[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8trn: Actin 1 from T. gondii in filaments bound to MgADP and jasplakinolide -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8trn | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Actin 1 from T. gondii in filaments bound to MgADP and jasplakinolide | |||||||||
 Components Components | Actin | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Actin / cytoskeleton / toxoplasmosis | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationHydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / cytoskeleton / hydrolase activity / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hvorecny, K.L. / Sladewski, T.E. / Heaslip, A.T. / Kollman, J.M. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Toxoplasma gondii actin filaments are tuned for rapid disassembly and turnover. Authors: Kelli L Hvorecny / Thomas E Sladewski / Enrique M De La Cruz / Justin M Kollman / Aoife T Heaslip /  Abstract: The cytoskeletal protein actin plays a critical role in the pathogenicity of the intracellular parasite, Toxoplasma gondii, mediating invasion and egress, cargo transport, and organelle inheritance. ...The cytoskeletal protein actin plays a critical role in the pathogenicity of the intracellular parasite, Toxoplasma gondii, mediating invasion and egress, cargo transport, and organelle inheritance. Advances in live cell imaging have revealed extensive filamentous actin networks in the Apicomplexan parasite, but there are conflicting data regarding the biochemical and biophysical properties of Toxoplasma actin. Here, we imaged the in vitro assembly of individual Toxoplasma actin filaments in real time, showing that native, unstabilized filaments grow tens of microns in length. Unlike skeletal muscle actin, Toxoplasma filaments intrinsically undergo rapid treadmilling due to a high critical concentration, fast monomer dissociation, and rapid nucleotide exchange. Cryo-EM structures of jasplakinolide-stabilized and native (i.e. unstabilized) filaments show an architecture like skeletal actin, with differences in assembly contacts in the D-loop that explain the dynamic nature of the filament, likely a conserved feature of Apicomplexan actin. This work demonstrates that evolutionary changes at assembly interfaces can tune the dynamic properties of actin filaments without disrupting their conserved structure. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8trn.cif.gz 8trn.cif.gz | 221.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8trn.ent.gz pdb8trn.ent.gz | 178.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8trn.json.gz 8trn.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tr/8trn https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tr/8trn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tr/8trn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tr/8trn | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41584MC  8trmC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 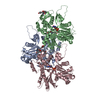
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 41956.711 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: P53476, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement #2: Chemical | #3: Chemical | #4: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Filament of Actin 1 from T. gondii with MgADP and jasplakinolide Type: COMPLEX Details: Actin protomers from T. gondii assemble into a two-start helix, stabilized by jasplakinolide Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 45000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 750 nm |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 5 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: -167 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 28.1 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 2682453 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj








