+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9bz8 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
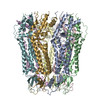
| Title | Pannexin 1 containing C-terminal activating domain | ||||||
 Components Components | Pannexin | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ATP release channel / large-pore / nanodisc / C-terminal activating domain | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of interleukin-1 production / gap junction / monoatomic cation transport / channel activity / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species | |||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Ehrlich, J.J. / Kawate, T. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024Title: The C-terminal activating domain promotes pannexin 1 channel opening. Authors: Erik Henze / Jacqueline J Ehrlich / Janice L Robertson / Eric Gelsleichter / Toshimitsu Kawate /  Abstract: Pannexin 1 (Panx1) constitutes a large pore channel responsible for the release of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from apoptotic cells. Strong evidence indicates that caspase-mediated cleavage of the C- ...Pannexin 1 (Panx1) constitutes a large pore channel responsible for the release of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from apoptotic cells. Strong evidence indicates that caspase-mediated cleavage of the C-terminus promotes the opening of the Panx1 channel by unplugging the pore. However, this simple pore-plugging mechanism alone cannot account for the observation that a Panx1 construct ending before the caspase cleavage site remains closed. Here, we show that a helical region located immediately before the caspase cleavage site, referred to as the "C-terminal activating domain (CAD)", plays a pivotal role in facilitating Panx1 activation. Electrophysiology and mutagenesis studies uncovered that two conserved leucine residues within the CAD play a pivotal role. Cryoelectron microscopy (Cryo-EM) analysis of the construct ending before reaching the CAD demonstrated that the N terminus extends into an intracellular pocket. In contrast, the construct including the CAD revealed that this domain occupies the intracellular pocket, causing the N terminus to flip upward within the pore. Analysis of electrostatic free energy landscape in the closed conformation indicated that the intracellular side of the ion permeation pore may be occupied by anions like ATP, creating an electrostatic barrier for anions attempting to permeate the pore. When the N terminus flips up, it diminishes the positively charged surface, thereby reducing the drive to accumulate anions inside the pore. This dynamic change in the electrostatic landscape likely contributes to the selection of permeant ions. Collectively, these experiments put forth a mechanism in which C-terminal cleavage liberates the CAD, causing the repositioning of the N terminus to promote Panx1 channel opening. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9bz8.cif.gz 9bz8.cif.gz | 444.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9bz8.ent.gz pdb9bz8.ent.gz | 367.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9bz8.json.gz 9bz8.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bz/9bz8 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bz/9bz8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bz/9bz8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bz/9bz8 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  45056MC  9bz7C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42812.848 Da / Num. of mol.: 7 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) Gene: panx1, PANX / Plasmid: pFBNT / Details (production host): Internal strepII tag / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: A0A803JW22 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: A0A803JW22Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: frog pannexin 1 / Type: COMPLEX Details: Engineered frog pannexin 1 containing c-terminal activating domain in lipid nanodiscs Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 43.5 kDa/nm / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism: | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain: BTI-Tn-5B1-4 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain: BTI-Tn-5B1-4 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 Details: Sample was subject to size exclusion chromatography with HEPES/NaCl buffer. | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: frPanx1 in lipid nanodiscs containing POPC, POPG, POPE and cholesterol. Sample eluted in a single peak from size-exclusion and was pooled and concentrated. | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 288.15 K Details: Grid was blotted for 4 seconds with a force of 7 before plunging into liquid ethane. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 20000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 8000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.27 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 Details: 50-frame movies were collected in counted super resolution mode. |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 15 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 10234069 Details: Particles picked with template picker and inspect particle picks was deployed to remove non-protein picks | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C7 (7 fold cyclic) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 31614 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE Details: Reconstructed in RELION using 3D classification and autorefinement Num. of class averages: 8 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6VD7 Accession code: 6VD7 / Details: Complete assembly of PDB entry 6VD7 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj