[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8soj: Cryo-EM structure of human CST bound to POT1(ESDL)/TPP1 in the ab... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8soj | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of human CST bound to POT1(ESDL)/TPP1 in the absence of telomeric ssDNA | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / telomere / shelterin / cst / complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of DNA strand elongation / positive regulation of telomeric D-loop disassembly / G-rich single-stranded DNA binding / CST complex / telomere assembly / segmentation / urogenital system development / 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine DNA binding / telomeric D-loop binding / regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining ...positive regulation of DNA strand elongation / positive regulation of telomeric D-loop disassembly / G-rich single-stranded DNA binding / CST complex / telomere assembly / segmentation / urogenital system development / 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine DNA binding / telomeric D-loop binding / regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / protection from non-homologous end joining at telomere / DEAD/H-box RNA helicase binding / telomerase inhibitor activity / establishment of protein localization to telomere / regulation of establishment of protein localization to telomere / telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening / telomeric D-loop disassembly / regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / shelterin complex / Telomere C-strand synthesis initiation / single-stranded telomeric DNA binding / Telomere C-strand (Lagging Strand) Synthesis / intermediate filament cytoskeleton / nuclear telomere cap complex / G-rich strand telomeric DNA binding / telomere capping / telomerase holoenzyme complex / Processive synthesis on the C-strand of the telomere / Polymerase switching on the C-strand of the telomere / bone marrow development / embryonic limb morphogenesis / Removal of the Flap Intermediate from the C-strand / protein localization to chromosome, telomeric region / hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / telomeric DNA binding / negative regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / positive regulation of telomere maintenance / replicative senescence / carbohydrate transmembrane transporter activity / Telomere Extension By Telomerase / maltose binding / maltose transport / maltodextrin transmembrane transport / telomere maintenance via telomerase / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex, substrate-binding subunit-containing / spleen development / symbiont-mediated suppression of host cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway via inhibition of MDA-5 activity / regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / DNA polymerase binding / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / telomere maintenance / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Meiotic synapsis / bioluminescence / thymus development / positive regulation of DNA replication / skeletal system development / picornain 2A / generation of precursor metabolites and energy / symbiont-mediated suppression of host mRNA export from nucleus / symbiont genome entry into host cell via pore formation in plasma membrane / intracellular protein transport / picornain 3C / T=pseudo3 icosahedral viral capsid / ribonucleoside triphosphate phosphatase activity / host cell cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / multicellular organism growth / fibrillar center / positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation / single-stranded DNA binding / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space / channel activity / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / RNA helicase activity / nuclear body / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / symbiont-mediated activation of host autophagy / RNA-directed RNA polymerase / cysteine-type endopeptidase activity / viral RNA genome replication / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / RNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / DNA-templated transcription / DNA damage response / virion attachment to host cell / protein-containing complex binding / host cell nucleus / structural molecule activity / proteolysis / RNA binding / zinc ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)  Human enterovirus 71 Human enterovirus 71 | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cai, S.W. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Cell / Year: 2024Title: POT1 recruits and regulates CST-Polα/primase at human telomeres. Authors: Sarah W Cai / Hiroyuki Takai / Arthur J Zaug / Teague C Dilgen / Thomas R Cech / Thomas Walz / Titia de Lange /  Abstract: Telomere maintenance requires the extension of the G-rich telomeric repeat strand by telomerase and the fill-in synthesis of the C-rich strand by Polα/primase. At telomeres, Polα/primase is bound ...Telomere maintenance requires the extension of the G-rich telomeric repeat strand by telomerase and the fill-in synthesis of the C-rich strand by Polα/primase. At telomeres, Polα/primase is bound to Ctc1/Stn1/Ten1 (CST), a single-stranded DNA-binding complex. Like mutations in telomerase, mutations affecting CST-Polα/primase result in pathological telomere shortening and cause a telomere biology disorder, Coats plus (CP). We determined cryogenic electron microscopy structures of human CST bound to the shelterin heterodimer POT1/TPP1 that reveal how CST is recruited to telomeres by POT1. Our findings suggest that POT1 hinge phosphorylation is required for CST recruitment, and the complex is formed through conserved interactions involving several residues mutated in CP. Our structural and biochemical data suggest that phosphorylated POT1 holds CST-Polα/primase in an inactive, autoinhibited state until telomerase has extended the telomere ends. We propose that dephosphorylation of POT1 releases CST-Polα/primase into an active state that completes telomere replication through fill-in synthesis. #1: Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2023 Title: POT1 recruits and regulates CST-Polα/Primase at human telomeres. Authors: Sarah W Cai / Hiroyuki Takai / Thomas Walz / Titia de Lange /  Abstract: Telomere maintenance requires extension of the G-rich telomeric repeat strand by telomerase and fill-in synthesis of the C-rich strand by Polα/Primase. Telomeric Polα/Primase is bound to Ctc1-Stn1- ...Telomere maintenance requires extension of the G-rich telomeric repeat strand by telomerase and fill-in synthesis of the C-rich strand by Polα/Primase. Telomeric Polα/Primase is bound to Ctc1-Stn1-Ten1 (CST), a single-stranded DNA-binding complex. Like mutations in telomerase, mutations affecting CST-Polα/Primase result in pathological telomere shortening and cause a telomere biology disorder, Coats plus (CP). We determined cryogenic electron microscopy structures of human CST bound to the shelterin heterodimer POT1/TPP1 that reveal how CST is recruited to telomeres by POT1. Phosphorylation of POT1 is required for CST recruitment, and the complex is formed through conserved interactions involving several residues mutated in CP. Our structural and biochemical data suggest that phosphorylated POT1 holds CST-Polα/Primase in an inactive auto-inhibited state until telomerase has extended the telomere ends. We propose that dephosphorylation of POT1 releases CST-Polα/Primase into an active state that completes telomere replication through fill-in synthesis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8soj.cif.gz 8soj.cif.gz | 766 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8soj.ent.gz pdb8soj.ent.gz | 604.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8soj.json.gz 8soj.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8soj_validation.pdf.gz 8soj_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8soj_full_validation.pdf.gz 8soj_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8soj_validation.xml.gz 8soj_validation.xml.gz | 70 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8soj_validation.cif.gz 8soj_validation.cif.gz | 105.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/so/8soj https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/so/8soj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/so/8soj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/so/8soj | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  40659MC  8sokC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 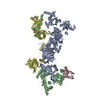
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 178300.609 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: His6-MBP-3C tagged human Ctc1 Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: malE, Z5632, ECs5017, CTC1, C17orf68 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P0AEY0, UniProt: Q2NKJ3 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P0AEY0, UniProt: Q2NKJ3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 115627.211 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Human enterovirus 71, (gene. exp.) Human enterovirus 71, (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: ACD, PIP1, PTOP, TINT1, TPP1, STN1, OBFC1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)References: UniProt: B6F2F5, UniProt: Q96AP0, UniProt: Q9H668, picornain 2A, nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase, picornain 3C, RNA-directed RNA polymerase | ||||
| #3: Protein | Mass: 13872.013 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TEN1, C17orf106 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TEN1, C17orf106 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q86WV5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q86WV5 | ||||
| #4: Protein | Mass: 72938.219 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: mPOT1b residues ESDL 323-326 are inserted into the human POT1 sequence between S320 and V321 Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POT1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POT1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NUX5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NUX5 | ||||
| #5: Chemical | | Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | N | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human CST-POT1(ESDL)/TPP1 complex / Type: COMPLEX / Details: CST-POT1(ESDL)/TPP1 complex in the absence of DNA / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.38 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.05 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50.3 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 132356 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj