[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8umu: Atomic model of the human CTF18-RFC-PCNA binary complex in the fo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8umu | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Atomic model of the human CTF18-RFC-PCNA binary complex in the four-subunit binding state (state 3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | REPLICATION/DNA / DNA clamp loader complex / REPLICATION-DNA complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationElg1 RFC-like complex / DNA replication factor C complex / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / positive regulation of deoxyribonuclease activity / dinucleotide insertion or deletion binding / PCNA-p21 complex / mitotic telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / purine-specific mismatch base pair DNA N-glycosylase activity / DNA clamp loader activity / nuclear lamina ...Elg1 RFC-like complex / DNA replication factor C complex / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / positive regulation of deoxyribonuclease activity / dinucleotide insertion or deletion binding / PCNA-p21 complex / mitotic telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / purine-specific mismatch base pair DNA N-glycosylase activity / DNA clamp loader activity / nuclear lamina / Polymerase switching / positive regulation of DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / MutLalpha complex binding / PCNA complex / Telomere C-strand (Lagging Strand) Synthesis / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH3 (MutSbeta) / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH6 (MutSalpha) / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by DREAM complex / Polymerase switching on the C-strand of the telomere / replisome / Processive synthesis on the C-strand of the telomere / response to L-glutamate / Removal of the Flap Intermediate from the C-strand / response to dexamethasone / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication / histone acetyltransferase binding / DNA synthesis involved in DNA repair / DNA polymerase processivity factor activity / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / leading strand elongation / G1/S-Specific Transcription / nuclear replication fork / replication fork processing / SUMOylation of DNA replication proteins / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / PCNA-Dependent Long Patch Base Excision Repair / response to cadmium ion / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / estrous cycle / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / mismatch repair / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / translesion synthesis / base-excision repair, gap-filling / DNA polymerase binding / epithelial cell differentiation / liver regeneration / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G2 Cell Cycle Arrest / positive regulation of DNA replication / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / positive regulation of DNA repair / replication fork / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / male germ cell nucleus / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / receptor tyrosine kinase binding / DNA-templated DNA replication / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / Dual Incision in GG-NER / cellular response to hydrogen peroxide / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / cellular response to UV / response to estradiol / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / heart development / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / damaged DNA binding / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / nuclear body / DNA repair / chromatin binding / centrosome / chromatin / protein-containing complex binding / enzyme binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / membrane / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.16 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, F. / He, Q. / Li, H. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM reveals a nearly complete PCNA loading process and unique features of the human alternative clamp loader CTF18-RFC. Authors: Qing He / Feng Wang / Michael E O'Donnell / Huilin Li /  Abstract: The DNA sliding clamp PCNA is a multipurpose platform for DNA polymerases and many other proteins involved in DNA metabolism. The topologically closed PCNA ring needs to be cracked open and loaded ...The DNA sliding clamp PCNA is a multipurpose platform for DNA polymerases and many other proteins involved in DNA metabolism. The topologically closed PCNA ring needs to be cracked open and loaded onto DNA by a clamp loader, e.g., the well-studied pentameric ATPase complex RFC (RFC1-5). The CTF18-RFC complex is an alternative clamp loader found recently to bind the leading strand DNA polymerase ε and load PCNA onto leading strand DNA, but its structure and the loading mechanism have been unknown. By cryo-EM analysis of in vitro assembled human CTF18-RFC-DNA-PCNA complex, we have captured seven loading intermediates, revealing a detailed PCNA loading mechanism onto a 3'-ss/dsDNA junction by CTF18-RFC. Interestingly, the alternative loader has evolved a highly mobile CTF18 AAA+ module likely to lower the loading activity, perhaps to avoid competition with the RFC and to limit its role to leading strand clamp loading. To compensate for the lost stability due to the mobile AAA+ module, CTF18 has evolved a unique β-hairpin motif that reaches across RFC2 to interact with RFC5, thereby stabilizing the pentameric complex. Further, we found that CTF18 also contains a separation pin to locally melt DNA from the 3'-end of the primer; this ensures its ability to load PCNA to any 3'-ss/dsDNA junction, facilitated by the binding energy of the E-plug to the major groove. Our study reveals unique structural features of the human CTF18-RFC and contributes to a broader understanding of PCNA loading by the alternative clamp loaders. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8umu.cif.gz 8umu.cif.gz | 527 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8umu.ent.gz pdb8umu.ent.gz | 415.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8umu.json.gz 8umu.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/um/8umu https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/um/8umu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/um/8umu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/um/8umu | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  42384MC  8umtC  8umvC  8umwC  8umyC  8un0C  8unjC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 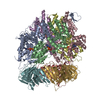
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 4 molecules AFGH
| #1: Protein | Mass: 108520.977 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CHTF18 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CHTF18Production host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: Q8WVB6 |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein | Mass: 28795.752 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PCNA Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PCNAProduction host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: P12004 |
-Replication factor C subunit ... , 4 types, 4 molecules BCDE
| #2: Protein | Mass: 39203.207 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC2 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC2Production host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: P35250 |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 38545.512 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC5 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC5Production host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: P40937 |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 39735.711 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC4 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC4Production host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: P35249 |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 40614.332 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC3 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC3Production host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: P40938 |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 7 molecules 




| #7: Chemical | | #8: Chemical | #9: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: the human clamp-clamp loader complex PCNA-CTF18 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#6 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.3 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 280 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.16 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 183349 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 123 / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj





















