[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8vr9: Structure of a synthetic antibody in complex with a class I MHC p... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8vr9 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of a synthetic antibody in complex with a class I MHC presenting a hapten-peptide conjugate | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / Complex / Synthetic antibody / MHC class I / covalently modified peptide | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of memory T cell activation / T cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target / TAP complex binding / positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation / CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation / Golgi medial cisterna / response to mineralocorticoid / positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation / GMP binding / forebrain astrocyte development ...positive regulation of memory T cell activation / T cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target / TAP complex binding / positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation / CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation / Golgi medial cisterna / response to mineralocorticoid / positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation / GMP binding / forebrain astrocyte development / LRR domain binding / regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic / negative regulation of epithelial cell differentiation / CD8 receptor binding / response to isolation stress / antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I / response to gravity / epithelial tube branching involved in lung morphogenesis / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I via ER pathway, TAP-dependent / beta-2-microglobulin binding / type I pneumocyte differentiation / endoplasmic reticulum exit site / Rac protein signal transduction / TAP binding / protection from natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / Signaling by RAS GAP mutants / Signaling by RAS GTPase mutants / Activation of RAS in B cells / positive regulation of Rac protein signal transduction / myoblast proliferation / RAS signaling downstream of NF1 loss-of-function variants / RUNX3 regulates p14-ARF / positive regulation of glial cell proliferation / skeletal muscle cell differentiation / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class Ib / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I via ER pathway, TAP-independent / SOS-mediated signalling / Activated NTRK3 signals through RAS / Activated NTRK2 signals through RAS / SHC1 events in ERBB4 signaling / cardiac muscle cell proliferation / Signalling to RAS / detection of bacterium / SHC-related events triggered by IGF1R / Activated NTRK2 signals through FRS2 and FRS3 / Estrogen-stimulated signaling through PRKCZ / SHC-mediated cascade:FGFR3 / glial cell proliferation / MET activates RAS signaling / T cell receptor binding / SHC-mediated cascade:FGFR2 / SHC-mediated cascade:FGFR4 / Signaling by PDGFRA transmembrane, juxtamembrane and kinase domain mutants / Signaling by PDGFRA extracellular domain mutants / PTK6 Regulates RHO GTPases, RAS GTPase and MAP kinases / Erythropoietin activates RAS / SHC-mediated cascade:FGFR1 / Signaling by FGFR4 in disease / Signaling by CSF3 (G-CSF) / FRS-mediated FGFR3 signaling / Signaling by FLT3 ITD and TKD mutants / FRS-mediated FGFR2 signaling / FRS-mediated FGFR4 signaling / p38MAPK events / FRS-mediated FGFR1 signaling / Signaling by FGFR3 in disease / protein-membrane adaptor activity / striated muscle cell differentiation / Tie2 Signaling / Signaling by FGFR2 in disease / GRB2 events in EGFR signaling / Signaling by FLT3 fusion proteins / SHC1 events in EGFR signaling / FLT3 Signaling / Signaling by FGFR1 in disease / EGFR Transactivation by Gastrin / NCAM signaling for neurite out-growth / CD209 (DC-SIGN) signaling / homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue / GRB2 events in ERBB2 signaling / Downstream signal transduction / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / SHC1 events in ERBB2 signaling / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / response to glucocorticoid / Constitutive Signaling by Overexpressed ERBB2 / Signaling by phosphorylated juxtamembrane, extracellular and kinase domain KIT mutants / early endosome lumen / Nef mediated downregulation of MHC class I complex cell surface expression / DAP12 interactions / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / small monomeric GTPase / Endosomal/Vacuolar pathway / FCERI mediated MAPK activation / Antigen Presentation: Folding, assembly and peptide loading of class I MHC / negative regulation of iron ion transport / lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane / T cell mediated cytotoxicity / cellular response to iron(III) ion / negative regulation of forebrain neuron differentiation Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.06 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Maso, L. / Bang, I. / Koide, S. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024Title: Molecular basis for antibody recognition of multiple drug-peptide/MHC complexes. Authors: Lorenzo Maso / Epsa Rajak / Injin Bang / Akiko Koide / Takamitsu Hattori / Benjamin G Neel / Shohei Koide /  Abstract: The HapImmune platform exploits covalent inhibitors as haptens for creating major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-presented tumor-specific neoantigens by design, combining targeted therapies with ...The HapImmune platform exploits covalent inhibitors as haptens for creating major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-presented tumor-specific neoantigens by design, combining targeted therapies with immunotherapy for the treatment of drug-resistant cancers. A HapImmune antibody, R023, recognizes multiple sotorasib-conjugated KRAS(G12C) peptides presented by different human leukocyte antigens (HLAs). This high specificity to sotorasib, coupled with broad HLA-binding capability, enables such antibodies, when reformatted as T cell engagers, to potently and selectively kill sotorasib-resistant KRAS(G12C) cancer cells expressing different HLAs upon sotorasib treatment. The loosening of HLA restriction could increase the patient population that can benefit from this therapeutic approach. To understand the molecular basis for its unconventional binding capability, we used single-particle cryogenic electron microscopy to determine the structures of R023 bound to multiple sotorasib-peptide conjugates presented by different HLAs. R023 forms a pocket for sotorasib between the V and V domains, binds HLAs in an unconventional, angled way, with V making most contacts with them, and makes few contacts with the peptide moieties. This binding mode enables the antibody to accommodate different hapten-peptide conjugates and to adjust its conformation to different HLAs presenting hapten-peptides. Deep mutational scanning validated the structures and revealed distinct levels of mutation tolerance by sotorasib- and HLA-binding residues. Together, our structural information and sequence landscape analysis reveal key features for achieving MHC-restricted recognition of multiple hapten-peptide antigens, which will inform the development of next-generation therapeutic antibodies. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8vr9.cif.gz 8vr9.cif.gz | 125.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8vr9.ent.gz pdb8vr9.ent.gz | 92.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8vr9.json.gz 8vr9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vr/8vr9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vr/8vr9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vr/8vr9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vr/8vr9 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  43478MC  8vraC  8vrbC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 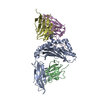
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 32047.309 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: extracellular domain Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HLA-A, HLAA / Plasmid: pET28 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HLA-A, HLAA / Plasmid: pET28 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 11892.291 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: B2M, CDABP0092, HDCMA22P / Plasmid: pHFT2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: B2M, CDABP0092, HDCMA22P / Plasmid: pHFT2 / Production host:  |
-Antibody , 2 types, 2 molecules DE
| #4: Antibody | Mass: 23518.178 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #5: Antibody | Mass: 24034.822 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
-Protein/peptide / Non-polymers , 2 types, 2 molecules C

| #3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 789.963 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: residues 8-16 / Mutation: G12C / Source method: obtained synthetically / Details: Cys12 conjugated to covalent inhibitor sotorasib / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P01116 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P01116 |
|---|---|
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-MOV / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.0927 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R0.6/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 900 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2 sec. / Electron dose: 57.72 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.06 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 178888 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj






















