[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
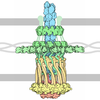
Yorodumi- PDB-8tuw: Type IV pilus from Pseudomonas PAO1 strain with PP7 Maturation protein -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8tuw | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Type IV pilus from Pseudomonas PAO1 strain with PP7 Maturation protein | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Type IV pilus / T4P / PAO1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationvirion attachment to host cell pilus / type IV pilus / single-species biofilm formation on inanimate substrate / type IV pilus-dependent motility / cell adhesion involved in single-species biofilm formation / pilus / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / virion component / host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane / cell surface ...virion attachment to host cell pilus / type IV pilus / single-species biofilm formation on inanimate substrate / type IV pilus-dependent motility / cell adhesion involved in single-species biofilm formation / pilus / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / virion component / host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane / cell surface / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas phage PP7 (virus) Pseudomonas phage PP7 (virus) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.9 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Thongchol, J. / Zhang, J. / Zeng, L. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 7items United States, 7items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2024 Journal: Science / Year: 2024Title: Removal of type IV pili by a small RNA virus. Authors: Jirapat Thongchol / Zihao Yu / Laith Harb / Yiruo Lin / Matthias Koch / Matthew Theodore / Utkarsh Narsaria / Joshua Shaevitz / Zemer Gitai / Yinghao Wu / Junjie Zhang / Lanying Zeng /  Abstract: The retractile type IV pilus (T4P) is important for virulence of the opportunistic human pathogen . The single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) phage PP7 binds to T4P and is brought to the cell surface through ...The retractile type IV pilus (T4P) is important for virulence of the opportunistic human pathogen . The single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) phage PP7 binds to T4P and is brought to the cell surface through pilus retraction. Using fluorescence microscopy, we discovered that PP7 detaches T4P, which impairs cell motility and restricts the pathogen's virulence. Using cryo-electron microscopy, mutagenesis, optical trapping, and Langevin dynamics simulation, we resolved the structure of PP7, T4P, and the PP7/T4P complex and showed that T4P detachment is driven by the affinity between the phage maturation protein and its bound pilin, plus the pilus retraction force and speed, and pilus bending. Pilus detachment may be widespread among other ssRNA phages and their retractile pilus systems and offers new prospects for antibacterial prophylaxis and therapeutics. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8tuw.cif.gz 8tuw.cif.gz | 828.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8tuw.ent.gz pdb8tuw.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8tuw.json.gz 8tuw.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tu/8tuw https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tu/8tuw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tu/8tuw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tu/8tuw | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41633MC  8tumC  8tuxC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 50763.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Pseudomonas phage PP7 (virus) / References: UniProt: Q38061 Pseudomonas phage PP7 (virus) / References: UniProt: Q38061 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 14878.889 Da / Num. of mol.: 16 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) / Gene: pilA, fimA, PA4525 / Production host: Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) / Gene: pilA, fimA, PA4525 / Production host:  Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: P04739 Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: P04739Has protein modification | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Type IV twitching pilus / Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.24 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 Details: 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 8 mM Na2HPO4, and 2 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.4 |
| Buffer component | Conc.: 1 x / Name: PBS |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 80 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50.85 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 5085 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: cryoSPARC / Category: 3D reconstruction |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE |
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 25763 |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 7.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 40493 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj