[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8fs7: Structure of S. cerevisiae Rad24-RFC loading the 9-1-1 clamp onto... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8fs7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of S. cerevisiae Rad24-RFC loading the 9-1-1 clamp onto a 10-nt gapped DNA in step 5 (closed 9-1-1 and stably bound chamber DNA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE/DNA / DNA damage repair / Rad24-RFC / 9-1-1 clamp / DNA clamp / alternative clamp loader / DNA damage signaling / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex / CELL CYCLE-DNA complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmeiotic DNA integrity checkpoint signaling / checkpoint clamp complex / Rad17 RFC-like complex / : / Elg1 RFC-like complex / DNA replication factor C complex / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / Polymerase switching / DNA clamp loader activity / Translesion synthesis by REV1 ...meiotic DNA integrity checkpoint signaling / checkpoint clamp complex / Rad17 RFC-like complex / : / Elg1 RFC-like complex / DNA replication factor C complex / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / Polymerase switching / DNA clamp loader activity / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / : / : / : / DNA replication checkpoint signaling / : / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / mitotic DNA replication checkpoint signaling / telomere maintenance via recombination / mitotic intra-S DNA damage checkpoint signaling / reciprocal meiotic recombination / recombinational repair / sister chromatid cohesion / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / leading strand elongation / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / Dual incision in TC-NER / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / mismatch repair / 3'-5' exonuclease activity / telomere maintenance / DNA damage checkpoint signaling / cellular response to ionizing radiation / meiotic cell cycle / nucleotide-excision repair / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / DNA-templated DNA replication / double-strand break repair / site of double-strand break / double-stranded DNA binding / damaged DNA binding / chromosome, telomeric region / DNA repair / chromatin binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / ATP binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.85 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zheng, F. / Georgescu, R. / Yao, Y.N. / O'Donnell, M.E. / Li, H. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2023 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2023Title: Structures of 9-1-1 DNA checkpoint clamp loading at gaps from start to finish and ramification to biology. Authors: Fengwei Zheng / Roxana E Georgescu / Nina Y Yao / Michael E O'Donnell / Huilin Li /  Abstract: Recent structural studies show the Rad24-RFC loads the 9-1-1 checkpoint clamp onto a recessed 5' end by binding the 5' DNA on Rad24 at an external surface site and threading the 3' ssDNA into the ...Recent structural studies show the Rad24-RFC loads the 9-1-1 checkpoint clamp onto a recessed 5' end by binding the 5' DNA on Rad24 at an external surface site and threading the 3' ssDNA into the well-established internal chamber and into 9-1-1. We find here that Rad24-RFC loads 9-1-1 onto DNA gaps in preference to a recessed 5' DNA end, thus presumably leaving 9-1-1 on a 3' ss/ds DNA after Rad24-RFC ejects from the 5' gap end and may explain reports of 9-1-1 directly functioning in DNA repair with various TLS polymerases, in addition to signaling the ATR kinase. To gain a deeper understanding of 9-1-1 loading at gaps we report high-resolution structures of Rad24-RFC during loading of 9-1-1 onto 10-nt and 5-nt gapped DNAs. At a 10-nt gap we captured five Rad24-RFC-9-1-1 loading intermediates in which the 9-1-1 DNA entry gate varies from fully open to fully closed around DNA using ATPγS, supporting the emerging view that ATP hydrolysis is not needed for clamp opening/closing, but instead for dissociation of the loader from the clamp encircling DNA. The structure of Rad24-RFC-9-1-1 at a 5-nt gap shows a 180° axially rotated 3'-dsDNA which orients the template strand to bridge the 3'- and 5'- junctions with a minimum 5-nt ssDNA. The structures reveal a unique loop on Rad24 that limits the length of dsDNA in the inner chamber, and inability to melt DNA ends unlike RFC, thereby explaining Rad24-RFC's preference for a preexisting ssDNA gap and suggesting a direct role in gap repair in addition to its checkpoint role. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8fs7.cif.gz 8fs7.cif.gz | 576 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8fs7.ent.gz pdb8fs7.ent.gz | 450.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8fs7.json.gz 8fs7.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8fs7_validation.pdf.gz 8fs7_validation.pdf.gz | 1.9 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8fs7_full_validation.pdf.gz 8fs7_full_validation.pdf.gz | 2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8fs7_validation.xml.gz 8fs7_validation.xml.gz | 85.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8fs7_validation.cif.gz 8fs7_validation.cif.gz | 129.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fs/8fs7 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fs/8fs7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fs/8fs7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fs/8fs7 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  29416MC  8fs3C 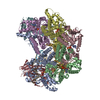 8fs4C  8fs5C 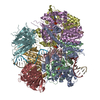 8fs6C 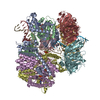 8fs8C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules AH
| #1: Protein | Mass: 62792.496 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: RAD24, YER173W, SYGP-ORF60 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #8: Protein | Mass: 69787.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: DDC1 / Production host:  |
-Replication factor C subunit ... , 4 types, 4 molecules BCDE
| #2: Protein | Mass: 36201.039 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: RFC4, YOL094C, O0923 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 37841.051 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: RFC3, YNL290W, N0533 / Production host:  |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 39794.473 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: RFC2, YJR068W, J1808 / Production host:  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 39993.582 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: RFC5, YBR087W, YBR0810 / Production host:  |
-DNA damage checkpoint control protein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules FG
| #6: Protein | Mass: 53207.797 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: MEC3, PIP3, PSO9, YLR288C, L8003.15 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #7: Protein | Mass: 45637.527 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: RAD17, GI527_G0005737 / Production host:  |
-DNA chain , 1 types, 1 molecules I
| #9: DNA chain | Mass: 15389.855 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|
-Primer strand ... , 2 types, 2 molecules JK
| #10: DNA chain | Mass: 6464.172 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #11: DNA chain | Mass: 6084.940 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 9 molecules 




| #12: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #13: Chemical | ChemComp-AGS / #14: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1300 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 64 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.85 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 292725 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj










































