[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
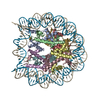
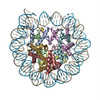
Yorodumi- PDB-9b3p: The cryo-EM structure of the H2A.Z-H3.3 double-variant nucleosome -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9b3p | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The cryo-EM structure of the H2A.Z-H3.3 double-variant nucleosome | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN/DNA / histone variant / nucleosome / chromatin / complex / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of chromosome condensation / Barr body / regulation of centromere complex assembly / pericentric heterochromatin formation / inner kinetochore / muscle cell differentiation / oocyte maturation / nucleus organization / spermatid development / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation ...negative regulation of chromosome condensation / Barr body / regulation of centromere complex assembly / pericentric heterochromatin formation / inner kinetochore / muscle cell differentiation / oocyte maturation / nucleus organization / spermatid development / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / single fertilization / RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / heterochromatin / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / nucleosomal DNA binding / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / telomere organization / embryo implantation / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Defective pyroptosis / cellular response to estradiol stimulus / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / euchromatin / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / multicellular organism growth / heterochromatin formation / Meiotic recombination / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / cellular response to insulin stimulus / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / osteoblast differentiation / male gonad development / structural constituent of chromatin / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / chromatin organization / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / positive regulation of cell growth / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / cell population proliferation / chromosome, telomeric region / protein heterodimerization activity / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / Amyloid fiber formation / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / DNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Tan, D. / Sokolova, V. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Epigenomes / Year: 2024 Journal: Epigenomes / Year: 2024Title: Structural and Biochemical Characterization of the Nucleosome Containing Variants H3.3 and H2A.Z. Authors: Harry Jung / Vladyslava Sokolova / Gahyun Lee / Victoria Rose Stevens / Dongyan Tan /  Abstract: Variant H3.3, along with H2A.Z, is notably enriched at promoter regions and is commonly associated with transcriptional activation. However, the specific molecular mechanisms through which H3.3 ...Variant H3.3, along with H2A.Z, is notably enriched at promoter regions and is commonly associated with transcriptional activation. However, the specific molecular mechanisms through which H3.3 influences chromatin dynamics at transcription start sites, and its role in gene regulation, remain elusive. Using a combination of biochemistry and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), we show that the inclusion of H3.3 alone does not induce discernible changes in nucleosome DNA dynamics. Conversely, the presence of both H3.3 and H2A.Z enhances DNA's flexibility similarly to H2A.Z alone. Interestingly, our findings suggest that the presence of H3.3 in the H2A.Z nucleosome provides slightly increased protection to DNA at internal sites within the nucleosome. These results imply that while H2A.Z at active promoters promotes the formation of more accessible nucleosomes with increased DNA accessibility to facilitate transcription, the simultaneous presence of H3.3 offers an additional mechanism to fine-tune nucleosome accessibility and the chromatin environment. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9b3p.cif.gz 9b3p.cif.gz | 255.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9b3p.ent.gz pdb9b3p.ent.gz | 196.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9b3p.json.gz 9b3p.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  9b3p_validation.pdf.gz 9b3p_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  9b3p_full_validation.pdf.gz 9b3p_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  9b3p_validation.xml.gz 9b3p_validation.xml.gz | 34.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  9b3p_validation.cif.gz 9b3p_validation.cif.gz | 51.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b3/9b3p https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b3/9b3p ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b3/9b3p ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b3/9b3p | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  44148MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 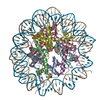
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 4 types, 8 molecules AEBFCGDH
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15360.983 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H3-3A, H3.3A, H3F3, H3F3A, PP781, H3-3B, H3.3B, H3F3B / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H3-3A, H3.3A, H3F3, H3F3A, PP781, H3-3B, H3.3B, H3F3B / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #3: Protein | Mass: 13581.796 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #4: Protein | Mass: 13965.265 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 45604.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 51269.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: nucleosome containing histone variants H3.3 and H2A.Z / Type: COMPLEX Details: The complex contains Xenopus histone H2B and H4, human H3.3, and mouse H2A.Z Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.288 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 / Details: 20mM Tris-HCl, 5mM NaCl |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.8 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K Details: Freezing condition: blot force 0, blot time 4.5 second |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Calibrated magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2250 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 / Num. of real images: 5140 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 10 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1291847 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 205792 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 87.42 / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL / Details: Phenix real-space refinement was used. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj