[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9dxr: Ligand-binding and transmembrane domains of kainate receptor GluK... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9dxr | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Ligand-binding and transmembrane domains of kainate receptor GluK2 in complex with positive allosteric modulator BPAM-344 and channel blocker Nephilatoxin-8 | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Glutamate receptor ionotropic, kainate 2 | |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Kainate receptor / GluK2 / Positive allosteric modulator / BPAM344 / Channel blocker / Nephilatoxin-8 | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmossy fiber rosette / detection of cold stimulus involved in thermoception / Activation of Na-permeable kainate receptors / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / kainate selective glutamate receptor complex / regulation of short-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / glutamate receptor activity / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding / negative regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / regulation of JNK cascade ...mossy fiber rosette / detection of cold stimulus involved in thermoception / Activation of Na-permeable kainate receptors / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / kainate selective glutamate receptor complex / regulation of short-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / glutamate receptor activity / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding / negative regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / regulation of JNK cascade / inhibitory postsynaptic potential / receptor clustering / kainate selective glutamate receptor activity / extracellularly glutamate-gated ion channel activity / modulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / ionotropic glutamate receptor complex / positive regulation of synaptic transmission / behavioral fear response / neuronal action potential / glutamate-gated receptor activity / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / dendrite cytoplasm / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse / SNARE binding / PDZ domain binding / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / excitatory postsynaptic potential / regulation of membrane potential / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / postsynaptic density membrane / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / terminal bouton / positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process / presynaptic membrane / neuron apoptotic process / scaffold protein binding / chemical synaptic transmission / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / perikaryon / postsynaptic membrane / postsynaptic density / axon / neuronal cell body / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / synapse / dendrite / glutamatergic synapse / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gangwar, S.P. / Yen, L.Y. / Newton, T.P. / Yelshanskaya, M.V. / Sobolevsky, A.I. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Trapping of spermine, Kukoamine A, and polyamine toxin blockers in GluK2 kainate receptor channels. Authors: Shanti Pal Gangwar / Maria V Yelshanskaya / Muhammed Aktolun / Laura Y Yen / Thomas P Newton / Kristian Strømgaard / Maria G Kurnikova / Alexander I Sobolevsky /   Abstract: Kainate receptors (KARs) are a subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR) channels, a superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels which mediate the majority of excitatory neurotransmission in the ...Kainate receptors (KARs) are a subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR) channels, a superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels which mediate the majority of excitatory neurotransmission in the central nervous system. KARs modulate neuronal circuits and plasticity during development and are implicated in neurological disorders, including epilepsy, depression, schizophrenia, anxiety, and autism. Calcium-permeable KARs undergo ion channel block, but the therapeutic potential of channel blockers remains underdeveloped, mainly due to limited structural knowledge. Here, we present closed-state structures of GluK2 KAR homotetramers in complex with ion channel blockers NpTx-8, PhTx-74, Kukoamine A, and spermine. We find that blockers reside inside the GluK2 ion channel pore, intracellular to the closed M3 helix bundle-crossing gate, with their hydrophobic heads filling the central cavity and positively charged polyamine tails spanning the selectivity filter. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of our structures illuminate interactions responsible for different affinity and binding poses of the blockers. Our structures elucidate the trapping mechanism of KAR channel block and provide a template for designing new blockers that can selectively target calcium-permeable KARs in neuropathologies. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9dxr.cif.gz 9dxr.cif.gz | 375.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9dxr.ent.gz pdb9dxr.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9dxr.json.gz 9dxr.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dx/9dxr https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dx/9dxr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dx/9dxr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dx/9dxr | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  47296MC  9dxqC  9dxsC 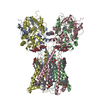 9dxtC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 4 molecules ABCD
| #1: Protein | Mass: 102509.977 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Mutation: I567V,Y571C Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P42260 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P42260 |
|---|
-Sugars , 2 types, 8 molecules
| #2: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #3: Polysaccharide | Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 21 molecules 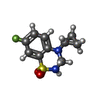


| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-2J9 / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-POV / ( #6: Chemical | ChemComp-A1BDS / | Mass: 572.743 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C29H48N8O4 / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Ligand-binding and transmembrane domains of kainate receptor GluK2 in complex with positive allosteric modulator BPAM-344 and channel blocker Nephilatoxin-8 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.11.1_2575: / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 199303 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj



