+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8bv3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
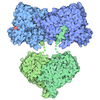
| Title | Bacillus subtilis DnaA domain III structure | ||||||
 Components Components | Chromosomal replication initiator protein DnaA | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / DnaA / DNA replication / DNA replication initiation / AAA+ superfamily / Initiator Clade | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDnaA-oriC complex / nucleoid / regulation of DNA replication / DNA replication origin binding / DNA replication initiation / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / DNA replication / lipid binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding ...DnaA-oriC complex / nucleoid / regulation of DNA replication / DNA replication origin binding / DNA replication initiation / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / DNA replication / lipid binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.38 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.38 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Pintar, S. / Hubbard, J.A. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: The bacterial replication origin BUS promotes nucleobase capture. Authors: Simone Pelliciari / Salomé Bodet-Lefèvre / Stepan Fenyk / Daniel Stevens / Charles Winterhalter / Frederic D Schramm / Sara Pintar / Daniel R Burnham / George Merces / Tomas T Richardson / ...Authors: Simone Pelliciari / Salomé Bodet-Lefèvre / Stepan Fenyk / Daniel Stevens / Charles Winterhalter / Frederic D Schramm / Sara Pintar / Daniel R Burnham / George Merces / Tomas T Richardson / Yumiko Tashiro / Julia Hubbard / Hasan Yardimci / Aravindan Ilangovan / Heath Murray /  Abstract: Genome duplication is essential for the proliferation of cellular life and this process is generally initiated by dedicated replication proteins at chromosome origins. In bacteria, DNA replication is ...Genome duplication is essential for the proliferation of cellular life and this process is generally initiated by dedicated replication proteins at chromosome origins. In bacteria, DNA replication is initiated by the ubiquitous DnaA protein, which assembles into an oligomeric complex at the chromosome origin (oriC) that engages both double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) to promote DNA duplex opening. However, the mechanism of DnaA specifically opening a replication origin was unknown. Here we show that Bacillus subtilis DnaA assembles into a continuous oligomer at the site of DNA melting, extending from a dsDNA anchor to engage a single DNA strand. Within this complex, two nucleobases of each ssDNA binding motif (DnaA-trio) are captured within a dinucleotide binding pocket created by adjacent DnaA proteins. These results provide a molecular basis for DnaA specifically engaging the conserved sequence elements within the bacterial chromosome origin basal unwinding system (BUS). | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8bv3.cif.gz 8bv3.cif.gz | 244.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8bv3.ent.gz pdb8bv3.ent.gz | 197.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8bv3.json.gz 8bv3.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8bv3_validation.pdf.gz 8bv3_validation.pdf.gz | 4.2 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8bv3_full_validation.pdf.gz 8bv3_full_validation.pdf.gz | 4.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8bv3_validation.xml.gz 8bv3_validation.xml.gz | 43.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8bv3_validation.cif.gz 8bv3_validation.cif.gz | 59 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bv/8bv3 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bv/8bv3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bv/8bv3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bv/8bv3 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8btgC  1l8qS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 27466.150 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Chemical | ChemComp-ANP / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-K / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 3.12 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 60.61 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293.15 K / Method: evaporation Details: Morpheus H3: 0.02 M DL-Glutamic acid monohydrate, 0.02 M DL-Alanine, 0.0 2M Glycine, 0.2M DL-Lysine monohydrochloride, 0.02M DL-Serine, 0.1 M Imidazole/ MES monohydrate pH 6.5, 20% v/v Glycerol, 20% w/v PEG 4000 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Diamond Diamond  / Beamline: I24 / Wavelength: 0.99987 Å / Beamline: I24 / Wavelength: 0.99987 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS3 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Feb 25, 2022 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.99987 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.38→74.399 Å / Num. obs: 56743 / % possible obs: 85.3 % / Redundancy: 9.7 % / CC1/2: 0.996 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.179 / Rpim(I) all: 0.06 / Rrim(I) all: 0.189 / Net I/σ(I): 10.1 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.38→2.52 Å / Redundancy: 6.7 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 1.461 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 1.5 / Num. unique obs: 2842 / CC1/2: 0.461 / Rpim(I) all: 0.599 / Rrim(I) all: 1.583 / % possible all: 27.2 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 1L8Q Resolution: 2.38→74.399 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.952 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.924 / SU B: 0.004 / SU ML: 0 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / ESU R: 0.206 / ESU R Free: 0.258 / Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD Details: HYDROGENS HAVE BEEN ADDED IN THE RIDING POSITIONS U VALUES : REFINED INDIVIDUALLY
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Ion probe radii: 0.8 Å / Shrinkage radii: 0.8 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.2 Å / Solvent model: MASK | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 117.19 Å2 / Biso mean: 50.058 Å2 / Biso min: 19.32 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 2.38→74.399 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 2.381→2.443 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0 / Total num. of bins used: 20
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj