[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
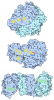
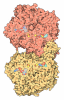
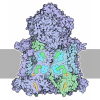
Yorodumi- PDB-8rbm: Cryo-EM structure of the NADH:ferredoxin oxidoreductase RNF from ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8rbm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the NADH:ferredoxin oxidoreductase RNF from Azotobacter vinelandii, ferricyanide oxidized | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | (Ion-translocating oxidoreductase complex subunit ...) x 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / NADH:ferredoxin oxidoreductase | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationTranslocases / endomembrane system / electron transport chain / transmembrane transport / FMN binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / electron transfer activity / metal ion binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.24 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang, L. / Einsle, O. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Germany, 5items Germany, 5items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2024Title: Architecture of the RNF1 complex that drives biological nitrogen fixation. Authors: Lin Zhang / Oliver Einsle /  Abstract: Biological nitrogen fixation requires substantial metabolic energy in form of ATP as well as low-potential electrons that must derive from central metabolism. During aerobic growth, the free-living ...Biological nitrogen fixation requires substantial metabolic energy in form of ATP as well as low-potential electrons that must derive from central metabolism. During aerobic growth, the free-living soil diazotroph Azotobacter vinelandii transfers electrons from the key metabolite NADH to the low-potential ferredoxin FdxA that serves as a direct electron donor to the dinitrogenase reductases. This process is mediated by the RNF complex that exploits the proton motive force over the cytoplasmic membrane to lower the midpoint potential of the transferred electron. Here we report the cryogenic electron microscopy structure of the nitrogenase-associated RNF complex of A. vinelandii, a seven-subunit membrane protein assembly that contains four flavin cofactors and six iron-sulfur centers. Its function requires the strict coupling of electron and proton transfer but also involves major conformational changes within the assembly that can be traced with a combination of electron microscopy and modeling. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8rbm.cif.gz 8rbm.cif.gz | 302.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8rbm.ent.gz pdb8rbm.ent.gz | 235.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8rbm.json.gz 8rbm.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rb/8rbm https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rb/8rbm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rb/8rbm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rb/8rbm | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  19032MC  8ahxC 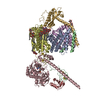 8rb8C  8rb9C  8rbqC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 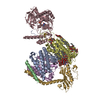
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Ion-translocating oxidoreductase complex subunit ... , 6 types, 7 molecules ACDEGBb
| #1: Protein | Mass: 19942.131 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: rnfA1, rnfA, Avin_50980 / Production host: Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: rnfA1, rnfA, Avin_50980 / Production host:  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: C1DMA8, Translocases Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: C1DMA8, Translocases |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 52234.195 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: rnfC1, rnfC, Avin_50960 / Production host: Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: rnfC1, rnfC, Avin_50960 / Production host:  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: C1DMA6, Translocases Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: C1DMA6, Translocases |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 39189.016 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: rnfD1, rnfD, Avin_50950 / Production host: Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: rnfD1, rnfD, Avin_50950 / Production host:  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: C1DMA5, Translocases Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: C1DMA5, Translocases |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 25576.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: rnfE, Avin_50930 / Production host: Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: rnfE, Avin_50930 / Production host:  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q9F5Y1, Translocases Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q9F5Y1, Translocases |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 24890.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: rnfG1, rnfG, Avin_50940 / Production host: Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: rnfG1, rnfG, Avin_50940 / Production host:  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: C1DMA4, Translocases Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: C1DMA4, Translocases |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 17704.572 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: rnfB1, rnfB, Avin_50970 / Production host: Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / Gene: rnfB1, rnfB, Avin_50970 / Production host:  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: C1DMA7, Translocases Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: C1DMA7, Translocases |
-Sugars , 1 types, 12 molecules 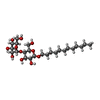
| #8: Sugar | ChemComp-LMT / |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 8 molecules 




| #7: Chemical | ChemComp-FES / | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #9: Chemical | | #10: Chemical | #11: Chemical | ChemComp-RBF / | #12: Chemical | ChemComp-PTY / | |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Heptameric complex NADH:ferredoxin oxidoreductase RNF1 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#6 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.188 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) Azotobacter vinelandii DJ (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 37 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.24 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 166974 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj