[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8qql: Cryo-EM structure of the human inward-rectifier potassium 2.1 cha... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8qql | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
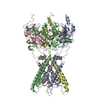
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human inward-rectifier potassium 2.1 channel (Kir2.1) - R312H mutant | |||||||||
 Components Components | Inward rectifier potassium channel 2 | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Ion channel / Potassium Channel / Kir channel | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationSensory perception of sour taste / Classical Kir channels / regulation of skeletal muscle contraction via regulation of action potential / relaxation of skeletal muscle / magnesium ion transport / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / Phase 4 - resting membrane potential / membrane repolarization during action potential / membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of membrane repolarization ...Sensory perception of sour taste / Classical Kir channels / regulation of skeletal muscle contraction via regulation of action potential / relaxation of skeletal muscle / magnesium ion transport / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / Phase 4 - resting membrane potential / membrane repolarization during action potential / membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of membrane repolarization / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of resting membrane potential / regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / inward rectifier potassium channel activity / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / regulation of cardiac muscle cell contraction / relaxation of cardiac muscle / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / intracellular potassium ion homeostasis / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / intercalated disc / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / T-tubule / potassium ion transport / cellular response to mechanical stimulus / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / dendritic spine / protein homotetramerization / postsynaptic membrane / neuronal cell body / glutamatergic synapse / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fernandes, C.A.H. / Zuniga, D. / Venien-Bryan, C. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  France, European Union, 2items France, European Union, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: FASEB J / Year: 2024 Journal: FASEB J / Year: 2024Title: Biochemical, biophysical, and structural investigations of two mutants (C154Y and R312H) of the human Kir2.1 channel involved in the Andersen-Tawil syndrome. Authors: Dania Zuniga / Andreas Zoumpoulakis / Rafael F Veloso / Laurie Peverini / Sophie Shi / Alexandre Pozza / Valérie Kugler / Françoise Bonneté / Tahar Bouceba / Renaud Wagner / Pierre-Jean ...Authors: Dania Zuniga / Andreas Zoumpoulakis / Rafael F Veloso / Laurie Peverini / Sophie Shi / Alexandre Pozza / Valérie Kugler / Françoise Bonneté / Tahar Bouceba / Renaud Wagner / Pierre-Jean Corringer / Carlos A H Fernandes / Catherine Vénien-Bryan /  Abstract: Inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) channels play a pivotal role in physiology by establishing, maintaining, and regulating the resting membrane potential of the cells, particularly contributing to ...Inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) channels play a pivotal role in physiology by establishing, maintaining, and regulating the resting membrane potential of the cells, particularly contributing to the cellular repolarization of many excitable cells. Dysfunction in Kir2.1 channels is implicated in several chronic and debilitating human diseases for which there are currently no effective treatments. Specifically, Kir2.1-R312H and Kir2.1-C154Y mutations are associated with Andersen-Tawil syndrome (ATS) in humans. We have investigated the impact of these two mutants in the trafficking of the channel to the cell membrane and function in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Despite both mutations being trafficked to the cell membrane at different extents and capable of binding PIP (phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate), the main modulator for channel activity, they resulted in defective channels that do not display K current, albeit through different molecular mechanisms. Coexpression studies showed that R312H and C154Y are expressed and associated with the WT subunits. While WT subunits could rescue R312H dysfunction, the presence of a unique C154Y subunit disrupts the function of the entire complex, which is a typical feature of mutations with a dominant-negative effect. Molecular dynamics simulations showed that Kir2.1-C154Y mutation induces a loss in the structural plasticity of the selectivity filter, impairing the K flow. In addition, the cryo-EM structure of the Kir2.1-R312H mutant has been reconstructed. This study identified the molecular mechanisms by which two ATS-causing mutations impact Kir2.1 channel function and provide valuable insights that can guide potential strategies for the development of future therapeutic interventions for ATS. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8qql.cif.gz 8qql.cif.gz | 222.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8qql.ent.gz pdb8qql.ent.gz | 180.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8qql.json.gz 8qql.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/8qql https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/8qql ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/8qql ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/8qql | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  18595MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 36148.816 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Mutation: R312H Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNJ2, IRK1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNJ2, IRK1 / Production host:  Komagataella pastoris (fungus) / References: UniProt: P63252 Komagataella pastoris (fungus) / References: UniProt: P63252Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human inward-rectifier potassium 2.1 channel (Kir2.1) containing the Andersen-syndrome related mutation R312H Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Komagataella pastoris (fungus) Komagataella pastoris (fungus) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 Details: 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 150 mM KCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.59 mM DDM |
| Buffer component | Conc.: 20 mM / Name: Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane hydrochloride / Formula: tris-hcl |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.6 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: Blotting force 0, blotting time 3s |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS Details: Preliminary grid screening was performed manually at a Glacios 2 microscope. |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 165000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: BASIC |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.35 sec. / Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 10762 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: TFS Selectris X |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2787753 Details: A blob picking followed by 2D classification was performed to generate templates for automated template-picking. Initially, 2,787,753 particles were selected after template-picking, which ...Details: A blob picking followed by 2D classification was performed to generate templates for automated template-picking. Initially, 2,787,753 particles were selected after template-picking, which were submitted to three rounds do 2D classification to remove false picks, ice contamination and classes with unclear features. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C4 (4 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 146539 / Num. of class averages: 4 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 7zdz Accession code: 7zdz / Chain residue range: 195-367 / Pdb chain residue range: 195-367 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj