[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8qqp: Mycobacterium smegmatis inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPD... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8qqp | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Mycobacterium smegmatis inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) ATP+GTP-bound form, super-compressed | ||||||
 Components Components | Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | OXIDOREDUCTASE / Octamer / ATP+GTP complex / Purine metabolism / IMPDH | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationIMP dehydrogenase / IMP dehydrogenase activity / GMP biosynthetic process / GTP biosynthetic process / nucleotide binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.35 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Bulvas, O. / Kouba, T. / Pichova, I. | ||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Deciphering the allosteric regulation of mycobacterial inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase. Authors: Ondřej Bulvas / Zdeněk Knejzlík / Jakub Sýs / Anatolij Filimoněnko / Monika Čížková / Kamila Clarová / Dominik Rejman / Tomáš Kouba / Iva Pichová /  Abstract: Allosteric regulation of inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH), an essential enzyme of purine metabolism, contributes to the homeostasis of adenine and guanine nucleotides. However, the ...Allosteric regulation of inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH), an essential enzyme of purine metabolism, contributes to the homeostasis of adenine and guanine nucleotides. However, the precise molecular mechanism of IMPDH regulation in bacteria remains unclear. Using biochemical and cryo-EM approaches, we reveal the intricate molecular mechanism of the IMPDH allosteric regulation in mycobacteria. The enzyme is inhibited by both GTP and (p)ppGpp, which bind to the regulatory CBS domains and, via interactions with basic residues in hinge regions, lock the catalytic core domains in a compressed conformation. This results in occlusion of inosine monophosphate (IMP) substrate binding to the active site and, ultimately, inhibition of the enzyme. The GTP and (p)ppGpp allosteric effectors bind to their dedicated sites but stabilize the compressed octamer by a common mechanism. Inhibition is relieved by the competitive displacement of GTP or (p)ppGpp by ATP allowing IMP-induced enzyme expansion. The structural knowledge and mechanistic understanding presented here open up new possibilities for the development of allosteric inhibitors with antibacterial potential. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8qqp.cif.gz 8qqp.cif.gz | 832.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8qqp.ent.gz pdb8qqp.ent.gz | 555.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8qqp.json.gz 8qqp.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8qqp_validation.pdf.gz 8qqp_validation.pdf.gz | 2.3 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8qqp_full_validation.pdf.gz 8qqp_full_validation.pdf.gz | 2.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8qqp_validation.xml.gz 8qqp_validation.xml.gz | 103.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8qqp_validation.cif.gz 8qqp_validation.cif.gz | 159.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/8qqp https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/8qqp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/8qqp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/8qqp | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  18600MC  8pw3C  8q65C  8qqqC  8qqrC  8qqtC  8qqvC  8qqwC  8qqxC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 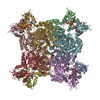
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 53388.988 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria)Strain: MC2 155 / Gene: guaB, MSMEG_1602 / Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-GTP / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Octameric assembly of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase in complex with ATP+GTP Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.426658 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 Details: 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 200 mM KCl, 5 mM DTT,4 mM MgCl2 Ligand: 0.5 mM ATP + 2 mM GTP + 1 mM IMP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 165000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 400 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: ZEMLIN TABLEAU |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2 sec. / Electron dose: 44 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 40440 |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 26489203 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.35 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 715534 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 47.35 / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: CC coefficient Details: Initial fitting was done in UCSF ChimeraX. Model refinement was done by iterative cycles of manual fitting with Coot and ISOLDE and automated fitting with phenix.real_space_refine. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Accession code: A0QSU3 / Source name: AlphaFold / Type: in silico model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 47.83 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj