[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9b7j: Cryo-EM structure of human dynactin complex bound to Chlamydia ef... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9b7j | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
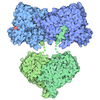
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of human dynactin complex bound to Chlamydia effector Dre1 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / Human dynactin / Chlamydia effector / host-pathogen interaction | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcell cortex region / retrograde axonal transport of mitochondrion / dynactin complex / centriolar subdistal appendage / positive regulation of neuromuscular junction development / centriole-centriole cohesion / F-actin capping protein complex / WASH complex / microtubule anchoring at centrosome / maintenance of synapse structure ...cell cortex region / retrograde axonal transport of mitochondrion / dynactin complex / centriolar subdistal appendage / positive regulation of neuromuscular junction development / centriole-centriole cohesion / F-actin capping protein complex / WASH complex / microtubule anchoring at centrosome / maintenance of synapse structure / ventral spinal cord development / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / Regulation of CDH1 Function / Formation of the polybromo-BAF (pBAF) complex / Formation of the non-canonical BAF (ncBAF) complex / Formation of the canonical BAF (cBAF) complex / Formation of the embryonic stem cell BAF (esBAF) complex / Formation of neuronal progenitor and neuronal BAF (npBAF and nBAF) / cytoskeleton-dependent cytokinesis / microtubule plus-end / sperm head-tail coupling apparatus / nuclear membrane disassembly / bBAF complex / cellular response to cytochalasin B / npBAF complex / XBP1(S) activates chaperone genes / nBAF complex / positive regulation of microtubule nucleation / brahma complex / regulation of transepithelial transport / cell junction assembly / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / Formation of annular gap junctions / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / barbed-end actin filament capping / GBAF complex / Gap junction degradation / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / melanosome transport / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / protein localization to adherens junction / actin polymerization or depolymerization / dense body / Tat protein binding / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / coronary vasculature development / non-motile cilium assembly / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / RHOD GTPase cycle / RSC-type complex / regulation of double-strand break repair / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / regulation of cell morphogenesis / protein localization to centrosome / Adherens junctions interactions / dynein complex / RHOF GTPase cycle / retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / adherens junction assembly / apical protein localization / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / tight junction / microtubule associated complex / SWI/SNF complex / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / lamellipodium assembly / cytoplasmic dynein complex / ventricular septum development / aorta development / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / nuclear migration / spectrin binding / apical junction complex / neuromuscular process / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / neuromuscular junction development / nitric-oxide synthase binding / transporter regulator activity / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / cell leading edge / motor behavior / Recycling pathway of L1 / dynein complex binding / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in pigmentation / cleavage furrow / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / brush border / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.49 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Pawar, K.I. / Verba, K.A. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2025 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2025Title: The Chlamydia effector Dre1 binds dynactin to reposition host organelles during infection. Authors: Jessica Sherry / Komal Ishwar Pawar / Lee Dolat / Erin Smith / I-Chang Chang / Khavong Pha / Robyn Kaake / Danielle L Swaney / Clara Herrera / Eleanor McMahon / Robert J Bastidas / Jeffrey R ...Authors: Jessica Sherry / Komal Ishwar Pawar / Lee Dolat / Erin Smith / I-Chang Chang / Khavong Pha / Robyn Kaake / Danielle L Swaney / Clara Herrera / Eleanor McMahon / Robert J Bastidas / Jeffrey R Johnson / Raphael H Valdivia / Nevan J Krogan / Cherilyn A Elwell / Kliment Verba / Joanne N Engel /  Abstract: The obligate intracellular pathogen Chlamydia trachomatis replicates in a specialized membrane-bound compartment where it repositions host organelles during infection to acquire nutrients and evade ...The obligate intracellular pathogen Chlamydia trachomatis replicates in a specialized membrane-bound compartment where it repositions host organelles during infection to acquire nutrients and evade host surveillance. We describe a bacterial effector, Dre1, that binds specifically to dynactin associated with host microtubule organizing centers without globally impeding dynactin function. Dre1 is required to reposition the centrosome, mitotic spindle, Golgi apparatus, and primary cilia around the inclusion and contributes to pathogen fitness in cell-based and mouse models of infection. We utilized Dre1 to affinity purify the megadalton dynactin protein complex and determined the first cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of human dynactin. Our results suggest that Dre1 binds to the pointed end of dynactin and uncovers the first bacterial effector that modulates dynactin function. Our work highlights how a pathogen employs a single effector to evoke targeted, large-scale changes in host cell organization that facilitate pathogen growth without inhibiting host viability. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9b7j.cif.gz 9b7j.cif.gz | 2.6 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9b7j.ent.gz pdb9b7j.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9b7j.json.gz 9b7j.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b7/9b7j https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b7/9b7j ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b7/9b7j ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b7/9b7j | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  44306MC  9b85C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 10 molecules ABCDEFGIHJ
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42670.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P61163 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P61163#2: Protein | | Mass: 41782.660 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P60709 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P60709#3: Protein | | Mass: 46360.863 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9NZ32 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9NZ32 |
|---|
-Dynactin subunit ... , 9 types, 13 molecules KLMPQpqRrSTUs
| #4: Protein | Mass: 52409.016 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UJW0 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UJW0 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #5: Protein | Mass: 20150.533 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BTE1 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BTE1 | ||||||||||
| #6: Protein | Mass: 20769.002 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O00399 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O00399 | ||||||||||
| #9: Protein | Mass: 44285.891 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q13561 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q13561#10: Protein | Mass: 21145.379 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75935 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75935#11: Protein | | Mass: 141920.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q14203 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q14203#12: Protein | | Mass: 7081.720 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)#13: Protein | | Mass: 7422.140 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)#14: Protein | | Mass: 141892.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q14203 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q14203 |
-F-actin-capping protein subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules NO
| #7: Protein | Mass: 32964.727 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P52907 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P52907 |
|---|---|
| #8: Protein | Mass: 30669.768 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P47756 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P47756 |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 12 molecules 




| #15: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / #16: Chemical | ChemComp-ANP / | #17: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human dynactin complex bound to Chlamydia effector Dre1 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#14 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.1 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 57.7 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.49 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 45091 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj