[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8opn: Human Coronavirus HKU1 spike glycoprotein in complex with an alph... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8opn | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
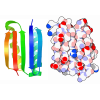
| Title | Human Coronavirus HKU1 spike glycoprotein in complex with an alpha2,8-linked 9-O-acetylated disialoside (1-up state) | |||||||||
 Components Components | Spike glycoprotein,General control transcription factor GCN4 | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / Virus / Coronavirus / HKU1 / Spike / Glycoprotein / Membrane fusion | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationFCERI mediated MAPK activation / protein localization to nuclear periphery / Activation of the AP-1 family of transcription factors / response to amino acid starvation / negative regulation of ribosomal protein gene transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of cellular response to amino acid starvation / mediator complex binding / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / amino acid biosynthetic process ...FCERI mediated MAPK activation / protein localization to nuclear periphery / Activation of the AP-1 family of transcription factors / response to amino acid starvation / negative regulation of ribosomal protein gene transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of cellular response to amino acid starvation / mediator complex binding / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / amino acid biosynthetic process / positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / cellular response to nutrient levels / cellular response to amino acid starvation / RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex / DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / transcription regulator complex / sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / intracellular signal transduction / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / chromatin binding / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / identical protein binding / membrane / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Human coronavirus HKU1 Human coronavirus HKU1 | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Pronker, M.F. / Creutznacher, R. / Hurdiss, D.L. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Netherlands, Netherlands,  China, 2items China, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Sialoglycan binding triggers spike opening in a human coronavirus. Authors: Matti F Pronker / Robert Creutznacher / Ieva Drulyte / Ruben J G Hulswit / Zeshi Li / Frank J M van Kuppeveld / Joost Snijder / Yifei Lang / Berend-Jan Bosch / Geert-Jan Boons / Martin Frank ...Authors: Matti F Pronker / Robert Creutznacher / Ieva Drulyte / Ruben J G Hulswit / Zeshi Li / Frank J M van Kuppeveld / Joost Snijder / Yifei Lang / Berend-Jan Bosch / Geert-Jan Boons / Martin Frank / Raoul J de Groot / Daniel L Hurdiss /    Abstract: Coronavirus spike proteins mediate receptor binding and membrane fusion, making them prime targets for neutralizing antibodies. In the cases of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, severe ...Coronavirus spike proteins mediate receptor binding and membrane fusion, making them prime targets for neutralizing antibodies. In the cases of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, spike proteins transition freely between open and closed conformations to balance host cell attachment and immune evasion. Spike opening exposes domain S1, allowing it to bind to proteinaceous receptors, and is also thought to enable protein refolding during membrane fusion. However, with a single exception, the pre-fusion spike proteins of all other coronaviruses studied so far have been observed exclusively in the closed state. This raises the possibility of regulation, with spike proteins more commonly transitioning to open states in response to specific cues, rather than spontaneously. Here, using cryogenic electron microscopy and molecular dynamics simulations, we show that the spike protein of the common cold human coronavirus HKU1 undergoes local and long-range conformational changes after binding a sialoglycan-based primary receptor to domain S1. This binding triggers the transition of S1 domains to the open state through allosteric interdomain crosstalk. Our findings provide detailed insight into coronavirus attachment, with possibilities of dual receptor usage and priming of entry as a means of immune escape. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8opn.cif.gz 8opn.cif.gz | 648.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8opn.ent.gz pdb8opn.ent.gz | 524.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8opn.json.gz 8opn.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/op/8opn https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/op/8opn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/op/8opn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/op/8opn | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  17077MC  8ohnC  8opmC  8opoC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 147770.344 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Human coronavirus HKU1, (gene. exp.) Human coronavirus HKU1, (gene. exp.)  Strain: Caen1 / Gene: GCN4, AAS101, AAS3, ARG9, YEL009C / Cell line (production host): HEK293 / Organ (production host): KIDNEY / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: E0YJ44, UniProt: P03069 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: E0YJ44, UniProt: P03069#2: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #3: Polysaccharide | Type: oligosaccharide / Mass: 642.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #4: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Trimeric spike glycoprotein / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.44 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Concentration of protein (N-linked glycans not included due to glycan heterogeneity). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.68 sec. / Electron dose: 46 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 4057 |
| EM imaging optics | Details: BioContinuum Imaging Filter / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Width: 5760 / Height: 4092 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 956697 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 36048 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 114 / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Accession code: 6nzk / Chain residue range: 14-1225 / Details: Phyre2 / Source name: Other / Type: in silico model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj