[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9bs1: Cryo-EM structure of the S. cerevisiae lipid flippase Neo1 bound ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9bs1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
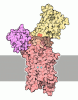
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the S. cerevisiae lipid flippase Neo1 bound with PI4P in the E2P state | |||||||||
 Components Components | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase NEO1 | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIPID TRANSPORT / lipid flippase / P4-ATPase / PI4P / phosphoinositide / neomycin resistance | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationlysophosphatidylserine flippase activity / trans-Golgi network membrane organization / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / phosphatidylserine flippase activity / phosphatidylserine floppase activity / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / vacuole organization / phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity / retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum / P-type phospholipid transporter ...lysophosphatidylserine flippase activity / trans-Golgi network membrane organization / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / phosphatidylserine flippase activity / phosphatidylserine floppase activity / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / vacuole organization / phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity / retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum / P-type phospholipid transporter / phospholipid translocation / trans-Golgi network / endocytosis / late endosome / protein transport / endosome / endosome membrane / Golgi membrane / magnesium ion binding / Golgi apparatus / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.71 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Duan, H.D. / Li, H. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Cell Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Cell Biol / Year: 2025Title: P4-ATPases control phosphoinositide membrane asymmetry and neomycin resistance. Authors: Bhawik K Jain / H Diessel Duan / Christina Valentine / Ariana Samiha / Huilin Li / Todd R Graham /  Abstract: The aminoglycoside antibiotic neomycin has robust antibacterial properties, yet its clinical utility is curtailed by its nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. The mechanism by which the polycationic ...The aminoglycoside antibiotic neomycin has robust antibacterial properties, yet its clinical utility is curtailed by its nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. The mechanism by which the polycationic neomycin enters specific eukaryotic cell types remains poorly understood. In budding yeast, NEO1 is required for neomycin resistance and encodes a phospholipid flippase that establishes membrane asymmetry. Here we show that mutations altering Neo1 substrate recognition cause neomycin hypersensitivity by exposing phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI4P) in the plasma membrane extracellular leaflet. Cryogenic electron microscopy reveals PI4P binding to Neo1 within the substrate translocation pathway. PI4P enters the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum and is flipped by Neo1 at the Golgi to prevent PI4P secretion to the cell surface. Deficiency of the orthologous ATP9A in human cells also causes exposure of PI4P and neomycin sensitivity. These findings unveil conserved mechanisms of aminoglycoside sensitivity and phosphoinositide homoeostasis, with important implications for signalling by extracellular phosphoinositides. #1: Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025 Title: P4-ATPase control over phosphoinositide membrane asymmetry and neomycin resistance. Authors: Bhawik K Jain / H Diessel Duan / Christina Valentine / Ariana Samiha / Huilin Li / Todd R Graham /  Abstract: Neomycin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic, has robust antibacterial properties, yet its clinical utility is curtailed by its nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. The mechanism by which the polycationic ...Neomycin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic, has robust antibacterial properties, yet its clinical utility is curtailed by its nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. The mechanism by which the polycationic neomycin enters specific eukaryotic cell types remains poorly understood. In budding yeast, is required for neomycin resistance and encodes a phospholipid flippase that establishes membrane asymmetry. Here, we show that mutations altering Neo1 substrate recognition cause neomycin hypersensitivity by exposing phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI4P) in the plasma membrane extracellular leaflet. Human cells also expose extracellular PI4P upon knockdown of ATP9A, a Neo1 ortholog and ATP9A expression level correlates to neomycin sensitivity. In yeast, the extracellular PI4P is initially produced in the cytosolic leaflet of the plasma membrane and then delivered by Osh6-dependent nonvesicular transport to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Here, a portion of PI4P escapes degradation by the Sac1 phosphatase by entering the ER lumenal leaflet. COPII vesicles transport lumenal PI4P to the Golgi where Neo1 flips this substrate back to the cytosolic leaflet. Cryo-EM reveals that PI4P binds Neo1 within the substrate translocation pathway. Loss of Neo1 activity in the Golgi allows secretion of extracellular PI4P, which serves as a neomycin receptor and facilitates its endocytic uptake. These findings unveil novel mechanisms of aminoglycoside sensitivity and phosphoinositide homeostasis, with important implications for signaling by extracellular phosphoinositides. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9bs1.cif.gz 9bs1.cif.gz | 191.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9bs1.ent.gz pdb9bs1.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9bs1.json.gz 9bs1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  9bs1_validation.pdf.gz 9bs1_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  9bs1_full_validation.pdf.gz 9bs1_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  9bs1_validation.xml.gz 9bs1_validation.xml.gz | 43.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  9bs1_validation.cif.gz 9bs1_validation.cif.gz | 64.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bs/9bs1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bs/9bs1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bs/9bs1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bs/9bs1 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  44850MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 131360.469 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: NEO1, YIL048W / Production host:  References: UniProt: P40527, P-type phospholipid transporter |
|---|---|
| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-BEF / |
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-A1ARJ / ( Mass: 943.086 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C45H84O16P2 / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Neo1 bound with PI4P / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.13 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1300 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 58 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.71 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 1082029 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj