+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ad5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | X-ray structure of NqrF(129-408)of Vibrio cholerae variant F406A | ||||||
 Components Components | Na(+)-translocating NADH-quinone reductase subunit F | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | FLAVOPROTEIN / NADH / FAD / Na+-NQR / NADH ubiquinone oxido reducatase | ||||||
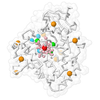
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationNADH:ubiquinone reductase (Na+-transporting) / oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H, quinone or similar compound as acceptor / sodium ion transport / 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.65 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.65 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Fritz, G. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1items Germany, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: Conformational coupling of redox-driven Na-translocation in Vibrio cholerae NADH:quinone oxidoreductase. Authors: Jann-Louis Hau / Susann Kaltwasser / Valentin Muras / Marco S Casutt / Georg Vohl / Björn Claußen / Wojtek Steffen / Alexander Leitner / Eckhard Bill / George E Cutsail / Serena DeBeer / ...Authors: Jann-Louis Hau / Susann Kaltwasser / Valentin Muras / Marco S Casutt / Georg Vohl / Björn Claußen / Wojtek Steffen / Alexander Leitner / Eckhard Bill / George E Cutsail / Serena DeBeer / Janet Vonck / Julia Steuber / Günter Fritz /   Abstract: In the respiratory chain, NADH oxidation is coupled to ion translocation across the membrane to build up an electrochemical gradient. In the human pathogen Vibrio cholerae, the sodium-pumping NADH: ...In the respiratory chain, NADH oxidation is coupled to ion translocation across the membrane to build up an electrochemical gradient. In the human pathogen Vibrio cholerae, the sodium-pumping NADH:quinone oxidoreductase (Na-NQR) generates a sodium gradient by a so far unknown mechanism. Here we show that ion pumping in Na-NQR is driven by large conformational changes coupling electron transfer to ion translocation. We have determined a series of cryo-EM and X-ray structures of the Na-NQR that represent snapshots of the catalytic cycle. The six subunits NqrA, B, C, D, E, and F of Na-NQR harbor a unique set of cofactors that shuttle the electrons from NADH twice across the membrane to quinone. The redox state of a unique intramembranous [2Fe-2S] cluster orchestrates the movements of subunit NqrC, which acts as an electron transfer switch. We propose that this switching movement controls the release of Na from a binding site localized in subunit NqrB. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ad5.cif.gz 8ad5.cif.gz | 144.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ad5.ent.gz pdb8ad5.ent.gz | 109.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ad5.json.gz 8ad5.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8ad5_validation.pdf.gz 8ad5_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8ad5_full_validation.pdf.gz 8ad5_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8ad5_validation.xml.gz 8ad5_validation.xml.gz | 27.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8ad5_validation.cif.gz 8ad5_validation.cif.gz | 40 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ad/8ad5 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ad/8ad5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ad/8ad5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ad/8ad5 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8a1tC  8a1uC  8a1vC  8a1wC  8a1xC  8a1yC  8acwC  8acyC  8ad3C  8ad4C  4u9uS C: citing same article ( S: Starting model for refinement |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 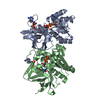
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 31940.084 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: F406A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Subunit NqrF, variant F406A residues 129-408; residues after cleavage of N-terminal His-tag residual residues after are GP Source: (gene. exp.)  Production host:  References: UniProt: A0A656ARB0, NADH:ubiquinone reductase (Na+-transporting) #2: Chemical | #3: Chemical | #4: Chemical | #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.44 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 49.56 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 292 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 5 Details: 0.1 M citrate, 0.2 M MgAcetate, 20-27 % PEG5000 MME |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SLS SLS  / Beamline: X06SA / Wavelength: 1 Å / Beamline: X06SA / Wavelength: 1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Jul 14, 2011 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.65→48.65 Å / Num. obs: 74065 / % possible obs: 97.7 % / Redundancy: 10.561 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 23.46 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.999 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.153 / Rrim(I) all: 0.161 / Χ2: 0.812 / Net I/σ(I): 12.87 / Num. measured all: 782172 / Scaling rejects: 127 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 4U9U Resolution: 1.65→48.65 Å / SU ML: 0.22 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.35 / Phase error: 23.79 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.1 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 85.75 Å2 / Biso mean: 27.8995 Å2 / Biso min: 13.29 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 1.65→48.65 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0 / Total num. of bins used: 26
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj