[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8dlv: Cryo-EM structure of SARS-CoV-2 Epsilon (B.1.429) spike protein i... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8dlv | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of SARS-CoV-2 Epsilon (B.1.429) spike protein in complex with human ACE2 (focused refinement of RBD and ACE2) | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / SARS-CoV-2 / glycoprotein / fusion protein / Viral Protein-Immune System complex / Epsilon / B.1.429 / ACE2 | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of amino acid transport / angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 / positive regulation of L-proline import across plasma membrane / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Metallocarboxypeptidases / angiotensin-mediated drinking behavior / positive regulation of gap junction assembly / regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by renin-angiotensin / tryptophan transport / regulation of cardiac conduction / maternal process involved in female pregnancy ...positive regulation of amino acid transport / angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 / positive regulation of L-proline import across plasma membrane / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Metallocarboxypeptidases / angiotensin-mediated drinking behavior / positive regulation of gap junction assembly / regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by renin-angiotensin / tryptophan transport / regulation of cardiac conduction / maternal process involved in female pregnancy / regulation of vasoconstriction / peptidyl-dipeptidase activity / transporter activator activity / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / carboxypeptidase activity / angiotensin maturation / Attachment and Entry / receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / metallocarboxypeptidase activity / viral life cycle / positive regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / regulation of cytokine production / blood vessel diameter maintenance / negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / brush border membrane / negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process / metallopeptidase activity / endocytic vesicle membrane / regulation of cell population proliferation / virus receptor activity / regulation of inflammatory response / endopeptidase activity / symbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / viral translation / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Potential therapeutics for SARS / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / membrane fusion / Attachment and Entry / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / cilium / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / apical plasma membrane / membrane raft / receptor ligand activity / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / virion attachment to host cell / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / cell surface / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / zinc ion binding / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.11 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhu, X. / Mannar, D. / Saville, J.W. / Srivastava, S.S. / Berezuk, A.M. / Zhou, S. / Tuttle, K.S. / Subramaniam, S. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 2items Canada, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: spike protein mutational analysis and epitope for broad neutralization. Authors: Dhiraj Mannar / James W Saville / Zehua Sun / Xing Zhu / Michelle M Marti / Shanti S Srivastava / Alison M Berezuk / Steven Zhou / Katharine S Tuttle / Michele D Sobolewski / Andrew Kim / ...Authors: Dhiraj Mannar / James W Saville / Zehua Sun / Xing Zhu / Michelle M Marti / Shanti S Srivastava / Alison M Berezuk / Steven Zhou / Katharine S Tuttle / Michele D Sobolewski / Andrew Kim / Benjamin R Treat / Priscila Mayrelle Da Silva Castanha / Jana L Jacobs / Simon M Barratt-Boyes / John W Mellors / Dimiter S Dimitrov / Wei Li / Sriram Subramaniam /   Abstract: Mutations in the spike glycoproteins of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern have independently been shown to enhance aspects of spike protein fitness. Here, we describe an antibody fragment (V ab6) that ...Mutations in the spike glycoproteins of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern have independently been shown to enhance aspects of spike protein fitness. Here, we describe an antibody fragment (V ab6) that neutralizes all major variants including the recently emerged BA.1 and BA.2 Omicron subvariants, with a unique mode of binding revealed by cryo-EM studies. Further, we provide a comparative analysis of the mutational effects within previously emerged variant spikes and identify the structural role of mutations within the NTD and RBD in evading antibody neutralization. Our analysis shows that the highly mutated Gamma N-terminal domain exhibits considerable structural rearrangements, partially explaining its decreased neutralization by convalescent sera. Our results provide mechanistic insights into the structural, functional, and antigenic consequences of SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations and highlight a spike protein vulnerability that may be exploited to achieve broad protection against circulating variants. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8dlv.cif.gz 8dlv.cif.gz | 188.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8dlv.ent.gz pdb8dlv.ent.gz | 128.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8dlv.json.gz 8dlv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8dlv_validation.pdf.gz 8dlv_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8dlv_full_validation.pdf.gz 8dlv_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8dlv_validation.xml.gz 8dlv_validation.xml.gz | 39.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8dlv_validation.cif.gz 8dlv_validation.cif.gz | 58.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dl/8dlv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dl/8dlv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dl/8dlv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dl/8dlv | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  27517MC  8dliC  8dljC  8dlkC  8dllC  8dlmC  8dlnC  8dloC  8dlpC  8dlqC  8dlrC  8dlsC  8dltC  8dluC  8dlwC  8dlxC  8dlyC  8dlzC  8dm0C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 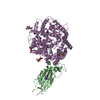
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 142356.453 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: S, 2 / Variant: Epsilon (B.1.429) / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DTC2 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DTC2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 70386.992 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ACE2, UNQ868/PRO1885 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ACE2, UNQ868/PRO1885 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BYF1 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BYF1 | ||||
| #3: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.11 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 74769 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 115.17 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






















 PDBj
PDBj







