+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8sro | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | FoxP3 tetramer on TTTG repeats | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION/DNA / FoxP3 / STRs / transcriptional factor / FKH / TRANSCRIPTION / TRANSCRIPTION-DNA complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationT cell tolerance induction / positive regulation of peripheral T cell tolerance induction / tolerance induction / CD4-positive, CD25-positive, alpha-beta regulatory T cell lineage commitment / establishment of endothelial blood-brain barrier / positive regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation / response to rapamycin / negative regulation of alpha-beta T cell proliferation / alpha-beta T cell proliferation / negative regulation of interleukin-4 production ...T cell tolerance induction / positive regulation of peripheral T cell tolerance induction / tolerance induction / CD4-positive, CD25-positive, alpha-beta regulatory T cell lineage commitment / establishment of endothelial blood-brain barrier / positive regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation / response to rapamycin / negative regulation of alpha-beta T cell proliferation / alpha-beta T cell proliferation / negative regulation of interleukin-4 production / : / RUNX1 and FOXP3 control the development of regulatory T lymphocytes (Tregs) / CD4-positive, CD25-positive, alpha-beta regulatory T cell differentiation / negative regulation of chronic inflammatory response / transforming growth factor beta1 production / negative regulation of T cell cytokine production / negative regulation of interleukin-5 production / regulation of isotype switching to IgG isotypes / tolerance induction to self antigen / negative regulation of defense response to virus / negative regulation of lymphocyte proliferation / negative regulation of T-helper 17 cell differentiation / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production / T cell anergy / T cell mediated immunity / negative regulation of immune response / immature T cell proliferation in thymus / positive regulation of T cell tolerance induction / lymphocyte proliferation / positive regulation of T cell anergy / CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation / positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus / positive regulation of CD4-positive, CD25-positive, alpha-beta regulatory T cell differentiation / CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation / regulatory T cell differentiation / negative regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation / negative regulation of isotype switching to IgE isotypes / isotype switching to IgE isotypes / negative regulation of interleukin-17 production / regulation of T cell anergy / regulation of immunoglobulin production / myeloid cell homeostasis / positive regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation / negative regulation of cytokine production / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production / : / negative regulation of interleukin-10 production / NFAT protein binding / histone acetyltransferase binding / positive regulation of interleukin-4 production / negative regulation of type II interferon production / B cell homeostasis / negative regulation of interleukin-6 production / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / T cell proliferation / : / negative regulation of T cell proliferation / T cell activation / negative regulation of inflammatory response / response to virus / histone deacetylase binding / transcription corepressor activity / T cell receptor signaling pathway / DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / gene expression / response to lipopolysaccharide / sequence-specific DNA binding / transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / chromatin remodeling / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / inflammatory response / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / negative regulation of gene expression / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / positive regulation of gene expression / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA-templated transcription / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein homodimerization activity / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Leng, F. / Hur, S. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: FOXP3 recognizes microsatellites and bridges DNA through multimerization. Authors: Wenxiang Zhang / Fangwei Leng / Xi Wang / Ricardo N Ramirez / Jinseok Park / Christophe Benoist / Sun Hur /  Abstract: FOXP3 is a transcription factor that is essential for the development of regulatory T cells, a branch of T cells that suppress excessive inflammation and autoimmunity. However, the molecular ...FOXP3 is a transcription factor that is essential for the development of regulatory T cells, a branch of T cells that suppress excessive inflammation and autoimmunity. However, the molecular mechanisms of FOXP3 remain unclear. Here we here show that FOXP3 uses the forkhead domain-a DNA-binding domain that is commonly thought to function as a monomer or dimer-to form a higher-order multimer after binding to TG repeat microsatellites. The cryo-electron microscopy structure of FOXP3 in a complex with TG repeats reveals a ladder-like architecture, whereby two double-stranded DNA molecules form the two 'side rails' bridged by five pairs of FOXP3 molecules, with each pair forming a 'rung'. Each FOXP3 subunit occupies TGTTTGT within the repeats in a manner that is indistinguishable from that of FOXP3 bound to the forkhead consensus motif (TGTTTAC). Mutations in the intra-rung interface impair TG repeat recognition, DNA bridging and the cellular functions of FOXP3, all without affecting binding to the forkhead consensus motif. FOXP3 can tolerate variable inter-rung spacings, explaining its broad specificity for TG-repeat-like sequences in vivo and in vitro. Both FOXP3 orthologues and paralogues show similar TG repeat recognition and DNA bridging. These findings therefore reveal a mode of DNA recognition that involves transcription factor homomultimerization and DNA bridging, and further implicates microsatellites in transcriptional regulation and diseases. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8sro.cif.gz 8sro.cif.gz | 131.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8sro.ent.gz pdb8sro.ent.gz | 89.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8sro.json.gz 8sro.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sr/8sro https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sr/8sro ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sr/8sro ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sr/8sro | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  40736MC 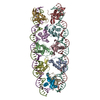 8srpC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 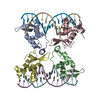
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 27282.246 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: DNA chain | Mass: 22073.490 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) #3: DNA chain | Mass: 22307.139 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: FoxP3-DNA complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2100 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 317175 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj






































