+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8bh1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
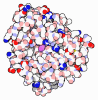
| Title | Core divisome complex FtsWIQBL from Pseudomonas aeruginosa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / bacterial cell division / peptidoglycan synthesis / membrane protein complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationFtsQBL complex / lipid-linked peptidoglycan transporter activity / peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase / peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase activity / cell septum / serine-type D-Ala-D-Ala carboxypeptidase / serine-type D-Ala-D-Ala carboxypeptidase activity / division septum assembly / FtsZ-dependent cytokinesis / cell division site ...FtsQBL complex / lipid-linked peptidoglycan transporter activity / peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase / peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase activity / cell septum / serine-type D-Ala-D-Ala carboxypeptidase / serine-type D-Ala-D-Ala carboxypeptidase activity / division septum assembly / FtsZ-dependent cytokinesis / cell division site / penicillin binding / peptidoglycan biosynthetic process / cell wall organization / regulation of cell shape / cell division / proteolysis / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kaeshammer, L. / van den Ent, F. / Jeffery, M. / Lowe, J. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM structure of the bacterial divisome core complex and antibiotic target FtsWIQBL. Authors: Lisa Käshammer / Fusinita van den Ent / Magnus Jeffery / Nicolas L Jean / Victoria L Hale / Jan Löwe /  Abstract: In most bacteria, cell division relies on the synthesis of new cell wall material by the multiprotein divisome complex. Thus, at the core of the divisome are the transglycosylase FtsW, which ...In most bacteria, cell division relies on the synthesis of new cell wall material by the multiprotein divisome complex. Thus, at the core of the divisome are the transglycosylase FtsW, which synthesises peptidoglycan strands from its substrate Lipid II, and the transpeptidase FtsI that cross-links these strands to form a mesh, shaping and protecting the bacterial cell. The FtsQ-FtsB-FtsL trimeric complex interacts with the FtsWI complex and is involved in regulating its enzymatic activities; however, the structure of this pentameric complex is unknown. Here, we present the cryogenic electron microscopy structure of the FtsWIQBL complex from Pseudomonas aeruginosa at 3.7 Å resolution. Our work reveals intricate structural details, including an extended coiled coil formed by FtsL and FtsB and the periplasmic interaction site between FtsL and FtsI. Our structure explains the consequences of previously reported mutations and we postulate a possible activation mechanism involving a large conformational change in the periplasmic domain. As FtsWIQBL is central to the divisome, our structure is foundational for the design of future experiments elucidating the precise mechanism of bacterial cell division, an important antibiotic target. #1:  Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM structure of the bacterial divisome core complex and antibiotic target FtsWIQBL. Authors: Lisa Käshammer / Fusinita van den Ent / Magnus Jeffery / Nicolas L Jean / Victoria L Hale / Jan Löwe /  Abstract: In most bacteria, cell division relies on the synthesis of new cell wall material by the multiprotein divisome complex. Thus, at the core of the divisome are the transglycosylase FtsW, which ...In most bacteria, cell division relies on the synthesis of new cell wall material by the multiprotein divisome complex. Thus, at the core of the divisome are the transglycosylase FtsW, which synthesises peptidoglycan strands from its substrate Lipid II, and the transpeptidase FtsI that cross-links these strands to form a mesh, shaping and protecting the bacterial cell. The FtsQ-FtsB-FtsL trimeric complex interacts with the FtsWI complex and is involved in regulating its enzymatic activities; however, the structure of this pentameric complex is unknown. Here, we present the cryogenic electron microscopy structure of the FtsWIQBL complex from Pseudomonas aeruginosa at 3.7 Å resolution. Our work reveals intricate structural details, including an extended coiled coil formed by FtsL and FtsB and the periplasmic interaction site between FtsL and FtsI. Our structure explains the consequences of previously reported mutations and we postulate a possible activation mechanism involving a large conformational change in the periplasmic domain. As FtsWIQBL is central to the divisome, our structure is foundational for the design of future experiments elucidating the precise mechanism of bacterial cell division, an important antibiotic target. #2:  Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2022 Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2022Title: Divisome core complex in bacterial cell division revealed by cryo-EM Authors: Kashammer, L. / van den Ent, F. / Jeffery, M. / Jean, N.L. / Hale, V.L. / Lowe, J. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8bh1.cif.gz 8bh1.cif.gz | 222.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8bh1.ent.gz pdb8bh1.ent.gz | 171 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8bh1.json.gz 8bh1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bh/8bh1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bh/8bh1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bh/8bh1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bh/8bh1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  16042MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 48241.430 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1 Gene: ftsW, PA4413 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q9HW00, peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 62933.082 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1 Gene: ftsI, pbpB, PA4418 / Production host:  References: UniProt: G3XD46, serine-type D-Ala-D-Ala carboxypeptidase |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 32290.223 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1 Gene: ftsQ, PA4409 / Production host:  |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 11150.034 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1 Gene: ftsL, PA4419 / Production host:  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 12295.922 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1 Gene: ftsB, PA3634 / Production host:  |
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: FtsWIQBL / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.164 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 41 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 136364 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj