[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
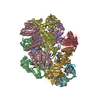
Yorodumi- PDB-8uh7: Structure of T4 Bacteriophage clamp loader bound to the T4 clamp,... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8uh7 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of T4 Bacteriophage clamp loader bound to the T4 clamp, primer-template DNA, and ATP analog | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | REPLICATION/DNA / Clamp loader / T4 / AAA+ATPase / REPLICATION / REPLICATION-DNA complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDNA clamp loader activity / bidirectional double-stranded viral DNA replication / viral DNA genome replication / DNA polymerase processivity factor activity / viral transcription / DNA-templated DNA replication / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / DNA replication / DNA repair / ATP hydrolysis activity ...DNA clamp loader activity / bidirectional double-stranded viral DNA replication / viral DNA genome replication / DNA polymerase processivity factor activity / viral transcription / DNA-templated DNA replication / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / DNA replication / DNA repair / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Tequatrovirus Tequatrovirus | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  FOURIER SYNTHESIS / Resolution: 2.628 Å FOURIER SYNTHESIS / Resolution: 2.628 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Gee, C.L. / Marcus, K. / Kelch, B.A. / Makino, D.L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: Autoinhibition of a clamp-loader ATPase revealed by deep mutagenesis and cryo-EM. Authors: Kendra Marcus / Yongjian Huang / Subu Subramanian / Christine L Gee / Kent Gorday / Sam Ghaffari-Kashani / Xiao Ran Luo / Lisa Zheng / Michael O'Donnell / Sriram Subramaniam / John Kuriyan /   Abstract: Clamp loaders are AAA+ ATPases that facilitate high-speed DNA replication. In eukaryotic and bacteriophage clamp loaders, ATP hydrolysis requires interactions between aspartate residues in one ...Clamp loaders are AAA+ ATPases that facilitate high-speed DNA replication. In eukaryotic and bacteriophage clamp loaders, ATP hydrolysis requires interactions between aspartate residues in one protomer, present in conserved 'DEAD-box' motifs, and arginine residues in adjacent protomers. We show that functional defects resulting from a DEAD-box mutation in the T4 bacteriophage clamp loader can be compensated by widely distributed single mutations in the ATPase domain. Using cryo-EM, we discovered an unsuspected inactive conformation of the clamp loader, in which DNA binding is blocked and the catalytic sites are disassembled. Mutations that restore function map to regions of conformational change upon activation, suggesting that these mutations may increase DNA affinity by altering the energetic balance between inactive and active states. Our results show that there are extensive opportunities for evolution to improve catalytic efficiency when an inactive intermediate is involved. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8uh7.cif.gz 8uh7.cif.gz | 453.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8uh7.ent.gz pdb8uh7.ent.gz | 363.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8uh7.json.gz 8uh7.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uh/8uh7 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uh/8uh7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uh/8uh7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uh/8uh7 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8uk9C  8unfC  8unhC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
-Sliding-clamp-loader ... , 2 types, 5 molecules ABCDE
| #1: Protein | Mass: 21391.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Tequatrovirus / Gene: 62 / Production host: Tequatrovirus / Gene: 62 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 36189.602 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Tequatrovirus / Gene: 44 / Production host: Tequatrovirus / Gene: 44 / Production host:  |
-Protein , 1 types, 3 molecules FGH
| #3: Protein | Mass: 25162.592 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Tequatrovirus / Gene: 45 / Production host: Tequatrovirus / Gene: 45 / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #4: DNA chain | Mass: 9172.891 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Tequatrovirus Tequatrovirus |
|---|---|
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 6136.008 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Tequatrovirus Tequatrovirus |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 42 molecules 






| #6: Chemical | | #7: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #8: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | #9: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.8 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 56.11 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 295 K / Method: vapor diffusion / pH: 7.5 / Details: 20% PEG4k, 0.1M Tris pH7.5, 10mM MgCl2, 20mM NaCl |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  ALS ALS  / Beamline: 8.2.2 / Wavelength: 0.9739 Å / Beamline: 8.2.2 / Wavelength: 0.9739 Å |
| Detector | Type: ADSC QUANTUM 315 / Detector: CCD / Date: Nov 25, 2008 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.9739 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.628→49.649 Å / Num. obs: 55509 / % possible obs: 92.9 % / Redundancy: 6.3 % / CC1/2: 0.978 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.325 / Rpim(I) all: 0.141 / Rrim(I) all: 0.355 / Net I/σ(I): 6.9 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.628→2.922 Å / Num. unique obs: 2775 / CC1/2: 0.306 / Rpim(I) all: 0.865 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  FOURIER SYNTHESIS / Resolution: 2.628→49.649 Å / SU ML: 0.34 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.36 / Phase error: 25.79 / Stereochemistry target values: ML FOURIER SYNTHESIS / Resolution: 2.628→49.649 Å / SU ML: 0.34 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.36 / Phase error: 25.79 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.628→49.649 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj









































