+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8oze | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | cryoEM structure of SPARTA complex dimer high resolution | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / SPARTA / TIR / prokaryotic argonaute | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Maribacter polysiphoniae (bacteria) Maribacter polysiphoniae (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.91 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Babatunde, E. / Dong, C.N. / Xu, H.L. / Henning, S. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, 2items Switzerland, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023Title: Activation mechanism of a short argonaute-TIR prokaryotic immune system. Authors: Dongchun Ni / Xuhang Lu / Henning Stahlberg / Babatunde Ekundayo /   Abstract: Short prokaryotic argonaute (pAgo) and toll/interleukin-1 receptor/resistance protein (TIR)-analog of PAZ (APAZ) form a heterodimeric SPARTA complex that provides immunity to its prokaryotic host ...Short prokaryotic argonaute (pAgo) and toll/interleukin-1 receptor/resistance protein (TIR)-analog of PAZ (APAZ) form a heterodimeric SPARTA complex that provides immunity to its prokaryotic host through an abortive infection mechanism. Monomeric SPARTA senses foreign RNA/DNA duplexes to assemble an active tetramer resulting in cell death by nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (oxidized form) (NAD) depletion via an unknown mechanism. We report nine structures of SPARTA in different functional states at a resolution range of 4.2 to 2.9 angstroms, revealing its activation mechanism. Inactive SPARTA monomers bind to RNA/DNA duplexes to form symmetric dimers mediated by the association of Ago subunits. The initiation of tetramer assembly induces flexibility of the TIR domains enabling a symmetry-breaking rotational movement of a TIR domain in the dimer units which facilitates the TIR oligomerization, resulting in the formation of the substrate binding pocket and the activation of the SPARTA complex's NADase activity. Our findings provide detailed structural and mechanistic insights into activating a short argonaute defense system. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8oze.cif.gz 8oze.cif.gz | 315.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8oze.ent.gz pdb8oze.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8oze.json.gz 8oze.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8oze_validation.pdf.gz 8oze_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8oze_full_validation.pdf.gz 8oze_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8oze_validation.xml.gz 8oze_validation.xml.gz | 56.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8oze_validation.cif.gz 8oze_validation.cif.gz | 85.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oz/8oze https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oz/8oze ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oz/8oze ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oz/8oze | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  17306MC  8oz6C  8ozcC  8ozdC  8ozfC  8ozgC  8oziC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 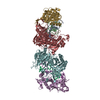
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 6505.880 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Maribacter polysiphoniae (bacteria) Maribacter polysiphoniae (bacteria)#2: DNA chain | Mass: 5075.327 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Maribacter polysiphoniae (bacteria) Maribacter polysiphoniae (bacteria)#3: Protein | Mass: 53270.594 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Maribacter polysiphoniae (bacteria) / Gene: LX92_01810 / Production host: Maribacter polysiphoniae (bacteria) / Gene: LX92_01810 / Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 58091.410 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Maribacter polysiphoniae (bacteria) / Gene: LX92_01809 / Production host: Maribacter polysiphoniae (bacteria) / Gene: LX92_01809 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: SPARTA complex dimer high resolution / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.3 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Maribacter polysiphoniae (bacteria) Maribacter polysiphoniae (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.91 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 121327 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 PDBj
PDBj































































