+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9avj | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
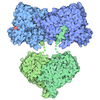
| Title | PS3 F1 ATPase Wild type | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ATPase / electron transfer / ATP hydrolysis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.72 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sobti, M. / Stewart, A.G. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1items Australia, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg / Year: 2025 Journal: Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg / Year: 2025Title: The molecular structure of an axle-less F-ATPase. Authors: Emily J Furlong / Ian-Blaine P Reininger-Chatzigiannakis / Yi C Zeng / Simon H J Brown / Meghna Sobti / Alastair G Stewart /  Abstract: FF ATP synthase is a molecular rotary motor that can generate ATP using a transmembrane proton motive force. Isolated F-ATPase catalytic cores can hydrolyse ATP, passing through a series of ...FF ATP synthase is a molecular rotary motor that can generate ATP using a transmembrane proton motive force. Isolated F-ATPase catalytic cores can hydrolyse ATP, passing through a series of conformational states involving rotation of the central γ rotor subunit and the opening and closing of the catalytic β subunits. Cooperativity in F-ATPase has long thought to be conferred through the γ subunit, with three key interaction sites between the γ and β subunits being identified. Single molecule studies have demonstrated that the F complexes lacking the γ axle still "rotate" and hydrolyse ATP, but with less efficiency. We solved the cryogenic electron microscopy structure of an axle-less Bacillus sp. PS3 F-ATPase. The unexpected binding-dwell conformation of the structure in combination with the observed lack of interactions between the axle-less γ and the open β subunit suggests that the complete γ subunit is important for coordinating efficient ATP binding of F-ATPase. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9avj.cif.gz 9avj.cif.gz | 522.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9avj.ent.gz pdb9avj.ent.gz | 418.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9avj.json.gz 9avj.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/av/9avj https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/av/9avj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/av/9avj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/av/9avj | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  43903MC 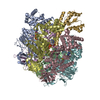 8u1hC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase subunit ... , 6 types, 6 molecules ABCDEF
| #1: Protein | Mass: 51689.055 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: A0A0M3VGF9, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 51788.184 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: A0A0M3VGF9, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 51875.262 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: A0A0M3VGF9, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 51552.531 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: A0A0M4U1P9, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 51584.598 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: A0A0M4U1P9, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 51669.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: A0A0M4U1P9, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase |
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules G
| #7: Protein | Mass: 31547.225 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 10 molecules 


| #8: Chemical | ChemComp-ANP / #9: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: PS3 F1 ATPase Wild type / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#7 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.72 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 153828 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj