+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 8g0l | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Semi-synthetic CoA-alpha-Synuclein Constructs Trap N-terminal Acetyltransferase NatB for Binding Mechanism Studies | ||||||
 要素 要素 |
| ||||||
 キーワード キーワード | TRANSFERASE / N-terminal acetyltransferase | ||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報N-terminal peptidyl-glutamine acetylation / N-terminal methionine Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatB / N-terminal peptidyl-aspartic acid acetylation / N-terminal peptidyl-glutamic acid acetylation / NatB complex / N-terminal protein amino acid acetylation / protein N-terminal-methionine acetyltransferase activity / protein-N-terminal amino-acid acetyltransferase activity / acetyltransferase activator activity / negative regulation of mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone ...N-terminal peptidyl-glutamine acetylation / N-terminal methionine Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatB / N-terminal peptidyl-aspartic acid acetylation / N-terminal peptidyl-glutamic acid acetylation / NatB complex / N-terminal protein amino acid acetylation / protein N-terminal-methionine acetyltransferase activity / protein-N-terminal amino-acid acetyltransferase activity / acetyltransferase activator activity / negative regulation of mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone / : / neutral lipid metabolic process / regulation of acyl-CoA biosynthetic process / negative regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / negative regulation of norepinephrine uptake / response to desipramine / positive regulation of SNARE complex assembly / positive regulation of hydrogen peroxide catabolic process / supramolecular fiber / regulation of synaptic vesicle recycling / mitochondrial membrane organization / negative regulation of chaperone-mediated autophagy / regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / negative regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of protein localization to cell periphery / negative regulation of exocytosis / regulation of glutamate secretion / dopamine biosynthetic process / response to iron(II) ion / SNARE complex assembly / positive regulation of neurotransmitter secretion / regulation of locomotion / negative regulation of dopamine metabolic process / positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process / regulation of macrophage activation / negative regulation of microtubule polymerization / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / synaptic vesicle transport / transporter regulator activity / synaptic vesicle priming / dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / protein kinase inhibitor activity / mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled electron transport / regulation of dopamine secretion / dynein complex binding / negative regulation of thrombin-activated receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of receptor recycling / cuprous ion binding / nuclear outer membrane / response to magnesium ion / positive regulation of endocytosis / positive regulation of exocytosis / synaptic vesicle exocytosis / kinesin binding / synaptic vesicle endocytosis / enzyme inhibitor activity / cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of serotonin uptake / response to type II interferon / regulation of presynapse assembly / alpha-tubulin binding / beta-tubulin binding / phospholipase binding / behavioral response to cocaine / supramolecular fiber organization / phospholipid metabolic process / cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus / inclusion body / axon terminus / Hsp70 protein binding / cellular response to epinephrine stimulus / cytoskeleton organization / response to interleukin-1 / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to copper ion / positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / adult locomotory behavior / SNARE binding / excitatory postsynaptic potential / regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization / protein tetramerization / phosphoprotein binding / microglial cell activation / fatty acid metabolic process / ferrous iron binding / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / synapse organization / protein destabilization / PKR-mediated signaling / phospholipid binding / receptor internalization / tau protein binding / long-term synaptic potentiation / terminal bouton / positive regulation of inflammatory response / synaptic vesicle membrane / actin cytoskeleton / actin binding / growth cone / cellular response to oxidative stress 類似検索 - 分子機能 | ||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | ||||||
| 手法 | 電子顕微鏡法 / 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 3.39 Å | ||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Gardner, S.M. / Marmorstein, R. | ||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 1件 米国, 1件
| ||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: J Am Chem Soc / 年: 2023 ジャーナル: J Am Chem Soc / 年: 2023タイトル: Semi-Synthetic CoA-α-Synuclein Constructs Trap N-Terminal Acetyltransferase NatB for Binding Mechanism Studies. 著者: Buyan Pan / Sarah M Gardner / Kollin Schultz / Ryann M Perez / Sunbin Deng / Marie Shimogawa / Kohei Sato / Elizabeth Rhoades / Ronen Marmorstein / E James Petersson /   要旨: N-terminal acetylation is a chemical modification carried out by N-terminal acetyltransferases. A major member of this enzyme family, NatB, acts on much of the human proteome, including α-synuclein ...N-terminal acetylation is a chemical modification carried out by N-terminal acetyltransferases. A major member of this enzyme family, NatB, acts on much of the human proteome, including α-synuclein (αS), a synaptic protein that mediates vesicle trafficking. NatB acetylation of αS modulates its lipid vesicle binding properties and amyloid fibril formation, which underlies its role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Although the molecular details of the interaction between human NatB (hNatB) and the N-terminus of αS have been resolved, whether the remainder of the protein plays a role in interacting with the enzyme is unknown. Here, we execute the first synthesis, by native chemical ligation, of a bisubstrate inhibitor of NatB consisting of coenzyme A and full-length human αS, additionally incorporating two fluorescent probes for studies of conformational dynamics. We use cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to characterize the structural features of the hNatB/inhibitor complex and show that, beyond the first few residues, αS remains disordered when in complex with hNatB. We further probe changes in the αS conformation by single molecule Förster resonance energy transfer (smFRET) to reveal that the C-terminus expands when bound to hNatB. Computational models based on the cryo-EM and smFRET data help to explain the conformational changes as well as their implications for hNatB substrate recognition and specific inhibition of the interaction with αS. Beyond the study of αS and NatB, these experiments illustrate valuable strategies for the study of challenging structural biology targets through a combination of protein semi-synthesis, cryo-EM, smFRET, and computational modeling. #1: ジャーナル: bioRxiv / 年: 2023 タイトル: Semi-synthetic CoA-α-Synuclein Constructs Trap N-terminal Acetyltransferase NatB for Binding Mechanism Studies. 著者: Buyan Pan / Sarah Gardner / Kollin Schultz / Ryann M Perez / Sunbin Deng / Marie Shimogawa / Kohei Sato / Elizabeth Rhoades / Ronen Marmorstein / E James Petersson 要旨: N-terminal acetylation is a chemical modification carried out by N-terminal acetyltransferases (NATs). A major member of this enzyme family, NatB, acts on much of the human proteome, including α- ...N-terminal acetylation is a chemical modification carried out by N-terminal acetyltransferases (NATs). A major member of this enzyme family, NatB, acts on much of the human proteome, including α-synuclein (αS), a synaptic protein that mediates vesicle trafficking. NatB acetylation of αS modulates its lipid vesicle binding properties and amyloid fibril formation, which underlies its role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Although the molecular details of the interaction between human NatB (hNatB) and the N-terminus of αS have been resolved, whether the remainder of the protein plays a role in interacting with the enzyme is unknown. Here we execute the first synthesis, by native chemical ligation, of a bisubstrate inhibitor of NatB consisting of coenzyme A and full-length human αS, additionally incorporating two fluorescent probes for studies of conformational dynamics. We use cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to characterize the structural features of the hNatB/inhibitor complex and show that, beyond the first few residues, αS remains disordered when in complex with hNatB. We further probe changes in the αS conformation by single molecule Förster resonance energy transfer (smFRET) to reveal that the C-terminus expands when bound to hNatB. Computational models based on the cryo-EM and smFRET data help to explain the conformational changes and their implications for hNatB substrate recognition and specific inhibition of the interaction with αS. Beyond the study of αS and NatB, these experiments illustrate valuable strategies for the study of challenging structural biology targets through a combination of protein semi-synthesis, cryo-EM, smFRET, and computational modeling. | ||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  8g0l.cif.gz 8g0l.cif.gz | 206.2 KB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb8g0l.ent.gz pdb8g0l.ent.gz | 161.8 KB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  8g0l.json.gz 8g0l.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  8g0l_validation.pdf.gz 8g0l_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | 表示 |  wwPDB検証レポート wwPDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  8g0l_full_validation.pdf.gz 8g0l_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  8g0l_validation.xml.gz 8g0l_validation.xml.gz | 44.4 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  8g0l_validation.cif.gz 8g0l_validation.cif.gz | 65.9 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g0/8g0l https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g0/8g0l ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g0/8g0l ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g0/8g0l | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  29657MC M: このデータのモデリングに利用したマップデータ C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 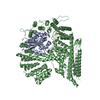
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- 要素
要素
| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 20390.133 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: NAA20, NAT5 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: NAA20, NAT5発現宿主:  参照: UniProt: P61599, N-terminal methionine Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatB |
|---|---|
| #2: タンパク質 | 分子量: 112444.258 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: NAA25, C12orf30, MDM20, NAP1 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: NAA25, C12orf30, MDM20, NAP1発現宿主:  参照: UniProt: Q14CX7 |
| #3: タンパク質・ペプチド | 分子量: 641.799 Da / 分子数: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 1-5 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: SNCA, NACP, PARK1 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: SNCA, NACP, PARK1 / 発現宿主:  |
| #4: 化合物 | ChemComp-CMC / |
| 研究の焦点であるリガンドがあるか | Y |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法: 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: PARTICLE / 3次元再構成法: 単粒子再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 | 名称: Ternary complex of NAA20, NAA25 and CoA-alpha-Synuclein タイプ: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / 由来: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 実験値: NO |
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 由来(組換発現) | 生物種:  株: sf9 |
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.5 |
| 試料 | 濃度: 4 mg/ml / 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色: NO / 凍結: YES |
| 急速凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE / 湿度: 100 % |
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 3000 nm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 1000 nm |
| 撮影 | 電子線照射量: 43.9 e/Å2 / フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / 撮影したグリッド数: 1 / 実像数: 5470 |
- 解析
解析
| CTF補正 | タイプ: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3次元再構成 | 解像度: 3.39 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 粒子像の数: 192518 / 対称性のタイプ: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 拘束条件 |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー



 PDBj
PDBj