excitonic interactions alone cannot explain far-red absorption, while charge transfer states were needed for accurate spectral simulations. Our findings demonstrate that the molecular mechanisms of light-harvesting under shaded conditions rely on very precise tuning of chromophore interactions, whose understanding is crucial for designing light-harvesting complexes with engineered absorption spectra. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9gc2.cif.gz 9gc2.cif.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9gc2.ent.gz pdb9gc2.ent.gz | 781.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9gc2.json.gz 9gc2.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gc/9gc2 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gc/9gc2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gc/9gc2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gc/9gc2 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  51227MC  9gbiC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Chlorophyll a-b binding protein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules 14
| #1: Protein | Mass: 22522.793 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 22298.283 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: N99H Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Photosystem I chlorophyll a/b-binding protein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules 23
| #2: Protein | Mass: 23448.623 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 25258.818 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: N103H Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #5: Protein | Mass: 83180.156 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein | Mass: 82448.695 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules C
| #7: Protein | Mass: 9049.509 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Photosystem I reaction center subunit ... , 10 types, 10 molecules DEFGHIJLKN
| #8: Protein | Mass: 17684.170 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #9: Protein | Mass: 10561.903 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 17319.160 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 11000.299 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 10366.769 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #13: Protein/peptide | Mass: 4137.024 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #14: Protein/peptide | Mass: 5021.978 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #15: Protein | Mass: 17982.693 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #16: Protein | Mass: 8468.770 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #17: Protein | Mass: 9720.043 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Sugars , 2 types, 3 molecules 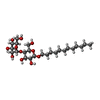

| #23: Sugar | | #28: Sugar | ChemComp-DGD / | |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 9 types, 203 molecules 







| #18: Chemical | ChemComp-CHL / #19: Chemical | ChemComp-CLA / #20: Chemical | ChemComp-LUT / ( #21: Chemical | ChemComp-XAT / ( #22: Chemical | ChemComp-LHG / #24: Chemical | ChemComp-BCR / #25: Chemical | #26: Chemical | #27: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Photosystem I supercomplex (PSI-LHCI), Lhca3/Lhca4 a603-NH mutant Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Entity ID: #1-#17 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R0.6/1 | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 120000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 115589 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.29 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 36596 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 9GBI Accession code: 9GBI / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 69.73 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj