+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 8tj2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
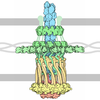
| タイトル | CryoEM structure of Myxococcus xanthus type IV pilus | ||||||
 要素 要素 | Type IV major pilin protein PilA | ||||||
 キーワード キーワード | CELL ADHESION / filament / helical reconstruction / CryoEM | ||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報 | ||||||
| 生物種 |  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (バクテリア) Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (バクテリア) | ||||||
| 手法 | 電子顕微鏡法 / らせん対称体再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 3 Å | ||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Zheng, W. / Egelman, E.H. | ||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 1件 米国, 1件
| ||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年: 2024 ジャーナル: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年: 2024タイトル: Tight-packing of large pilin subunits provides distinct structural and mechanical properties for the type IVa pilus. 著者: Anke Treuner-Lange / Weili Zheng / Albertus Viljoen / Steffi Lindow / Marco Herfurth / Yves F Dufrêne / Lotte Søgaard-Andersen / Edward H Egelman /    要旨: Type IVa pili (T4aP) are ubiquitous cell surface filaments important for surface motility, adhesion to surfaces, DNA uptake, biofilm formation, and virulence. T4aP are built from thousands of copies ...Type IVa pili (T4aP) are ubiquitous cell surface filaments important for surface motility, adhesion to surfaces, DNA uptake, biofilm formation, and virulence. T4aP are built from thousands of copies of the major pilin subunit and tipped by a complex composed of minor pilins and in some systems also the PilY1 adhesin. While major pilins of structurally characterized T4aP have lengths of <165 residues, the major pilin PilA of is unusually large with 208 residues. All major pilins have a conserved N-terminal domain and a variable C-terminal domain, and the additional residues of PilA are due to a larger C-terminal domain. We solved the structure of the T4aP (T4aP) at a resolution of 3.0 Å using cryo-EM. The T4aP follows the structural blueprint of other T4aP with the pilus core comprised of the interacting N-terminal α1-helices, while the globular domains decorate the T4aP surface. The atomic model of PilA built into this map shows that the large C-terminal domain has more extensive intersubunit contacts than major pilins in other T4aP. As expected from these greater contacts, the bending and axial stiffness of the T4aP is significantly higher than that of other T4aP and supports T4aP-dependent motility on surfaces of different stiffnesses. Notably, T4aP variants with interrupted intersubunit interfaces had decreased bending stiffness, pilus length, and strongly reduced motility. These observations support an evolutionary scenario whereby the large major pilin enables the formation of a rigid T4aP that expands the environmental conditions in which the T4aP system functions. #1: ジャーナル: bioRxiv / 年: 2023 タイトル: Large pilin subunits provide distinct structural and mechanical properties for the type IV pilus. 著者: Anke Treuner-Lange / Weili Zheng / Albertus Viljoen / Steffi Lindow / Marco Herfurth / Yves F Dufrêne / Lotte Søgaard-Andersen / Edward H Egelman 要旨: Type IV pili (T4P) are ubiquitous bacterial cell surface filaments important for surface motility, adhesion to biotic and abiotic surfaces, DNA uptake, biofilm formation, and virulence. T4P are built ...Type IV pili (T4P) are ubiquitous bacterial cell surface filaments important for surface motility, adhesion to biotic and abiotic surfaces, DNA uptake, biofilm formation, and virulence. T4P are built from thousands of copies of the major pilin subunit and tipped by a complex composed of minor pilins and in some systems also the PilY1 adhesin. While the major pilins of structurally characterized T4P have lengths of up to 161 residues, the major pilin PilA of is unusually large with 208 residues. All major pilins have a highly conserved N-terminal domain and a highly variable C-terminal domain, and the additional residues in the PilA are due to a larger C-terminal domain. We solved the structure of the T4P (T4P ) at a resolution of 3.0 Å using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). The T4P follows the structural blueprint observed in other T4P with the pilus core comprised of the extensively interacting N-terminal α1-helices while the globular domains decorate the T4P surface. The atomic model of PilA built into this map shows that the large C-terminal domain has much more extensive intersubunit contacts than major pilins in other T4P. As expected from these greater contacts, the bending and axial stiffness of the T4P is significantly higher than that of other T4P and supports T4P-dependent motility on surfaces of different stiffnesses. Notably, T4P variants with interrupted intersubunit interfaces had decreased bending stiffness and strongly reduced motility on all surfaces. These observations support an evolutionary scenario whereby the large major pilin enables the formation of a rigid T4P that expands the environmental conditions in which the T4P system functions. | ||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  8tj2.cif.gz 8tj2.cif.gz | 1.2 MB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb8tj2.ent.gz pdb8tj2.ent.gz | 1 MB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  8tj2.json.gz 8tj2.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  8tj2_validation.pdf.gz 8tj2_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | 表示 |  wwPDB検証レポート wwPDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  8tj2_full_validation.pdf.gz 8tj2_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  8tj2_validation.xml.gz 8tj2_validation.xml.gz | 101.2 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  8tj2_validation.cif.gz 8tj2_validation.cif.gz | 148.6 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tj/8tj2 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tj/8tj2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tj/8tj2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tj/8tj2 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  41298MC M: このデータのモデリングに利用したマップデータ C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- 要素
要素
| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 21932.318 Da / 分子数: 18 / 由来タイプ: 天然 由来: (天然)  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (バクテリア) Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (バクテリア)参照: UniProt: Q59589 Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法: 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: FILAMENT / 3次元再構成法: らせん対称体再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 | 名称: Myxococcus xanthus type IV pilus / タイプ: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / 由来: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 実験値: NO |
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (バクテリア) Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (バクテリア) |
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.5 |
| 試料 | 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色: NO / 凍結: YES |
| 急速凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2500 nm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 1000 nm |
| 試料ホルダ | 凍結剤: NITROGEN 試料ホルダーモデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| 撮影 | 電子線照射量: 55 e/Å2 / フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- 解析
解析
| EMソフトウェア |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF補正 | タイプ: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| らせん対称 | 回転角度/サブユニット: 100.7 ° / 軸方向距離/サブユニット: 10 Å / らせん対称軸の対称性: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3次元再構成 | 解像度: 3 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 粒子像の数: 1300000 / 対称性のタイプ: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 拘束条件 |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー



 PDBj
PDBj