[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9b40: Pseudomonas phage Pa193 5-fold vertex (capsid, decorating, and sc... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9b40 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Pseudomonas phage Pa193 5-fold vertex (capsid, decorating, and scaffolding proteins) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / phage / bacteriophage / gene product 24 (gp24) / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / gene product 25 (gp25) / scaffolding protein / decorating protein / major capsid protein / gene product 26 (gp26) | ||||||
| Function / homology | Uncharacterised conserved protein UCP029215 / Uncharacterized protein conserved in bacteria (DUF2213) / : / Structural cement protein (E217 gp24/Pam3 gp6) / Virion protein / Capsid and scaffold protein / Capsid and scaffold protein Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  Pseudomonas virus Pa193 Pseudomonas virus Pa193 | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Iglesias, S.M. / Cingolani, G. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM analysis of Pseudomonas phage Pa193 structural components. Authors: Stephano M Iglesias / Chun-Feng David Hou / Johnny Reid / Evan Schauer / Renae Geier / Angela Soriaga / Lucy Sim / Lucy Gao / Julian Whitelegge / Pierre Kyme / Deborah Birx / Sebastien Lemire / Gino Cingolani /  Abstract: The World Health Organization has designated Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a critical pathogen for the development of new antimicrobials. Bacterial viruses, or bacteriophages, have been used in various ...The World Health Organization has designated Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a critical pathogen for the development of new antimicrobials. Bacterial viruses, or bacteriophages, have been used in various clinical settings, commonly called phage therapy, to address this growing public health crisis. Here, we describe a high-resolution structural atlas of a therapeutic, contractile-tailed Pseudomonas phage, Pa193. We used bioinformatics, proteomics, and cryogenic electron microscopy single particle analysis to identify, annotate, and build atomic models for 21 distinct structural polypeptide chains forming the icosahedral capsid, neck, contractile tail, and baseplate. We identified a putative scaffolding protein stabilizing the interior of the capsid 5-fold vertex. We also visualized a large portion of Pa193 ~ 500 Å long tail fibers and resolved the interface between the baseplate and tail fibers. The work presented here provides a framework to support a better understanding of phages as biomedicines for phage therapy and inform engineering opportunities. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9b40.cif.gz 9b40.cif.gz | 818.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9b40.ent.gz pdb9b40.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9b40.json.gz 9b40.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b4/9b40 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b4/9b40 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b4/9b40 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b4/9b40 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  44163MC  9b41C 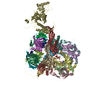 9b42C  9b45C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 41610.918 Da / Num. of mol.: 11 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Pseudomonas virus Pa193 / References: UniProt: A0A5P1KVB7 Pseudomonas virus Pa193 / References: UniProt: A0A5P1KVB7#2: Protein | Mass: 21677.443 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Pseudomonas virus Pa193 / References: UniProt: A0A5P1KV95 Pseudomonas virus Pa193 / References: UniProt: A0A5P1KV95#3: Protein | Mass: 51908.012 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Pseudomonas virus Pa193 / References: UniProt: A0A5Q5ANU8 Pseudomonas virus Pa193 / References: UniProt: A0A5Q5ANU8Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Pseudomonas virus Pa193 / Type: VIRUS / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Pseudomonas virus Pa193 Pseudomonas virus Pa193 |
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: NO / Isolate: OTHER / Type: VIRION |
| Natural host | Organism: Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: OTHER / Nominal magnification: 64000 X / Calibrated magnification: 64000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1750 nm / Nominal defocus min: 750 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 750 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 1750 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 34.4 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 12520 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 46075 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C5 (5 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 8278 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj