+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8duo | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | DNA-free T4 Bacteriophage gp41 hexamer | |||||||||
 Components Components | DnaB-like replicative helicase | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | REPLICATION/DNA/RNA / phage / complex / helicase / REPLICATION-DNA-RNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbidirectional double-stranded viral DNA replication / DNA replication, synthesis of primer / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / DNA helicase activity / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / hydrolase activity / DNA binding / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Escherichia phage T4 (virus) Escherichia phage T4 (virus) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Feng, X. / Li, H. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis of the T4 bacteriophage primosome assembly and primer synthesis. Authors: Xiang Feng / Michelle M Spiering / Ruda de Luna Almeida Santos / Stephen J Benkovic / Huilin Li /  Abstract: The T4 bacteriophage gp41 helicase and gp61 primase assemble into a primosome to couple DNA unwinding with RNA primer synthesis for DNA replication. How the primosome is assembled and how the primer ...The T4 bacteriophage gp41 helicase and gp61 primase assemble into a primosome to couple DNA unwinding with RNA primer synthesis for DNA replication. How the primosome is assembled and how the primer length is defined are unclear. Here we report a series of cryo-EM structures of T4 primosome assembly intermediates. We show that gp41 alone is an open spiral, and ssDNA binding triggers a large-scale scissor-like conformational change that drives the ring closure and activates the helicase. Helicase activation exposes a cryptic hydrophobic surface to recruit the gp61 primase. The primase binds the helicase in a bipartite mode in which the N-terminal Zn-binding domain and the C-terminal RNA polymerase domain each contain a helicase-interacting motif that bind to separate gp41 N-terminal hairpin dimers, leading to the assembly of one primase on the helicase hexamer. Our study reveals the T4 primosome assembly process and sheds light on the RNA primer synthesis mechanism. #1: Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2023 Title: Structural basis of the T4 bacteriophage primosome assembly and primer synthesis. Authors: Xiang Feng / Michelle M Spiering / Ruda de Luna Almeida Santos / Stephen J Benkovic / Huilin Li /  Abstract: The T4 bacteriophage gp41 helicase and gp61 primase assemble into a primosome complex to couple DNA unwinding with RNA primer synthesis for DNA replication. How a primosome is assembled and how the ...The T4 bacteriophage gp41 helicase and gp61 primase assemble into a primosome complex to couple DNA unwinding with RNA primer synthesis for DNA replication. How a primosome is assembled and how the length of the RNA primer is defined in the T4 bacteriophage, or in any model system, are unclear. Here we report a series of cryo-EM structures of T4 primosome assembly intermediates at resolutions up to 2.7 Å. We show that the gp41 helicase is an open spiral in the absence of ssDNA, and ssDNA binding triggers a large-scale scissor-like conformational change that drives the open spiral to a closed ring that activates the helicase. We found that the activation of the gp41 helicase exposes a cryptic hydrophobic primase-binding surface allowing for the recruitment of the gp61 primase. The primase binds the gp41 helicase in a bipartite mode in which the N-terminal Zn-binding domain (ZBD) and the C-terminal RNA polymerase domain (RPD) each contain a helicase-interacting motif (HIM1 and HIM2, respectively) that bind to separate gp41 N-terminal hairpin dimers, leading to the assembly of one primase on the helicase hexamer. Based on two observed primosome conformations - one in a DNA-scanning mode and the other in a post RNA primer-synthesis mode - we suggest that the linker loop between the gp61 ZBD and RPD contributes to the T4 pentaribonucleotide primer. Our study reveals T4 primosome assembly process and sheds light on RNA primer synthesis mechanism. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8duo.cif.gz 8duo.cif.gz | 505 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8duo.ent.gz pdb8duo.ent.gz | 414.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8duo.json.gz 8duo.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/du/8duo https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/du/8duo ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/du/8duo ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/du/8duo | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  27724MC  8dtpC  8dueC  8dvfC  8dviC  8dw6C  8dwjC  8g0zC  8gaoC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 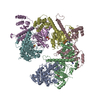
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 53662.848 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Escherichia phage T4 (virus) / Gene: 41 / Production host: Escherichia phage T4 (virus) / Gene: 41 / Production host:  References: UniProt: P04530, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement #2: Chemical | ChemComp-AGS / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex of bacteriophage T4 helicase gp41 hexamer with nucleotide bound Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Escherichia phage T4 (virus) Escherichia phage T4 (virus) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.8 Details: 20 mM HEPES pH 7.8, 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2 and 2 mM DTT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1400 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 66 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20_4459: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 5.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 50003 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj





